Abstract
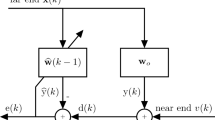
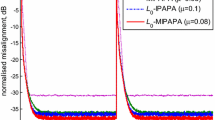
In order to reduce the steady-state misalignment of real-coefficient proportionate affine projection sign algorithm (RP-APSA) for sparse impulse responses, a memory RP-APSA is proposed in this paper by exploiting the historical values of proportionate factors, called MP-APSA. Further, to improve the robustness of MP-APSA and the recently proposed memory-improved RP-APSA (MIP-APSA) for impulse responses with mutative sparseness, two sparseness-controlled algorithms (SC-MP-APSA and SC-MIP-APSA) are developed by estimating the sparseness of the impulse response at each iteration. Simulation results in the context of acoustic echo cancellation show that the proposed algorithms retain good robustness against impulsive interferences. More importantly, the proposed sparseness-controlled algorithms can not only obtain low steady-state misalignment in both the sparse and dispersive situations, but also adapt to the variations in the sparseness of the impulse response.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Albu, H.K. Kwan, Memory improved proportionate affine projection sign algorithm. Electron. Lett. 48(20), 1279–1281 (2012). doi:10.1049/el.2012.2403
J. Benesty, Y. Huang, Adaptive Signal Processing-Applications to Real-World Problems (Springer, Berlin, 2003)
J. Benesty, S. L. Gay, An improved PNLMS algorithm, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), USA, II-1881-II-1884 (2002)
J. Benesty, Y.A. Huang, J. Chen, P.A. Naylor, Adaptive algorithms for the identification of sparse impulse responses, in Selected Methods for Acoustic Echo and Noise Control, ed. by E. Hänsler, G. Schmidt (Springer, New York, 2006), pp. 125–153. ch. 5
B.K. Das, M. Chakraborty, Sparse adaptive filtering by an adaptive convex combination of the LMS and the ZA-LMS algorithms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 61(5), 1499–1507 (2014). doi:10.1109/TCSI.2013.2289407
D.L. Duttweiler, Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptation in echo cancellers. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 8(5), 508–518 (2000). doi:10.1109/89.861368
G. W. Elko, E. Diethorn, T. Gänsler, Room impulse response variation due to thermal fluctuation and its impact on acoustic echo cancellation, in Proceedings of International Workshop Acoustic Echo Noise Control (2003), pp. 67–70
T. Gansler, J. Benesty, S. L. Gay, M. Sondhi, A robust proportionate affine projection algorithm for network echo cancellation, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Istanbul, 2000), pp. 793–796
O. Hoshuyama, R. A. Goubran, A. Sugiyama, A generalized proportionate variable step-size algorithm for fast changing acoustic environments, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Montreal, 2004) IV-161-IV-164
W. H. Khong, P. A. Naylor, Efficient use of sparse adaptive filters, in Proceedings of the 40th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, ACSSC’06 (2006), pp. 1375–1379
P. Loganathan, A.W.H. Khong, P.A. Naylor, A class of sparseness-controlled algorithms for echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 17(8), 1591–1601 (2009). doi:10.1109/TASL.2009.2025903
L. Liao and A. W. H. Khong, Sparseness-controlled affine projection algorithm for echo cancelation, in Proceedings of APSIPA Annual Summit and Conference 2010 (Biopolis, 2010), pp. 355–361
U. Mahbub, S.A. Fattah, A single-channel acoustic echo cancellation scheme using gradient-based adaptive filtering. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(5), 1541–1572 (2014). doi:10.1007/s00034-013-9715-z
R. Nath, Adaptive echo cancellation based on a multipath model of acoustic channel. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(4), 1673–1698 (2013). doi:10.1007/s00034-012-9529-4
C. Paleologu, S. Ciochina, J. Benesty, An efficient proportionate affine projection algorithm for echo cancellation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(2), 165–168 (2010). doi:10.1109/LSP.2009.2035665
L. Shi, Y. Lin, X. Xie, Combination of affine projection sign algorithms for robust adaptive filtering in non-Gaussian impulsive interference. Electron. Lett. 50(6), 466–467 (2014). doi:10.1049/el.2013.3997
F.C.D. Souza, O.J. Tobias, R. Seara, D.R. Morgan, A PNLMS algorithm with individual activation factors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(4), 2036–2047 (2010). doi:10.1109/TSP.2009.2038420
T. Shao, Y.R. Zheng, J. Benesty, An affine projection sign algorithm robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(4), 327–330 (2010). doi:10.1109/LSP.2010.2040203
Z. L. Yang, Y. R. Zheng, S. L. Grant, Proportionate affine projection sign algorithms for sparse system identification in impulsive interference, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (Prague, 2011) pp. 4068–4071
Z.L. Yang, Y.R. Zheng, S.L. Grant, Proportionate affine projection sign algorithms for network echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 19(8), 2273–2284 (2011). doi:10.1109/TASL.2011.2125955
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, An efficient memory-improved proportionate affine projection sign algorithm based on \(l_{0}\)-norm for sparse system identification, in Foundations of Intelligent Systems (Springer, Berlin, 2014), pp. 509–518
H. Zhao, Y. Yu, S. Gao, X. Zeng, Z. He, Memory proportionate APA with individual activation factors for acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 22(6), 1047–1055 (2014). doi:10.1109/TASLP.2014.2318519
H. Zhao, Y. Yu, Improved efficient proportionate affine projection algorithm based on \(l_{0}\)-norm for sparse system identification. J. Eng. 1(1), 1–4 (2014). doi:10.1049/joe.2013.0129
S. Zhang, J. Zhang, Modified variable step-size affine projection sign algorithm. Electron. Lett. 49(20), 1264–1265 (2013). doi:10.1049/el.2013.2337
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. M. N. S. Swamy, the Editor-in-Chief for his help in improving the presentation of the paper. This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants: 61271340, 61134002, 61372152, 61433011, U1234203), the Sichuan Provincial Youth Science and Technology Fund (Grant: 2012JQ0046), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant: SWJTU12CX026) and the Postgraduate Innovative Experimental and Practice Project of Southwest Jiaotong University (Grant: YC201403211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zhao, H. & Chen, B. Sparseness-Controlled Proportionate Affine Projection Sign Algorithms for Acoustic Echo Cancellation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 34, 3933–3948 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0040-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0040-6