Abstract
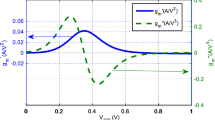
A third-order intermodulation cancelation technique using a non-linear feedback is proposed to design a low-power low-distortion mixer in a 65 nm standard CMOS technology. The IM3 cancelation is achieved by estimating distorting error at a non-linear feedback element and subtracting it from the input. The linearization technique is utilized in the input trans-conductance of the mixer. The circuit functionality is analyzed using Volterra series. The covering frequency range of the mixer is 800 MHz to 5 GHz. The technique increases the input-referred third-order intercept point (IIP3) and input 1 dB compression point to +16.4 dBm and −1.87 dBm, respectively. It obtains a gain of 9 dB and an input-referred noise of 1.84 nV\(/\sqrt{}\)Hz while consumes 8.75 mA from 1.2 V supply. The layout of the mixer occupies 0.315 mm × 0.296 mm of silicon area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Aparin, L.E. Larson, Linearization of monolithic LNA’s using low-frequency, low-impedance input termination, in Proc. IEEE Eur. Solid State Circuits Conf. (2003), pp. 137–140
B. Bakkaloglu, et al., A 1.5-V multi-mode quad-band RF receiver for GSM/EDGE/CDMA2K in 90 nm digital CMOS process. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 41(5), 1149–1159 (2006)
W.-H. Chen, et al., A highly linear broadband CMOS LNA employing noise and distortion cancellation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43(5), 1164–1176 (2008)
H. Darabi, A.A. Abidi, Noise in RF-CMOS mixers: a simple physical model. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 35(1), 15–25 (2000)
Y. Ding, R. Harjani, An +18 dBm IIP3 LNA in 0.35 μm CMOS, in ISSCC 2001 Dig. Tech. Papers (2001), pp. 162–163
Y. Ding, R. Harjani, High-Linearity CMOS RF Front-End Circuit (Springer, Berlin, 2005)
K.L. Fong, High-frequency analysis of linearity improvement technique of common-emitter trans-conductance stage using a low frequency trap network. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 35, 1249–1252 (2000)
B. Gilbert, Design consideration monolithic multiplier using active feedback. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits SC-9(6), 364–373 (1974)
J. Han, R. Gharpurey, A 3.5 mW 900 MHz down-converter with multiband feedback and device trans-conductance reuse, in CICC (2007), pp. 527–530
K. Iizuka, et al., A 184 mW fully integrated DVB-H tuner with a linearized variable gain LNA and quadrature mixers using cross-coupled trans-conductor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(4), 862–871 (2007)
N. Kim, et al., A cellular-band CDMA 0.25 μm CMOS LNA linearized using active post-distortion. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 41(7), 1530–1534 (2006)
W. Kim, et al., A mixer with third-order nonlinearity cancellation technique for CDMA applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 17(1), 76–78 (2007)
B.H. Leung, VLSI for Wireless Communication (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 2002)
S.-T. Lim, et al., A low-voltage broadband feed-forward linearized BJT mixer. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 41(9), 2177–2187 (2006)
A. Liscidini, C. Ghezzi, E. Depaoli, G. Albasini, R. Castello, Common gate transformer feedback LNA in a high IIP3 current mode RF CMOS front-end, in Custom Integrated Circuits Conference 2006 Proceedings of the IEEE (2006), pp. 300–304
S. Otaka, et al., A +10-dBm IIP3 SiGe mixer with IM3 cancellation technique. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39(12), 2333–2341 (2004)
P. Rossi, et al., A variable gain RF front end based on a voltage-voltage feedback LNA for multi-standard applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 40(3), 690–697 (2005)
L. Sheng, L.E. Larson, An Si–SiGe BiCMOS direct-conversion mixer with second order and third order nonlinearity cancellation for WCDMA applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 51, 2211–2220 (2003)
P. Wambacq, W. Sansen, Distortion Analysis of Analog Integrated Circuits (Kluwer Academic, Norwell, 1998)
D.R. Webster, et al., Derivative super-position a linearization technique for ultra broadband systems, in Proc. IEE Collq., Wideband Circuits, Modeling and Techniques (1996), pp. 3/1–3/14
Y.-S. Youn, et al., A 2 GHz 16 dBm IIP3 low-noise amplifier in 0.25 μm CMOS technology, in ISSCC (2003 Dig. Tech. Papers) (2003), pp. 452–453
H. Zhang, et al., A low-power, linearized, ultra-wideband LNA design technique. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(2), 320–330 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirabadi, A., Chehelcheraghi, M. & Kamarei, M. High IIP3 and Low-Noise CMOS Mixer Using Non-linear Feedback Technique. Circuits Syst Signal Process 30, 721–739 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-011-9301-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-011-9301-1