Abstract
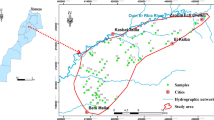
A total of sixteen composite soil and sediment samples were collected during the rainy and dry season in Asientos, Aguascalientes, Mexico, an area recently affected by increased mining operations. Physicochemical characterization showed that substrates were moderately to strongly calcareous with predominantly neutral to slightly alkaline pH, moderate to high cation-exchange capacity and high organic matter content. Due to these conditions, Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn were not water leachable despite high concentrations; up to 105.3, 7052.8, 414.7 and 12,263.2 mg kg−1 respectively. However, Cd and Pb were considered to be easily mobilizable as they were found predominantly associated with exchangeable and carbonate fractions, whereas Cu and Zn were found associated with Fe/Mn oxide and organic matter fractions. The results highlighted the influence of physicochemical substrate properties on the mobility of metals and its importance during the evaluation of the potential current and future risk metal contamination presents in affected areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JA, Jansen B, Kalbitz K et al (2011) Salinity increases mobility of heavy metals in soils. Chemosphere 85:1318–1324. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.046
Anju M, Banerjee DK (2010) Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for heavy metal partitioning in mine tailings. Chemosphere 78:1393–1402. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.12.064
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Arenas-Lago D, Andrade ML, Lago-Vila M et al (2014) Sequential extraction of heavy metals in soils from a copper mine: distribution in geochemical fractions. Geoderma 230–231:108–118. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.04.011
Ashraf MA, Maah MJ, Yusoff I (2012) Chemical speciation and potential mobility of heavy metals in the soil of former tin mining catchment. Sci World J 2012:125608. doi:10.1100/2012/125608
Carrillo-González R, Šimůnek J, Sauvé S, Adriano D (2006) Mechanisms and pathways of trace element mobility in soils. Adv Agron 91:111–178. doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(06)91003-7
CCME (2015) Canadian environmental quality guidelines. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnepeg
Clarke LW, Jenerette GD, Bain DJ (2015) Urban legacies and soil management affect the concentration and speciation of trace metals in Los Angeles community garden soils. Environ Pollut 197:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.11.015
EL-Hefnawy ME, Selim EM, Assaad FF et al (2014) The effect of chloride and sulfate ions on the adsorption of Cd2, the effect of chloride and sulfate ions on the adsorption of Cd2. Sci World J 2014:e806252. doi:10.1155/2014/806252
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2006) Guidelines for Soil Description. Food & Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations
Fernández Linares LC, Rojas Avelizapa NG, Roldán Carrillo TG, Ramírez Islas ME, Zegarra Martínez HG, Hernández Romeo RU, Reyes Ávila J, Flores Hernández D, Arce Ortega JM (2006) Manual de técnicas de análisis de suelos aplicadas a la remediación de sitios contaminados. Instituto Mexicano del Petróleo, D.F. Mexico
Fijałkowski K, Kacprzak M, Grobelak A, Placek A (2012) The influence of selected soil parameters on the mobility of heavy metals in soils. Inżynieria i Ochrona Środowiska T. 15(1):81–92
Gasparatos D, Mavromati G, Kotsovilis P, Massas I (2015) Fractionation of heavy metals and evaluation of the environmental risk for the alkaline soils of the Thriassio plain: a residential, agricultural, and industrial area in Greece. Environ Earth Sci 74:1099–1108. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4096-1
Gutiérrez-Ruiz M, Romero FM, González-Hernández G (2007) Suelos y sedimentos afectados por la dispersión de jales inactivos de sulfuros metálicos en la zona minera de Santa Bárbara, Chihuahua, México. Revista mexicana de ciencias geológicas 24:170–184
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Haydar CM, Nehme N, Awad S et al (2014) Assessing Contamination Level of Heavy Metals in the Lake of Qaraaoun. Lebanon. Phys Procedia 55:285–290. doi:10.1016/j.phpro.2014.07.041
Hernandez-Soriano MC, Jimenez-Lopez JC (2012) Effects of soil water content and organic matter addition on the speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 423:55–61. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.033
Kottek MJ, Grieser C, Beck B, Rubel F (2006) World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol Z 15:259–263. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0130
Lottermoser B (2010) Mine wastes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Maier RM, Pepper IL (2009) Chapter 4—earth environments. In: Gerba RMMLPP (ed) Environmental microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 57–82
Müller G (1979) Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine-Changes seity. 1971. Umsch Wiss Tech 79:778–783
Nazif W, Marzouk ER, Perveen S (2015) Zinc solubility and fractionation in cultivated calcareous soils irrigated with wastewater. Sci Total Environ 518–519:310–319. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.016
Neagoe A, Iordache V, Fărcăşanu IC (2012) The role of organic matter in the mobility of metals in contaminated catchments. In: Kothe E, Varma A (eds) Bio-geo interactions in metal-contaminated soils. Springer, Berlin, pp 297–325
Ramos-Gómez M, Avelar J, Medel-Reyes A et al (2012) Movilidad De Metales En Jales Procedentes Del Distrito Minero De Guanajuato, México. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental. http://oai.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=37023172005. Accessed 4 Nov 2015
Rashid MA (1985) Geochemistry of marine humic compounds. Springer, New York
Rayment GE, Lyons DJ (2011) Soil chemical methods: Australasia. Csiro Publishing, Clayton
Robledo-Santoyo E, Maldonado-Torres R (1997) Manual de Procedimientos para el Analisis de Suelo. Universidad Autónoma de Chapingo, Chapingo
Sato JH, de Figueiredo CC, Marchão RL et al (2014) Methods of soil organic carbon determination in Brazilian savannah soils. Sci Agric 71:302–308. doi:10.1590/0103-9016-2013-0306
SEMARNAT (2000) NOM-021-SEMARNAT-2000—Que Establece Las Especificaciones de Fertilidad, Salinidad y Clasificación de Suelos Estudio, Muestreo y Análisis. Mexico DF
SEMARNAT (2006) NMX-AA-132-SCFI-2006—Soil Sampling for Metal and Semimetal Identification and Quantification, and Sample Handling. Mexico DF
Servicio Geológico Mexico (2011) Panorama Minero del Estado de Aguascalientes. Servicio Geológicos Mexicano, Pachuca
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J (2014) Geochemical fractions of chromium, copper, and zinc and their vertical distribution in floodplain soil profiles along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Geoderma 228–229:142–159. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.10.012
Singh R, Gautam N, Mishra A, Gupta R (2011) Heavy metals and living systems: an overview. Indian J Pharmacol 43:246–253. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.81505
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. EXS 101:133–164. doi:10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844–851. doi:10.1021/ac50043a017
USEPA (1992) Preparation of soil sampling protocols: sampling techniques and strategies. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Las Vegas
USEPA (2007) Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry (EPA Method 7000B). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington
Weiner ER (2012) Applications of environmental aquatic chemistry: a practical guide, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Young S (2011) Dynamics and bioavailability of heavy metals in the rootzone—edited by Magdi Selim, H. Eur J Soil Sci 62:914. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2011.01399.x
Zhao S, Feng C, Wang D et al (2013) Salinity increases the mobility of Cd, Cu, Mn, and Pb in the sediments of Yangtze Estuary: relative role of sediments’ properties and metal speciation. Chemosphere 91:977–984. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.001
Zheng S, Zhang M (2011) Effect of moisture regime on the redistribution of heavy metals in paddy soil. J Environ Sci 23:434–443. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60428-7
Zimmerman AJ, Weindorf DC (2010) Heavy metal and trace metal analysis in soil by sequential extraction: a review of procedures. Int J Anal Chem 2010:387803. doi:10.1155/2010/387803
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Council of Science and Technology (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología), Mexico by means of the research scholarship used for the completion this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, K.N., Ramos Gómez, M.S., Guerrero Barrera, A.L. et al. Evaluation of Environmental Risk of Metal Contaminated Soils and Sediments Near Mining Sites in Aguascalientes, Mexico. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97, 216–224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1820-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1820-9