Summary.
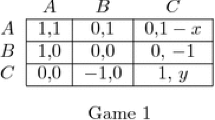
We present a family of mechanisms which implement Lindahl allocations in Nash equilibrium. With quasilinear utility functions this family of mechanisms are supermodular games, which implies that they converge to Nash equilibrium under a wide class of learning dynamics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: April 27, 2000; revised version: January 16, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y. A family of supermodular Nash mechanisms implementing Lindahl allocations. Econ Theory 19, 773–790 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001990100174
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001990100174