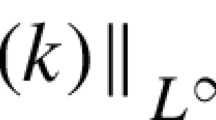Abstract.
We study a damped stochastic non-linear Schrödinger (NLS) equation driven by an additive noise. It is white in time and smooth in space. Using a coupling method, we establish convergence of the Markov transition semi-group toward a unique invariant probability measure. This kind of method was originally developed to prove exponential mixing for strongly dissipative equations such as the Navier-Stokes equations. We consider here a weakly dissipative equation, the damped nonlinear Schrödinger equation in the one-dimensional cubic case. We prove that the mixing property holds and that the rate of convergence to equilibrium is at least polynomial of any power.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debussche, A., Odasso, C. Ergodicity for a weakly damped stochastic non-linear Schrödinger equation. J. evol. equ. 5, 317–356 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00028-005-0195-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00028-005-0195-x