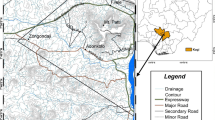
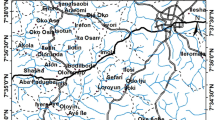
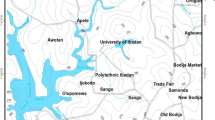
Abstract
Prediction of groundwater resources potential is a spatial decision problem that involves a set of multiple evaluation parameters. In order to produce a groundwater resources potential prediction model of higher reliability and precision in a given study area, the effects of all the important parameters that can contribute to the groundwater occurrence in the area must be integrated. However, the methodology of integrating these parameters such that the relative importance of each is reflected is still a challenge that has not been efficiently handled. In this study, the principle of multi-criteria decision analysis in the context of the analytical hierarchy process is proposed as a technique that can yield a prediction model of higher reliability and precision. The proposed technique was applied to geoelectric and geologic parameters, derived from the results of the interpretation of 2D resistivity imaging data acquired from the study area. The advantage of the proposed technique is that it reduces bias in decision making. The main objective of the study is to produce groundwater potential map for the area. Furthermore, an attempt was also made in the study to characterize the aquifer of the area by estimating the Dar-Zarrouk parameters, using the integration of borehole and 2D resistivity data. The success rate (accuracy) of the prediction was established to be 80 %. Furthermore, the regression line fitted to the aquifer transmissivity and transverse resistance data shows linear relationship with a high regression coefficient of 0.79. The prediction success rate obtained showed that the method proposed in this study is reliable, accurate, and an improved technique of integrating multiple parameters for holistic evaluation of groundwater resources.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Nassir, S.S., Loke, M.H., Lee, C.Y., and Nawawi, M.N.M. (2000). Salt-water intrusion mapping by geoelectrical imaging surveys. Geophysical Prospecting, 48, 647–661.
Abdul, R.S., Umar, H., and Zuraidah, R. (2001). Geophysical investigation of the Olak Lempit Quaternary Basin, Selangor, Malaysia. In: Proceedings of 10th GEOSEA regional congress on geology, mineral and energy resources, Jogjakarta, Indonesia, pp 280–282.
Abu-Shariah, M.I.I. (2009). Determination of cave geometry by using a geoelectrical resistivity inverse model. Engineering Geology 105, 239–244. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.02.006.
Aizebeokhai, A.P., Olayinka, A.I., and Singh, V.P. (2010). Application of 2D and 3D geoelectrical resistivity imaging for engineering site investigation in a crystalline basement terrain, southwestern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 61:1481–1492. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0464-z.
Alonso, J. A., and Lamata, M. T. (2006). Consistency in the analytic hierarchy process: a new approach. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems Vol. 14, No. 4, 445–459.
Al-Zoubi, A.S., Abueladas, A.A., Al-Rzouq, R.I., Camerlynck, C., Akkawi, E., Ezarsky, M., et al., (2007). Use of 2D Multi Electrodes Resistivity Imagining for Sinkholes Hazard Assessment along the Eastern Part of the Dead Sea, Jordan. American Journal of Environmental Science.
Arafin, M.S., and Lee, C.Y. (1985). A resistivity survey for groundwater in Perlis using offset Wenner technique. Paper presented at the Kars Water Resources (Proceedings of the Ankara–Antalya Symposium, July 1985).
Ariff, H., Salit, M. S., Ismail, N., and Nukman, Y. (2008). Use of Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) for selecting the best design concept. Jurnal Teknologi, 49(A):1–18.
Azizi, M. (2009). Analytical hierarchy process for optimised choice of machines for secondary wood industries. The Journal of the Institute of Wood Science Vol 19. doi:10.1179/002032009X12536100262079 .
Batayneh, A.T. (2006). Use of electrical resistivity methods for detecting subsurface fresh and saline water and delineating their interfacial configuration: a case study of the eastern Dead Sea coastal aquifers, Jordan. Hydrogeology Journal 14:1277–1283 doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0034-3.
Bauer, P., Supper, R., Zimmermann, S., and Kinzelbach, W. (2006). Geoelectrical imaging of groundwater salinization in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Applied Geophysics 60 126–141 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2006.01.003.
Bernstone, C., and Dahlin, T. (1999). Assessment of two automated electrical resistivity data acquisition systems for landfill location surveys: two case histories. J Environ Eng Geophys 4:113–122.
Bhattacharya, P.K., and Patra, H.P. (1968). Direct current geoelectric sounding, Elsveier, Amsterdam, 139 pp.
Buselli, G. and Lu, K. (2001). Groundwater contamination monitoring with multichannel electrical and electromagnetic methods. Journal of Applied Geophysics 48,11–23.
Cardarelli, E. (2002). Geoelectric survey by ERT to investigate marble ruins at the Roman Forum, Rome Italy. European Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics 7, 219–228.
Cardarelli, E., and Fischanger, F. (2006). 2D Data modelling by electrical resistivity tomography for complex subsurface geology. Geophysical Prospecting 54, 121–133.
Cardarelli, E., Fishanger, F., and Piro, S. (2008). Integrated geophysical survey to detect buried structures for archaeological prospecting. A case-history at Sabine Necropolis (Rome Italy). Near Surface Geophysics 6, 15–20.
David, P., Panagiotis, T., and Konstantinos, A. (2009). Electrical resistivity tomography mapping of beachrocks:application to the island of Thassos (N. Greece). Environ Earth Sci (2009) 59:233–240. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0021-9.
de Ara′ujo, C.C., and Macedo, A.B. (2002). Multicriteria Geologic Data Analysis for Mineral Favorability Mapping: Application to a Metal Sulphide Mineralized Area, Ribeira Valley Metallogenic Province, Brazil. Natural Resources Research, Vol. 11, No. 1.
De Souza, H., and Sampaio, E. (2001). Apparent resistivity and spectral induced polarization in the submarine environment. An AcadBras Cienc 73(3):429–444.
Drahor, G.M., Gokturkler, G., Berge, A.M., and Kurtulmus, T.O. (2006). Application of electrical resistivity tomography technique for investigation of landslides: a case study from Turkey. Environ Geol 50:147–155.
Dweiri, F., and Al-Oqla, F. M. (2006). Material Selection Using Analytical Hierarchy Process. International Journal of Computer Applications in Technology. 26(4):82–189.
Eastman, JR (1996). Multi-criteria Evaluation and Geographical Information Systems Eds. Longley PA, Goodchild MF, Magurie DJ and Rhind DW, Second edition,1 (John Wiley and sons, New York):493–502.
Edet, A.E., and Okereke, C.S. (1996). Assessment of hydrogeological conditions in basement aquifers of the Precambrian Oban massif, southwestern Nigeria. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 36(1997), 195–204.
Ewusi, A., Kuma, J.S., and Voigt, H.J. (2009). Utility of the 2-D Multi-Electrode Resistivity Imaging Technique in Groundwater Exploration in the Voltaian Sedimentary Basin, Northern Ghana Natural Resources Research, Vol. 18, No. 4.
Fadhilah, A., Suhailan, S., Yazid, M.S.M., Hasni, H., and Fatimah, G. (2011). Instant Messaging and Guided AHP for Human Resource Selection. International Conference on Future Information Technology, IPCSIT vol. 13 (2011), IACSIT Press, Singapore.
Fechner, G.T. (1965). Elements of Psychophysics. Volume 1, (Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York 1965); translation by H.E.Adler of Elemente der Psychophysik. (Breitkopf und Hârtel, Leipzig 1860).
Ghamgosar, M., Haghyghy, M., Mehrdoust, F., and Arshad, N. (2011). Multicriteria Decision Making Based on Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) in GIS for Tourism. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 10 (4):501–507.
Gowd, S.S. (2004). Electrical resistivity survey to delineate groundwater potential aquifers in Peddavanka watershed, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 46, 118–131.
Griffith, D.H., and Turnbull, J. (1985). A multielectrode array for resistivity surveying. First Break 3(7):16–20.
Griffith, D.H., Turnbull, J., and Olayinka, A.I. (1990). Two-dimensional resistivity mapping with a computer controlled array. First Break 8:121–129.
Hamza, U., Yaacup, R., Samsudin, A.R., and Ayub, M.S. (2006). Electrical imaging of the groundwater aquifer at Banting, Selangor, Malaysia. Environ Geol (2006) 49: 1156–1162.
Ho, W. (2008). Integrated Analytic Hierarchy Process and Its Applications–—A Literature Review. Journal of European Journal of Operation Research. 186: 211–228.
Hoque, M. A., Khan, A. A., Shamsudduha, M., Hossain, M.S., Islam, T., and Chowdhury, S.H. (2009). Near surface lithology and spatial variation of arsenic in the shallow groundwater: southeastern Bangladesh. Environ Geol 56:1687–1695. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1267-3.
Ibrahim, A.N., Harith, Z.Z.T., and Nawawi, M.N.M (2003). Resistivity imaging and borehole investigation of the Banting area aquifer, Selangor, Malaysia. The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology. (Volume 11, 2003) Available on the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com.
Johnston, K., Hoef, J.M.V., Krivoruchko, K., and Lucas, N. (2003). Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst, Printed in the United States of America.
Jupp, D.L.B., and Vozoff, K. (1975). Joint inversion of geophysical data. Geophys J Roy Astron Soc 42:977–991.
Kardi, T. (2006). Analytic Hierarch Process (AHP) Tutorial http://people.revoledu.com/kardi/tutorial/ahp/ (accessed on the 10th June, 2009).
Kaya, M. A., Özürlan, G., and Şengül, E. (2007). Delineation of soil and groundwater contamination using geophysical methods at a waste disposal site in Çanakkale, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 135:441–446. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9662-x.
Kelly, W.E., and Reiter, P.F. (1984). Influence of anisotropy on relation between aquifer hydraulic and electrical properties. J. Hydrol 74:311–321.
Kiker, G.A., Bridges, T.S., Varghese, A., Seager, T.P., and Linkov, I. (2005). Application of Multicriteria Decision Analysis in Environmental Decision Making. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, Volume 1, Number 2, pp. 95–108.
Koefoed, O. (1979). Geosounding principles 1: resistivity sounding measurements. Elsevier Science Publishing Co, Amsterdam.
Lee, C.C., Yang, C.H., Liu, H.C., Wen, K.L., Wang, Z.B., and Chen, Y.J. (2008). A Study of the hydrogeological environment of the lishan landslide area using resistivity image profiling and borehole data. Engineering Geology 98 (2008) 115–125. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.01.012.
Linkov, I., Satterstrom, F. K., Kiker, G., Seager, T. P., Bridges, T., Gardner, K. H., et al . (2006). Multicriteria Decision Analysis: A Comprehensive Decision Approach for Management of Contaminated Sediments. Risk Analysis, Vol. 26, No. 1, 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1539-6924.2006.00713.x.
Loke, M.H. (2001). The use of 3-D electrical imaging surveys for mapping complex subsurface structures. In: Proceedings of geological society of Malaysia seminar on the recent advances in engineering geophysics, Kuala Lumpur, pp 47–59.
Loke, M.H., and Barker, R.D (1996). Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudo sections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophysical Prospecting, 44, 131–152.
Maillet, R (1947). The fundamental equation of electrical prospecting. Geophysics, 12, 529–556.
Majumdar, R.K., and Das, D. (2011). Hydrological Characterization and Estimation of Aquifer Properties from Electrical Sounding Data in Sagar Island Region, South 24 Parganas, West bengal, India. Asian Journal of earth Sciences 4(2);60–74, 2011. doi:10.3923/ajes.2011.60.74.
Malczewski, J. (1999). GIS and Multicriteria decision analysis.pp 177–192, published by: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. United States of America.
Massoud, U., Santos, F., Khalil, M.A., Taha, A., and Abbas, A. M. (2010). Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surface geophysical measurements: a case study of the Upper Cretaceous aquifer, central Sinai, Egypt. Hydrogeology Journal 18:699–710. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0551-y.
Matsui, T., Park, S.G., Park, M.K., and Matsuura, S. (2000). Relationship between electrical resistivity and physical properties of rocks Paper presented at the GeoEng, Melbourne Convention Centre, Melbourne, Australia. November 19–24 2000.
Mazac, O., Kelly, W.E., and Landa, I. (1985). A hydrogeophysical model for relation between electrical and hydrualic properties of aquifers.J. Hydrol 79:1–9.
Minerals and Geoscience Department, Malaysia (2004). Impact of the 26th December 2004 Tsunami on Groundwater Systems and Groundwater Based Water Supplies in Malaysia.
Mondal, N.C., Rao, A.V., and Singh, V.P. (2009). Efficacy of electrical resistivity and induced polarization methods for revealing fluoride contaminated groundwater in granite terrain. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1094-3.
Montazar, A., and Behbahani, S.M. (2007). Development of an optimised irrigation system selection model using analytical hierarchy process. Bio Systems Engineering 98, 155–165. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2007.06.003.
Navalgund, R.R. (1997). Revised development plan of Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority Area—2011. Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority and Space Applications Centre, Ahmedabad, India, Technical Report 1 SAC/RSAG/TR/12/AUG/1997:142.
Nawawi, M.N.M., Harith, Z.Z.T., Ayub, M.S., Ibrahim, A.N., and Alphonse, A. (2001). Modeling of an undergroundwater aquifer using 2-D electrical imaging technique in Brooklands Plantation, Selangor, Malaysia. In: Proceedings of the second international symposium on geophysics, Egypt, pp 293–297.
Niwas, S., and Singhal, D.C. (1981). Estimation of aquifer transmissivity from Dar-Zarrouck parameters in porous media. J. Hydrol., 50, 393–399.
Olorunfemi, M.O. (1990). The hydrogeological implication of topographic variation with overburden thickness in Basement Complex area of S.W.Nigeria. J. Min. Geol., 26(1), 145–152.
Onuoha, K.M., and Mbazi, F.C.C. (1988). Aquifer transmissivity from Electrical Sounding Data: The Case of Ajali sandstone Aquifers South West of Enugu, Nigeria, In: Groundwater and mineral Resources of Nigeria, Ofoeglu, C.O. (Ed). Vieweg-Verlag, Nigeria, pp: 17–30.
Park, G., Park, S., Yi, M.-J., Rim, H., Cho, S.-J., and Kim, J.-H. (2010). Geostatistical integration using 2-D electrical resistivity and 3-D gravity methods for detecting cavities in a karst area. Environ Earth Sci 60:965–974. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0232-0.
Pietersen, K. (2006). Multiple criteria decision analysis (MCDA): A tool to support sustainable management of groundwater resources in South Africa. Water SA Vol. 32 No. 2.
Pujari, P. R., Pardhi, P., Muduli, P., Harkare, P., and Nanoti, M. V. (2007). Assessment of Pollution Near Landfill Site in Nagpur, India by Resistivity Imaging and GPR. Environ Monit Assess 131:489–500. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9494-0.
Rahim, B.E., Yusoff, I., Samsudin, A.R., Yaacob, W.Z., and Rafek, A.G. (2010). Deterioration of groundwater quality in the vicinity of an active open-tipping site in West Malaysia. Hydrogeology Journal 18:997–1006. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0567-3.
Rao, B.V., and Briz-Kishore, B.H. (1991). A methodology for locating potential aquifers in a typical semi-arid region in India using resistivity and hydrogeologic parameters. Geoexploration, 27, 55–64.
Rubin, Y., and Hubbard, S. (2005). Hydrogeophysics. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 523 pp.
Saaty, T.L. (1980). The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Saaty, T.L (1994). Fundamental of Decision Making and Priority Theory with AHP. RWS Publications, Pittsburgh, PA, USA. 1994.
Sasaki, Y. (1992). Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation. Geophys Prospect 40:453–463.
Sathish, S., Elango, L., Rajesh, R., and Sarma, V. S. (2011). Assessment of seawater mixing in a coastal aquifer by high resolutionelectrical resistivity tomography. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 8(3), 483–492.
Shahid, S., and Nath, SK. (2002). GIS integration of remote sensing and electrical sounding data for hydrogeological exploration. J Spat Hydrol 2(1), 1–10.
Sudha, K., Israil, M., Mittal, S., and Rai, J. (2009). Soil characterization using electrical resistivity tomography and geotechnical investigations. Journal of Applied Geophysics 67 74–79. doi:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.09.012 .
Sumanovac, F., and Weisser, M. (2001). Evaluation of resistivity and seismic methods for hydrogeological mapping in karst terrains. Journal of Applied Geophysics 46 189–200 Volume: 47, Issue: 1, Pages: 13–28. doi:10.1016/S0926-9851(01)00044-1.
Tecle, A., and Duckstein, L. (1994). Concepts of multicriterion decision making. In: Bogardi JJ and Nachtnebel HP (eds.) Multicriteria Analysis in Water Resources Management. UNESCO, Paris: 33–62.
Thurstone, L.L. (1927). A law of comparative judgements, Psychological Reviews 34:273–286.
Tizro, T. A., Voudouris, K.S., and Mashayekhi, M.S (2010). Hydrogeological framework and estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters using geoelectrical data: a case study from West Iran. Hydrogeology Journal (2010) 18:917–929. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0580-6.
Tizro Taheri, A (2006). Groundwater recharge assessment in Kangavar Basin, Kermanshah Province, Iran. International Congress on Groundwater in Mediterranean Countries (AQUAinMED), Malaga, Spain, 24–28 April 2006.
Tizro Taheri, A, Voudouris, K, and Eini, M (2007). Groundwater balance, safe yield and recharge feasibility in a semi-arid environment: a case study from western part of Iran. J Appl Sci 7(2): 2967–2976.
Vahidnia, M.H., Alesheikh, A.A., and Alimohammadi, A. (2009). Hospital site selection using fuzzy AHP and its derivatives. Journal of Environmental Management 90. 3048–3056. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.010.
Winston, W.L. (1991). “Operation Research-Applications and Algorithms” International Thomson publish, 1991.
Yang, C.H., You, J.I., and Lin, C.P. (2002). Delineating lake bottom structure by resistivity image profiling on water surface. TAO 13(1):39–52.
Zhou, W., Beck, B.F., and Stephenson, J.B. (2000). Reliability of dipole-dipole electrical resistivity tomography for defining depth to bedrock in covered karst terranes. Environ Geol 39(7):760–766.
Acknowledgment
This project was funded by the Universiti Sains Malaysia Short Term Research Grant No. 304/PFIZIK/6310057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adiat, K.A.N., Nawawi, M.N.M. & Abdullah, K. Application of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis to Geoelectric and Geologic Parameters for Spatial Prediction of Groundwater Resources Potential and Aquifer Evaluation. Pure Appl. Geophys. 170, 453–471 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0501-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0501-9