Abstract
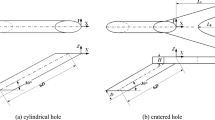
DLR Lampoldshausen carried out a cold flow test series to study the boundary layer separation and the related flow field in a truncated ideal contour nozzle. A special focus was set on low nozzle pressure ratios to identify the origin of a locally re-attached flow condition that was detected in previous test campaigns. A convex shaped Mach disc was found for nozzle pressure ratios less than 10 and a slight concave one for nozzle pressure ratios more than 20. Due to boundary layer transition at low nozzle pressure ratios the convex Mach disc is temporary tilted and redirects the flow towards the nozzle wall. A simple separation criterion for turbulent nozzle flows is presented that fits well for both cold and hot flows. It is shown that the oblique separation shock recompresses the flow to 90% of the ambience. The separation zone of the presented film cooled nozzle is compared with a conventional one around 40% longer. Furthermore a relation between shear layer shape and forced side loads is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciezki, H.: Entwicklung eines Farbschlierenverfahrens unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des Einsatzes an einem Stosswellenrohr. Diploma Thesis, Technical University Aachen (1985)
Cords P.: A high resolution, high sensitivity colour schlieren method. S. P. I. E. J. 6, 85–88 (1968)
Donaldson, C., Lange, R.: Study of the Pressure Rise across Shock Waves Required to Separate Laminar and Turbulent Boundary Layers, NACA RM L52C21 (1952)
Frey, M.: Behandlung von Strömungsproblemen in Raketendüsen bei Überexpansion. PhD Thesis, Universität Stuttgart (2001)
Frey, M., Hagemann, G.: Flow Separation and Side-Loads in Rocket Nozzles, AIAA Paper 1999–2815 (1999)
Hagemann, G., et al.: The Calorimeter Nozzle Programme, AIAA Paper 2002–3998 (2002)
Hagemann, G., et al.: Technology Investigation for High Area Ratio Nozzle Concepts, AIAA Paper 2003–4912 (2003)
Kwan, W., Stark, R.: Flow Separation Phenomena in Subscale Rocket Nozzles, AIAA Paper 2002–4229 (2002)
Lawrence, R.: Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Flow Separation in Supersonic Nozzles, NASA CR 92587 (1967)
Nasuti, F., Onofri, M., Pietropoli, E.: Prediction of Shock Generated Vortices in Rocket Nozzles, AIAA Paper 2005–317 (2005)
Pilinski C., Nebbache A.: Flow separation in a truncated ideal contour nozzle. J. Turbulence 20, 1–24 (2004)
Preuss, A.: An analytical approach for the flowfield analysis of overexpanded rocket nozzles. In: 51st Iternational Astronautical Congress, Rio de Janeiro (2000)
Schlichting H.: Grenzschicht-Theorie. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Schmucker, H.: Strömungsvorgänge beim Betrieb überexpandierender Düsen chemischer Raketentriebwerke, Teil 1: Strömungsablösung. TU München, reprint, NASA CR-143044 and NASA TM-77396 (1973)
Shapiro, A.: The Dynamics and Thermodynamics of Compressible Fluid Flow, vol. 2. Krieger, Malabar (1985)
Stark, R., Hagemann, G.: Current status of numerical flow prediction for separated nozzle flows. In: 2nd European Conference for Aerospace Science, Brussels (2007)
Stark, R., Wagner, B.: Experimental Flow Investigation of a Truncated Ideal Contour Nozzle, AIAA Paper 2006–5208 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Hadjadj.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stark, R., Wagner, B. Experimental study of boundary layer separation in truncated ideal contour nozzles. Shock Waves 19, 185–191 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-008-0174-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-008-0174-6