Abstract
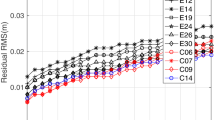
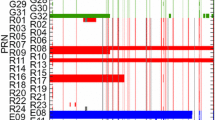
In order to explore the precision and accuracy of International GNSS Service (IGS) orbits, we difference geocentric satellite positions midway between successive daily Final orbits for the period starting 5 November 2006, when the IGS switched its method of antenna calibration, through 31 December 2007. This yields a time series of orbit repeatabilities analogous to the classical geodetic test for position determinations. If we compare our average positional discontinuities to the official IGS accuracy codes, root-sum-squared (RSS) for each pair of days, we find the discontinuities are not well correlated with the predicted performance values. If instead the IGS weighted root-mean-square (WRMS) values from the Final combination long-arc analyses are taken as the measure of IGS accuracy, we find the position differences and long-arc values are correlated, but the long-arc values are exaggerated, particularly around eclipses, despite the fact that our day-boundary position differences apply to a single epoch each day and the long-arc analyses consider variations over a week. Our method is not well suited to probe the extent to which systematic effects dominate over random orbit errors, as indicated by satellite laser ranging residuals, but eclipsing satellites often display the most problematic behavior. A better metric than the current IGS orbit accuracy codes would probably be one based on the orbit discontinuities between successive days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beutler G, Brockmann E, Gurtner W, Hugentobler U, Mervart L, Rothacher M (1994) Extended orbit modeling techniques at the CODE Processing Center of the international GPS service for geodynamics (IGS): theory and initial results. Manuscr Geod 19: 367–386
Beutler G, Kouba J, Springer T (1995) Combining the orbits of the IGS Analysis Centers. Bull Geod 69: 200–222 doi:10.1007/BF00806733
Beutler G, Rothacher M, Schaer S, Springer T, Kouba J, Neilan RE (1999) The International GPS Service (IGS): an interdisciplinary service in support of earth sciences. Adv Space Res 23(4): 631–653 doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(99)00160-X
Kouba J, Mireault Y, Lahaye F (1995) 1994 IGS orbit/clock combination and evaluation, Appendix 1 of the analysis coordinator report, international GPS Service For Geodynamics 1994 Annual Report, Jet Propulsion Laboratory publication 95-18, pp 70–94
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (2001) Numerical recipes in Fortran 77: the art of scientific computing (2nd edition). vol 1 of Fortran numerical recipes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 992 pp
Ray J, Altamimi Z, Collilieux X, Van Dam T (2008) Anomolous harmonics in the spectra of GPS position estimates. GPS Solut 12(1): 55–64 doi:10.1007/s10291-007-0067-7
Schmid R, Steigenberger P, Gendt G, Ge M, Rothacher M (2007) Generation of a consistent absolute phase-center correction model for GPS receiver and satellite antennas. J Geod 81(12): 781–798 doi:10.1007/s00190-007-0148-y
Spofford PR, Remondi BW (1995) The National Geodetic Survey standard GPS Format SP3. NOAA, National Geodetic Survey. ftp://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/data/format/sp3_docu.txt
Urschl C, Beutler G, Gurtner W, Hugentobler U, Schaer S (2007) Contribution of SLR tracking data to GNSS orbit determination. Adv Space Res 39(10): 1515–1523 doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.01.038
Williams SDP, Bock Y, Fang P, Jamason P, Nikolaidis RM, Prawirodirdjo L et al (2004) Error analysis of continuous GPS position time series. J Geophys Res 109: B03412 doi:10.1029/2003JB002741
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffiths, J., Ray, J.R. On the precision and accuracy of IGS orbits. J Geod 83, 277–287 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0237-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0237-6