Abstract
Background
Nodal metastases are linked to poor outcome in men with penile or prostate cancer. Early detection and resection are important for staging and for the prognosis. However, lymphadenectomy is associated with morbidity and may miss metastases when performed solely on the basis of anatomical templates.
Methods
In this article we describe the technique and benefits of sentinel node biopsy (SNB) and provide a review of the literature.
Results
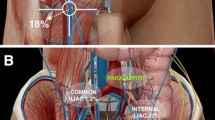
Dynamic sentinel node techniques using both radioactive and optical (hybrid) tracers have been proven effective in penile cancer. For prostate cancer, SNB added to extended nodal dissection may further tailor dissection to the highly variable lymphatic drainage patterns in the pelvis. The sensitivity of SNB was found to be superior to conventional imaging methods; however, false-negative SNB procedures can occur and a complementary extensive lymphadenectomy is required to remove additional positive nodes that were not detected in the SNB template.
Conclusion
SNB is a standard method for early detection of nodal metastases in penile cancer and provides superior diagnostic accuracy to conventional imaging modalities in prostate cancer.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund
Eine lymphogene Metastasierung stellt einen ungünstigen prognostischen Faktor beim Penis- und Prostatakarzinom dar. Daher ist die frühe Erkennung und Resektion nicht nur zum korrekten Staging notwendig, sondern könnte auch für die Patienten von prognostischer Bedeutung sein. Die Lymphadenektomie ist jedoch mit einer gewissen Morbidität vergesellschaftet und birgt auch das Risiko, dass Lymphknotenmetastasen übersehen werden, vor allem, wenn sie sich nur an anatomischen Template-Feldern orientiert.
Methodik
Es erfolgt die Beschreibung der Technik und der Vorteile der Wächterlymphknotenresektion („sentinel node biopsy“, SNB) sowie eine Literaturübersicht.
Ergebnisse
Die Technik der dynamischen SNB, die radioaktive oder optische Tracer verwendet, ist beim Peniskarzinom etabliert. Beim Prostatakarzinom und dem hochgradig variablen Lymphabfluss im kleinen Becken könnte die SNB in Kombination mit einer ausgedehnten pelvinen Lymphknotendissektion von zusätzlichem Nutzen sein. Die Sensitivität der SNB ist der konventionellen Bildgebung überlegen, wobei jedoch auch hier falsch-negative Ergebnisse beobachtet werden, sodass bei diesen Patienten noch eine ergänzende ausgedehnte pelvine Lymphknotendissektion benötigt wird.
Schlussfolgerung
Die SNB ist eine Standardmethode zum frühen Erkennen von Lymphknotenmetastasen beim Peniskarzinom und ermöglicht eine erhöhte diagnostische Sicherheit im Vergleich zur konventionellen Bildgebung beim Prostatakarzinom.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thuret R, Sun M, Lughezzani G, Budaus L, Liberman D, Abdollah F et al (2011) A contemporary population-based assessment of the rate of lymph node dissection for penile carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 18(2):439–446
Acar C, Kleinjan GH, van den Berg NS, Wit EM, van Leeuwen FW, van der Poel HG (2015) Advances in sentinel node dissection in prostate cancer from a technical perspective. Int J Urol 22(10):898–909
Stuiver MM, Westerduin E, ter Meulen S, Vincent AD, Nieweg OE, Wouters MW (2014) Surgical wound complications after groin dissection in melanoma patients – a historical cohort study and risk factor analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 40(10):1284–1290
Wawroschek F, Vogt H, Bachter D, Weckermann D, Hamm M, Harzmann R (2000) First experience with gamma probe guided sentinel lymph node surgery in penile cancer. Urol Res 28(4):246–249
Valdes Olmos RA, Tanis PJ, Hoefnagel CA, Jansen L, Nieweg OE, Meinhardt W et al (2001) Penile lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel node identification. Eur J Nucl Med 28(5):581–585
Perdona S, Autorino R, De Sio M, Di Lorenzo G, Gallo L, Damiano R et al (2005) Dynamic sentinel node biopsy in clinically node-negative penile cancer versus radical inguinal lymphadenectomy: a comparative study. Urology 66(6):1282–1286
Cabanas RM (1977) An approach for the treatment of penile carcinoma. Cancer 39(2):456–466
Horenblas S, Jansen L, Meinhardt W, Hoefnagel CA, de Jong D, Nieweg OE (2000) Detection of occult metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the penis using a dynamic sentinel node procedure. J Urol 163(1):100–104
Sadeghi R, Gholami H, Zakavi SR, Kakhki VR, Tabasi KT, Horenblas S (2012) Accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy for inguinal lymph node staging of penile squamous cell carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. J Urol 187(1):25–31
Neto AS, Tobias-Machado M, Ficarra V, Wroclawski ML, Amarante RD, Pompeo AC et al (2011) Dynamic sentinel node biopsy for inguinal lymph node staging in patients with penile cancer: a systematic review and cumulative analysis of the literature. Ann Surg Oncol 18(7):2026–2034
Brennhovd B, Johnsrud K, Berner A, Bogsrud T, Waehre H, Giercksky KE et al (2006) Sentinel node procedure in low-stage/low-grade penile carcinomas. Scand J Urol Nephrol 40(3):204–207
Akduman B, Fleshner NE, Ehrlich L, Klotz L (2001) Early experience in intermediate-risk penile cancer with sentinel node identification using the gamma probe. Urology 58(1):65–68
Hakenberg OW, Comperat EM, Minhas S, Necchi A, Protzel C, Watkin N (2015) EAU guidelines on penile cancer: 2014 update. Eur Urol 67(1):142–150
Graafland NM, Valdes Olmos RA, Meinhardt W, Bex A, van der Poel HG, van Boven HH et al (2010) Nodal staging in penile carcinoma by dynamic sentinel node biopsy after previous therapeutic primary tumour resection. Eur Urol 58(5):748–751
Graafland NM, Leijte JA, Olmos RA, Van Boven HH, Nieweg OE, Horenblas S (2010) Repeat dynamic sentinel node biopsy in locally recurrent penile carcinoma. BJU Int 105(8):1121–1124
Kroon BK, Horenblas S, Deurloo EE, Nieweg OE, Teertstra HJ (2005) Ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology before sentinel node biopsy in patients with penile carcinoma. BJU Int 95(4):517–521
Kroon BK, Horenblas S, Estourgie SH, Lont AP, Valdes Olmos RA, Nieweg OE (2004) How to avoid false-negative dynamic sentinel node procedures in penile carcinoma. J Urol 171(6):2191–2194
Leijte JA, van der Ploeg IM, Valdes Olmos RA, Nieweg OE, Horenblas S (2009) Visualization of tumor blockage and rerouting of lymphatic drainage in penile cancer patients by use of SPECT/CT. J Nucl Med 50(3):364–367
Brouwer OR, van den Berg NS, Matheron HM, van der Poel HG, van Rhijn BW, Bex A et al (2014) A hybrid radioactive and fluorescent tracer for sentinel node biopsy in penile carcinoma as a potential replacement for blue dye. Eur Urol 65(3):600–609
Hadway P, Smith Y, Corbishley C, Heenan S, Watkin NA (2007) Evaluation of dynamic lymphoscintigraphy and sentinel lymph-node biopsy for detecting occult metastases in patients with penile squamous cell carcinoma. BJU Int 100(3):561–565
Kroon BK, Horenblas S, Meinhardt W, van der Poel HG, Bex A, van Tinteren H et al (2005) Dynamic sentinel node biopsy in penile carcinoma: evaluation of 10 years experience. Eur Urol 47(5):601–606 (discussion 6)
Ornellas AA, Kinchin EW, Nobrega BL, Wisnescky A, Koifman N, Quirino R (2008) Surgical treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: Brazilian National Cancer Institute long-term experience. J Surg Oncol 97(6):487–495
Djajadiningrat RS, Graafland NM, van Werkhoven E, Meinhardt W, Bex A, van der Poel HG et al (2014) Contemporary management of regional nodes in penile cancer-improvement of survival? J Urol 191(1):68–73
Leijte JA, Kirrander P, Antonini N, Windahl T, Horenblas S (2008) Recurrence patterns of squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: recommendations for follow-up based on a two-centre analysis of 700 patients. Eur Urol 54(1):161–168
Briganti A, Chun FK, Salonia A, Gallina A, Farina E, Da Pozzo LF et al (2006) Validation of a nomogram predicting the probability of lymph node invasion based on the extent of pelvic lymphadenectomy in patients with clinically localized prostate cancer. BJU Int 98(4):788–793
Cagiannos I, Karakiewicz P, Eastham JA, Ohori M, Rabbani F, Gerigk C et al (2003) A preoperative nomogram identifying decreased risk of positive pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer. J Urol 170(5):1798–1803
Eifler JB, Feng Z, Lin BM, Partin MT, Humphreys EB, Han M et al (2013) An updated prostate cancer staging nomogram (Partin tables) based on cases from 2006 to 2011. BJU Int 111(1):22–29
Abdollah F, Gandaglia G, Suardi N, Capitanio U, Salonia A, Nini A et al (2014) More extensive pelvic lymph node dissection improves survival in patients with node-positive prostate cancer. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.05.011
Briganti A, Blute ML, Eastham JH, Graefen M, Heidenreich A, Karnes JR et al (2009) Pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer. Eur Urol 55(6):1251–1265
Weckermann D, Dorn R, Holl G, Wagner T, Harzmann R (2007) Limitations of radioguided surgery in high-risk prostate cancer. Eur Urol 51(6):1549–1556 (discussion 56–8)
Bonilla-Damia A, Roberto Brouwer O, Meinhardt W, Valdes-Olmos RA (2012) Lymphatic drainage in prostate carcinoma assessed by lymphoscintigraphy and SPECT/CT: its importance for the sentinel node procedure. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol 31(2):66–70
Wawroschek F, Vogt H, Weckermann D, Wagner T, Harzmann R (1999) The sentinel lymph node concept in prostate cancer–first results of gamma probe-guided sentinel lymph node identification. Eur Urol 36(6):595–600
Wengenmair H, Kopp J, Vogt H, Wawroschek F, Grober S, Dorn R et al (2002) Sentinel lymph node diagnosis in prostatic carcinoma: II. Biokinetics and dosimetry of 99mTc-Nanocolloid after intraprostatic injection. Nuklearmedizin 41(2):102–107
Wawroschek F, Vogt H, Weckermann D, Wagner T, Hamm M, Harzmann R (2001) Radioisotope guided pelvic lymph node dissection for prostate cancer. J Urol 166(5):1715–1719
Vogt H, Wawroschek F, Wengenmair H, Wagner T, Kopp J, Dorn R et al (2002) Sentinel lymph node diagnosis in prostatic carcinoma: I: Method and clinical evaluation. Nuklearmedizin 41(2):95–101
Rudoni M, Sacchetti GM, Leva L, Inglese E, Monesi G, Minocci D et al (2002) Recent applications of the sentinel lymph node concept: preliminary experience in prostate cancer. Tumori 88(3):16–17
Buckle T, Brouwer OR, Valdes Olmos RA, van der Poel HG, van Leeuwen FW (2012) Relationship between intraprostatic tracer deposits and sentinel lymph node mapping in prostate cancer patients. J Nucl Med 53(7):1026–1033
Brenot-Rossi I, Bastide C, Garcia S, Dumas S, Esterni B, Pasquier J et al (2005) Limited pelvic lymphadenectomy using the sentinel lymph node procedure in patients with localised prostate carcinoma: a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32(6):635–640
Wawroschek F, Vogt H, Wengenmair H, Weckermann D, Hamm M, Keil M et al (2003) Prostate lymphoscintigraphy and radio-guided surgery for sentinel lymph node identification in prostate cancer. Technique and results of the first 350 cases. Urol Int 70(4):303–310
Joniau S, Van den Bergh L, Lerut E, Deroose CM, Haustermans K, Oyen R et al (2012) Mapping of pelvic lymph node metastases in prostate cancer. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.057
Warncke SH, Mattei A, Fuechsel FG, Z’Brun S, Krause T, Studer UE (2007) Detection rate and operating time required for gamma probe-guided sentinel lymph node resection after injection of technetium-99m nanocolloid into the prostate with and without preoperative imaging. Eur Urol 52(1):126–132
Holl G, Dorn R, Wengenmair H, Weckermann D, Sciuk J (2009) Validation of sentinel lymph node dissection in prostate cancer: experience in more than 2,000 patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36(9):1377–1382
Egawa M, Fukuda M, Takashima H, Imao T, Namiki M (2005) Application of sentinel node navigation surgery to prostate cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 32(1):117–120
Bastide C, Brenot-Rossi I, Garcia S, Dumas S, Anfossi E, Ragni E et al (2004) Feasibility and value of the isotope sentinel node mapping technique in prostate cancer. Prog Urol 14(4):501–506
Weckermann D, Hamm M, Dorn R, Wagner T, Wawroschek F, Harzmann R (2006) Sentinel lymph node dissection in prostate cancer. Experience after more than 800 interventions. Urologe A 45(6):723–727
Hautmann S, Beitz S, Naumann M, Lutzen U, Seif C, Stubinger SH et al (2008) Extended sentinel lymph node dissection in radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: a study in the Kiel risk population. Urologe A 47(3):299–303
Corvin S, Schilling D, Eichhorn K, Hundt I, Hennenlotter J, Anastasiadis AG et al (2006) Laparoscopic sentinel lymph node dissection – a novel technique for the staging of prostate cancer. Eur Urol 49(2):280–285
Meinhardt W, Valdes Olmos RA, van der Poel HG, Bex A, Horenblas S (2008) Laparoscopic sentinel node dissection for prostate carcinoma: technical and anatomical observations. BJU Int 102(6):714–717
van der Poel HG, Buckle T, Brouwer OR, Valdes Olmos RA, van Leeuwen FW (2011) Intraoperative laparoscopic fluorescence guidance to the sentinel lymph node in prostate cancer patients: clinical proof of concept of an integrated functional imaging approach using a multimodal tracer. Eur Urol 60(4):826–833
Jeschke S, Beri A, Grull M, Ziegerhofer J, Prammer P, Leeb K et al (2008) Laparoscopic radioisotope-guided sentinel lymph node dissection in staging of prostate cancer. Eur Urol 53(1):126–132
Grasso M, Blanco S, Grasso AA, Crespi A, De Ponti E, Zucchini N et al (2016) Radio guided radical prostatectomy. Evaluation of feasibility, safety and clinical outcomes. Minerva Urol Nefrol 68(1):3–8
Mattei A, Fuechsel FG, Bhatta Dhar N, Warncke SH, Thalmann GN, Krause T et al (2008) The template of the primary lymphatic landing sites of the prostate should be revisited: results of a multimodality mapping study. Eur Urol 53(1):118–125
Jeschke S, Lusuardi L, Myatt A, Hruby S, Pirich C, Janetschek G (2012) Visualisation of the lymph node pathway in real time by laparoscopic radioisotope- and fluorescence-guided sentinel lymph node dissection in prostate cancer staging. Urology 80(5):1080–1086
Harisinghani MG, Barentsz J, Hahn PF, Deserno WM, Tabatabaei S, van de Kaa CH et al (2003) Noninvasive detection of clinically occult lymph-node metastases in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 348(25):2491–2499
Turkbey B, Hoyt RF Jr., Agarwal HK, Bernardo M, Sankineni S, Johnson L et al (2015) Magnetic resonance sentinel lymph node imaging of the prostate with gadofosveset trisodium-albumin: preliminary results in a canine model. Acad Radiol 22(5):646–652
Winter A, Woenkhaus J, Wawroschek F (2014) A novel method for intraoperative sentinel lymph node detection in prostate cancer patients using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a handheld magnetometer: the initial clinical experience. Ann Surg Oncol 21(13):4390–4396
Wit EM, Acar C, Grivas N, Yuan C, Horenblas S, Liedberg F et al (2016) Sentinel node procedure in prostate cancer: a systematic review to assess diagnostic accuracy. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.09.007
Maurer T, Eiber M, Schwaiger M, Gschwend JE (2016) Current use of PSMA-PET in prostate cancer management. Nat Rev Urol 13(4):226–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
H. G. van der Poel, P. Meershoek, N. Grivas,G. KleinJan, F. W.B. van Leeuwen and S. Horenblas declare that they have no competing interests.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Poel, H.G., Meershoek, P., Grivas, N. et al. Sentinel node biopsy and lymphatic mapping in penile and prostate cancer. Urologe 56, 13–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00120-016-0270-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00120-016-0270-7