Abstract
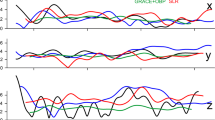
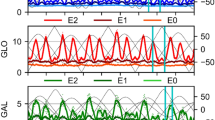
As any satellite geodesy technique, DORIS can monitor geocenter variations associated to mass changes within the Earth–Atmosphere–Continental hydrosphere–Oceans system. However, especially for the Z-component, corresponding to a translation of the Earth along its rotation axis, the estimated geocenter is usually affected by large systematic errors of unknown cause. By reprocessing old DORIS data, and by analyzing single satellite solutions in the frequency domain, we show that some of these errors are satellite-dependent and related to the current DORIS orbit determination strategy. In particular, a better handling of solar pressure radiation effects on SPOT-2 and TOPEX satellites is proposed which removes a large part of such artifacts. By empirically multiplying the current solar pressure model with a single coefficient (1.03 for TOPEX/Poseidon after 1993.57, and 0.96 before; and 1.08 for SPOT-2) estimated over a long time period, we can improve the measurement noise of the Z-geocenter component from 47.5 to 30.4 mm for the RMS and from 35 to 6 mm for the amplitude of the annual signal. However, the estimated SRP coefficient for SPOT-2 presents greater temporal variability, indicating that a new, dedicated solar radiation pressure model is still needed for precise geodetic applications. In addition, for the TOPEX satellite, a clear discontinuity of unknown cause is also detected on July 27, 1993.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altamimi Z, Boucher C, Willis P (2005) Terrestrial Reference Frame requirements within GGOS perspective. J Geodyn 40(4–5): 363–374. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2005.06.002
Altamimi Z, Collilieux X, Legrand J, Garayt B, Boucher C (2007) ITRF2005, A new release of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame based on time series of station positions and earth orientation parameters. J Geophys Res 112(B9): B09401. doi:10.1029/2007JB004949
Amalvict M, Willis P, Wöppelmann G, Ivins E, Bouin MN, Testud L, Hindered J Isostatic stability of the East Antarctic station Dumont d’Urville from long-term geodetic observations and geophysical models. Polar Res (in press). doi:10.1111/j.1751-8369.2008.00091x
Antreasian PG (1992) Precision radiation force modeling for the TOPEX/Poseidon mission (Photon thrust). Ph.D. Thesis, Boulder, U. Colorado, USA
Antreasian PG, Rosborough GW (1992) Prediction of radiant energy forces on the TOPEX/Poseidon spacescraft. J Spacecr Rockets 29(1): 81–90. doi:10.2514/3.26317
Bar-Sever Y, Russ KM (1997) New and Improved Solar Radiation Models for GPS Satellites Based on Flight Data, JPL Final Report (RF-182/808), 30pp
Beckley BD, Lemoine FG, Luthcke SB, Ray RD, Zelensky NP (2007) Reassesment of global and regional mean sea level trends from TOPEX and Jason-1 altimetry based on revised reference frame and orbits. Geophys Res Lett 34(14): L14608. doi:10.1029/2007GL030002
Crétaux JF, Soudarin L, Davidson FJM, Gennero MC, Berge-Nguyen M, Cazenave A (2002) Seasonal and interannual geocenter motion from SLR and DORIS measurements, comparison with surface loading data. J Geophys Res 107(B12): 2374. doi:10.1029/2002JB001820
Dong D, Dickey JO, Cheng MK (1997) Geocenter variations caused by atmosphere, ocean and surface ground water. Geophys Res Lett 24(15): 1867–1870. doi:10.1029/97GL01849
Dong D, Yunck T, Heflin M (2003) Origin of the international terrestrial reference frame. J Geophys Res 108(B4): 2200. doi:10.1029/2002JB002035
Doornbos E, Willis P (2007) Analysis of DORIS range-rate residuals for TOPEX/Poseidon, Jason, ENVISAT and SPOT. Acta Astronaut 60(8–9): 611–621. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.07.012
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Gendt G (2005) The international GPS service (IGS): celebrating the 10th anniversary and looking to the next decade. Adv Space Res 36(3): 320–326. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.05.125
Feissel-Vernier M, de Viron O, Le Bail K (2007) Stability of VLBI, SLR, DORIS and GPS positioning. Earth Planets Space 59(6): 475–497
Ferland R, Kouba J, Hutchison D (2000) Analysis methodology and recent results of the IGS network combination. Earth Planets Space 52: 953–957
Fliegel HF, Gallini TE, Swift ER (1992) Global Positioning System radiation force model for geodetic applications. J Geophys Res 97(B1): 559–568. doi:10.1029/91JB02564
Haines B, Bar-Sever Y, Bertiger W, Desai S, (2004) One-centimeter orbit determination for Jason-1: new GPS-based strategies. MARINE GEOD 27(1–2): 299–318
Lavallée DA, van Dam T, Blewitt G, Clarke PJ (2006) Geocenter motions from GPS, a unified observation model. J Geophys Res 111(B5): B05405. doi:10.1029/2005JB003784
Lemoine JM, Capdeville H (2006) A corrective model for Jason-1 DORIS Doppler data in relation to the South Atlantic Anomaly. J Geod 80(8–11): 507–523. doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0068-2
Luthcke SB, Marshall SA (1992) Non-conservative force model parameter estimation strategy for TOPEX/Poseidon Precision Orbit Determination, NASA Techn Memo
Marquis W, Krier C (2000) Examination of the GPS block IIR solar pressure model. ION GPS 2000, 19–22 September 2000, Salt Lake City, UT, pp 407–415
Marshall JA, Luthcke SB (1992) Nonconservative force model parameter estimation strategy for TOPEX/Poseidon precision orbit determination, NASA Techn. Memo 104575, Goddard Space Flight Center, 39pp
Marshall JA, Luthcke SB (1994) Modeling radiation forces acting on TOPEX Poseidon for precise orbit determination. J Spacecr Rockets 31(1): 99–105. doi:10.2514/3.26408
Marshall JA, Luthcke SB, Antreasian PG, Rosborough GW (1992) Modelling radiation forces acting on Topex/Poseidon for precise orbit determination, NASA Techn. Memo 104564, Goddard Space Flight Center, 75pp
Marshall JA, Zelensky NP, Klosko SM, Luthcke SB, Rachlin KE, Williamson RG (1995) The temporal and spatial characteristics of TOPEX/POSEIDON radial orbit error. J Geophys Res 100(C12): 25331–25352. doi:10.1029/95JC01845
Meisel B, Angermann D, Krugel M, Drewes H, Gerstl M, Kelm R, Muller H, Seemuller W, Tesmer V (2005) Refined approaches for terrestrial reference frame computations. Adv Space Res 36(3): 350–357. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.04.057
Moore P, Wang J (2003) Geocentre variation from Laser tracking of LAGEOS 1/2 and loading data. Adv Space Res 31(8): 1927–1933. doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(03)00170-4
Morel L, Willis (2002) Parameter sensitivity of TOPEX orbit and derived mean sea level to DORIS station coordinates. Adv Space Res 30(2): 255–263. doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00293-4
Morel L, Willis P (2005) Terrestrial reference frame effects on sea level rise determined by TOPEX/Poseidon. Adv Space Res 36(3): 358–368. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.05.113
Springer TA, Beutler G, Rothacher M (1999) Improving the orbit estimates of GPS satellites. J Geod 73(3): 147–157. doi:10.1007/s001900050230
Tapley BD, Ries J, Bettadpur S, Chambers D, Cheng M, Condi F, Gunter B, Kang Z, Nagel P, Pastor R, Pekker T, Poole S, Wang F (2005) GGM02, an improved Earth gravity model from GRACE. J Geod 79(8): 467–478. doi:10.1007/s00190-005-0480-z
Tavernier G, Fagard H, Feissel-Vernier M, Lemoine F, Noll C, Ries J, Soudarin L, Willis P (2005) The international DORIS service. Adv Space Res 36(3): 333–341. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.102
Tavernier G, Fagard H, Feissel-Vernier M, Le Bail K, Lemoine F, Noll C, Noomen R, Ries JC, Soudarin L, Valette JJ, Willis P (2006) The international DORIS service: genesis and early achievements. J Geod 80(8–11): 403–417. doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0082-4
Urschl C, Beutler G, Gurtner W, Hugentobler U, Schaer S (2007) Contribution of SLR tracking data to GNSS orbit determination. Adv Space Res 39(10): 1515–1523. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.01.038
Williams SDP, Willis P (2006) Error analysis of weekly station coordinates in the DORIS network. J Geod 80(8–11): 525–539. doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0056-6
Willis P, Haines B, Berthias JP, Sengenes P, Le Mouel JL (2004) Behavior of the DORIS/Jason oscillator over the South Atlantic Anomaly. C R Geosci 336(9): 839–846. doi:10.1016/j.crte.2004.01.004
Willis P, Bar-Sever YE, Tavernier G (2005a) DORIS as a potential part of a Global Geodetic Observing System. J Geodyn 40(4–5): 494–501. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2005.06.011
Willis P, Boucher C, Fagard H, Altamimi Z (2005b) Geodetic applications of the DORIS system at the French Institut Géographique National. C R Geosci 337(7): 653–662. doi:10.1016/j.crte.2005.03.002
Willis P, Berthias J-P, Bar-Sever YE (2006) Systematic errors in the Z-geocenter derived using satellite tracking data, a case study from SPOT-4 DORIS data in 1998. J Geod 79(10–11): 567–572. doi:10.1007/s00190-005-0013-9
Willis P, Soudarin L, Jayles C, Rolland L (2007a) DORIS applications for solid Earth and atmospheric sciences. C R Geosci 339(16): 949–959. doi:10.1016/j.crte.2007.09.015
Willis P, Haines BJ, Kuang D (2007b) DORIS satellite phase center determination and consequences on the derived scale of the Terrestrial Reference Frame. Adv Space Res 39(10): 1589–1596. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2007.01.007
Ziebart M (2004) Generalized analytical solar radiation pressure modelling algorithm for spacecraft of complex shape. J Spacecr Rockets 41(5): 840–848. doi:10.2514/1.13097
Ziebart M, Adhya S, Sibthorpe A, Edwards S, Cross PA (2005) Combined radiation pressure and thermal modelling of complex satellites: algorithms and on-orbit tests. Adv Space Res 36(3): 424–430. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.01.014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gobinddass, M.L., Willis, P., de Viron, O. et al. Systematic biases in DORIS-derived geocenter time series related to solar radiation pressure mis-modeling. J Geod 83, 849–858 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0303-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0303-8