Abstract
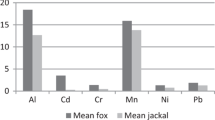
Our aim were to establish the metal (Cu, Ni, Zn, Co, Cd, and Pb) levels of red fox liver and the kidney samples (n = 10) deriving from central part of Hungary and compare the results with other countries’ data. According to our results the concentrations of residues of the targeted elements (mg/kg dry weight) in liver and kidney samples were, respectively in liver: Cu: 21.418, Zn: 156.928, Ni: 2.079, Co: 1.611, Pb: 1.678 and Cd: 0.499; and kidney samples: Cu: 9.236; Zn: 87.159; Ni: 2.514; Co: 2.455; Pb: 2.63 and Cd: 0.818. Pb levels of Hungarian red fox liver samples significantly exceed the values of Italian specimens’ samples, whilst the same element’s concentrations of Hungarian red fox kidney samples were higher than the results published in Germany.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adie GU, Osibanjo O (2009) Assessment of soil-pollution by slag from an automobile battery manufacturing plant in Nigeria. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 3(9):239–250
Alloway BJ (ed) (1990) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic & Professional, Glasgow-London, p 339
Ansorge HK, Graeser H, Fink G (1993) Schwermetallruckstande beim Rotfuchs (Vulpes vulpes). Beitr Jagd-Wildforsch 18:79–82
Corsolini S, Focardi S, Leonzio S, Lovari S, Monaci F, Romeo G (1999) Heavy metals and chlorinated hydrocarbon concentrations in the red fox in relation to some biological parameters. Environ Monit Assess 54:87–100
Dehn LA, Follmann EH, Thomas DL, Sheffield GG, Rosa C, Duffy LK, O’Hara TM (2006) Trophic relationships in an Arctic food web and implications for trace metal transfer. Sci Total Environ 362:103–123
Dip R, Stieger C, Deplazes P, Hegglin D, Muller U, Dafflon O, Koch H, Naegeli H (2001) Comparison of heavy metal concentration in tissues of red foxes from adjacent urban, suburban and rural areas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:551–556
Driscoll CT, Han YJ, Chen CY, Evers DC, Lambert KF, Holsen TM, Kamman NC, Munson RK (2007) Mercury contamination in forest and freshwater ecosystems in the northwestern United States. Bioscience 57:17–28
Goyer R (1996) Toxic effects of metals. In: Klaassen CD (ed) Casarett & Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 691–736
Heltai, M (ed) (2010) Emlős ragadozók Magyarországon. Mezőgazda Kiadó, Budapest 240 pp. ISBN: 978-963-286-593-5 Mammal predators in Hungary (in Hungarian)
Kalisińska E, Palczewska-Komsa M (2011) Teeth of the red fox Vulpes vulpes (L., 1758) as a bioindicator. Acta Theriol 56:343–351
Lanszki J, Heltai M, Szabó L (2006) Feeding habits and trophic niche overlap between sympatric golden jackal (Canis aureus) and red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in the Pannonian ecoregion (Hungary). Can J Zool 84(11):1647–1656
Lucy T, Venugopal B (1977) Metal toxicity in mammals. In: Physiology and Chemical basis for metal Toxicity, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York-London. p 238
Nicholson FA, Smith SR, Alloway BJ, Carlton- Smith C, Chambers BJ (2003) An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci Total Environ 311:205–219
Sawicka-Kapusta K (1979) Roe deer antlers as bioindicators of environmental polution in Southern Poland. Int J Environ Pollut 19(4):283–293
Tataruch F, Kierdorf H (2004) Mammals as biomornitors. In: Markert AA, Breure AM, Zechmeister HG (eds) Bioindicators and biomonitors. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 737–772
Torres KC, Johnson ML (2001) Bioaccumulation of metals in plants, arthropods, and mice at a seasonal wetland. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2617–2626
Xaвeзoв И and Цaлeв Д (1980) Aтoмнo-aбcopбциoнeн aнaлиз, Hayкa и изкycтвo. Coфия. 188 pp. (Havezov, I, D Tsalev. 1980. Atomic absorption analysis, the Science and Art. Sofia. 188 pp)
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments as well as Judit Galló and Ferenc Markolt for the language revision of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Department of Game Management and Fishery of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heltai, M., Markov, G. Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus, 1758) as Biological Indicator for Environmental Pollution in Hungary. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89, 910–914 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0755-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0755-z