Abstract
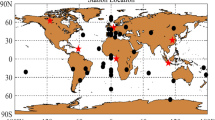
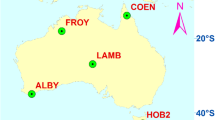
Ionosphere delay is a key factor in the single-frequency Precise Point Positioning (SFPPP). In tradition, two SFPPP models are applied, i.e., ionosphere-corrected (IC) and ionosphere-free-half (IFH) models. The ionospheric delays are directly corrected in IC model with external ionospheric products, while they are eliminated by forming the ionosphere-free combination with code and phase in IFH model. However, almost all studies focus on the numerical performance of these two models and lack the comprehensive study on the estimability and solvability of SFPPP model with either code division multiple access (CDMA) or frequency division multiple access (FDMA) system, respectively. In this paper, we dedicate to the analytical study on SFPPP models for both CDMA and FDMA systems. To assimilate the impact of ionospheric delays on positioning, a general SFPPP model, i.e., ionosphere-weighted (IW) model, is first formulated to identify the varying situations with the different uncertainties of ionospheric constraints. Then, we mathematically show how the IC, IFH and ionosphere-float (IF) models are reduced from IW model. The numerical comparison with GPS and GLONASS data with geodetic and cost-effective receivers effectively confirms our theoretical inference on the relationship of IC, IF and IW models and indicates the best results of IW model for all situations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelazeem M, Çelik RN, El-Rabbany A (2016) An improved regional ionospheric model for single-frequency GNSS users. Surv Rev 49(354):153–159
Aggrey J (2018) Assessment of global and regional ionospheric corrections in multi-GNSS PPP. ION GNSS + 2018, pp 3967–3981. Miami, Florida, September 24–28, 2018
Ashby N (2003) Relativity and the global positioning system. Transl World Seismol 55(5):41–47
Bock H, Jäggi A, Dach R, Schaer S, Beutler G (2009) GPS single-frequency orbit determination for low earth orbiting satellites. Adv Space Res 43(5):783–791
Bona P (2000) Precision, cross correlation, and time correlation of GPS phase and code observations. GPS Solut 4(2):3–13
Cai C, Liu Z, Luo X (2013) Single-frequency ionosphere-free precise point positioning using combined GPS and GLONASS observations. J Navig 66(3):417
Choy S, Silcock D (2011) Single frequency ionosphere-free precise point positioning: a Cross-correlation Problem. J Geod Sci 1(4):314–323
Choy S, Zhang K, Silcock D (2008) An evaluation of various ionospheric error mitigation methods used in single frequency PPP. Positioning 7(1):62–71
Collins J, Langley B (1997) A tropospheric delay model for the user of the wide area augmentation system. Tech. Rep. No. 187, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University of New Brunswick
Dach R, Bock H, Fridez P, Gäde A, Hugentobler U, Jäggi A, Adrian, Mervart, Leos, Meindl, Michael; Walser, Peter and Beutler, Gerhard (2007) Bernese GPS software. Schweizerische Geodätische Kommission
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Rizos C (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geod 83(3–4):191–198
Gao Y, Zhang Y, Chen K (2006) Development of a real-time single-frequency precise point positioning system and test results. Proceedings of ION GNSS 2006, September 26-29, Fort Worth, TX, USA 2006, pp 2297–2303
Geng J, Bock Y (2016) GLONASS fractional-cycle bias estimation across inhomogeneous receivers for PPP ambiguity resolution. J Geod 90:379–396
Ghoddousi-Fard R, Lahaye F (2016) Evaluation of single frequency GPS precise point positioning assisted with external ionosphere sources. Adv Space Res 57(10):2154–2166
Guo F, Zhang X, Wang J, Ren X (2016) Modeling and assessment of triple-frequency BDS precise point positioning. J Geod 90(11):1223–1235
IGS (2007) International GNSS Service. http://www.igs.org/products. Accessed Sept 2018)
Klobuchar J (1996) Ionospheric effects on GPS. Glob. Position Syst Theory Appl 1:485–515
Kouba J (2009) A guide to using international GNSS service (IGS) products. http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/ pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf
Le AQ, Tiberius C (2007) Single-frequency precise point positioning with optimal filtering. GPS Solut 11(1):61–69
Li B, Teunissen PJG (2014) GNSS antenna array-aided cors ambiguity resolution. J Geod 88(4):363–376
Li B, Verhagen S, Teunissen PJG (2014) Robustness of GNSS integer ambiguity resolution in the presence of atmospheric biases. GPS Solut 18(2):283–296
Li X, Zhang X, Ren X, Fritsche M, Wickert J, Schuh H (2015) Precise positioning with current multi-constellation global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. Sci Rep 5:8328
Li B, Li Z, Zhang Z, Tan Y (2017) ERTK: extra-wide-lane RTK of triple-frequency GNSS signals. J Geod 91(9):1031–1047
Lou Y, Zheng F, Gu S, Wang C, Guo H, Feng Y (2016) Multi-GNSS precise point positioning with raw single-frequency and dual-frequency measurement models. GPS Solut 20(4):1–14
Montenbruck O (2003) Kinematic GPS positioning of LEO satellites using ionosphere-free single frequency measurements. Aerosp Sci 7(5):396–405
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Teunissen P, Nakamura S (2013) Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut 17(2):211–222
Oladipo OA, Schüler T (2012) GNSS single frequency ionospheric range delay corrections: NeQuick data ingestion technique. Adv Space Res 50(9):1204–1212
Øvstedal O (2002) Absolute positioning with single-frequency GPS receivers. GPS Solut 5(4):33–44
Petit G, Luzum B, Al E (2010) IERS conventions (2010). IERS Technical Note 36, Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankurt am Main
Schmid R, Steigenberger P, Gendt G, Ge M, Rothacher M (2007) Generation of a consistent absolute phase-center correction model for GPS receiver and satellite antennas. J Geod 81(12):781–798
Schüler T, Diessongo H, Pokugyamfi Y (2011) Precise ionosphere-free single-frequency GNSS positioning. GPS Solut 15(2):139–147
Shi C, Gu S, Lou Y, Ge M (2012) An improved approach to model ionospheric delays for single-frequency precise point positioning. Adv Space Res 49(12):1698–1708
Sterle O, Stopar B, Prešeren PP (2015) Single-frequency precise point positioning: an analytical approach. J Geod 89(8):793–810
Wu J, Wu S, Hajj G, Bertiger W, Lichten S (1993) Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr Geod 18:91–98
Yunck TP (1993) Coping with the atmosphere and ionosphere in precise satellite and ground positioning. In: Vallance-Jones A (ed.), Environmental effects on spacecraft positioning and trajectories. Geophysical Monograph, vol 73(13), pp 1–16. IUGG
Zang N, Li B, Shen Y (2017) Comparison and Analysis of Three GPS + BDS PPP models. Acta Geod Cartogr Sin 46(12):1929–1938 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhao Q, Wang Y, Gu S, Zheng F, Shi C, Ge M, Schuh H (2019) Refining ionospheric delay modeling for undifferenced and uncombined GNSS data processing. J Geod 93(4):545–560
Zhou F, Dong D, Li W, Jiang X, Wickert J, Schuh H (2018) GAMP: an open-source software of multi-GNSS precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut 22:33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0699-9
Acknowledgements
This study is sponsored by National Natural Science Funds of China (41874030, 41622401, 41574023 and 41730102), The Scientific and Technological Innovation Plan from Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (18511101801), The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0603102, 2016YFB0501802), and The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The authors thank the efforts of the IGS MGEX campaign for providing multi-GNSS data and products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Zang, N., Ge, H. et al. Single-frequency PPP models: analytical and numerical comparison. J Geod 93, 2499–2514 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01311-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01311-4