Abstract
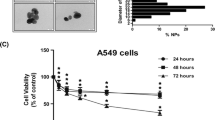
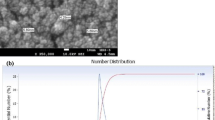
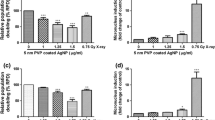
Nanomaterials, especially silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs), are used in a rapidly increasing number of commercial products. Accordingly, the hazards associated with human exposure to nanomaterials should be investigated to facilitate the risk assessment process. A potential route of exposure to NPs is through the respiratory system. In the present study, we investigated the effects of well-characterized PVP-coated Ag NPs and silver ions (Ag+) in the human, alveolar cell line, A549. Dose-dependent cellular toxicity caused by Ag NPs and Ag+ was demonstrated by the MTT and annexin V/propidium iodide assays, and evidence of Ag NP uptake could be measured indirectly by atomic absorption spectroscopy and flow cytometry. The cytotoxicity of both silver compounds was greatly decreased by pretreatment with the antioxidant, N-acetyl-cysteine, and a strong correlation between the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial damage (r s = −0.8810; p = 0.0039) or early apoptosis (r s = 0.8857; p = 0.0188) was observed. DNA damage induced by ROS was detected as an increase in bulky DNA adducts by 32P postlabeling after Ag NP exposure. The level of bulky DNA adducts was strongly correlated with the cellular ROS levels (r s = 0.8810, p = 0.0039) and could be inhibited by antioxidant pretreatment, suggesting Ag NPs as a mediator of ROS-induced genotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora S, Jain J, Rajwade JM, Paknikar KM (2008) Cellular responses induced by silver nanoparticles: in vitro studies. Toxicol Lett 179(2):93–100
AshaRani PV, Low Kah MG, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 3(2):279–290
Auffan M, Rose J, Bottero JY, Lowry GV, Jolivet JP, Wiesner MR (2009) Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental, health and safety perspective. Nat Nanotechnol 4(10):634–641
Bak H, Autrup H, Thomsen BL, Tjonneland A, Overvad K, Vogel U, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Loft S (2006) Bulky DNA adducts as risk indicator of lung cancer in a Danish case-cohort study. Int J Cancer 118(7):1618–1622
Braydich-Stolle L, Hussain S, Schlager JJ, Hofmann MC (2005) In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci 88(2):412–419
Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, Schlager JJ (2008) Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B 112(43):13608–13619
Foldbjerg R, Olesen P, Hougaard M, Dang DA, Hoffmann HJ, Autrup H (2009) PVP-coated silver nanoparticles and silver ions induce reactive oxygen species, apoptosis and necrosis in THP-1 monocytes. Toxicol Lett 190(2):156–162
Hsin YH, Chen CF, Huang S, Shih TS, Lai PS, Chueh PJ (2008) The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 179(3):130–139
Hussain SM, Hess KL, Gearhart JM, Geiss KT, Schlager JJ (2005) In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol In Vitro 19(7):975–983
Hussain SM, Javorina AK, Schrand AM, Duhart HM, Ali SF, Schlager JJ (2006) The interaction of manganese nanoparticles with PC-12 cells induces dopamine depletion. Toxicol Sci 92(2):456–463
Ip M, Lui SL, Poon VKM, Lung I, Burd A (2006) Antimicrobial activities of silver dressings: an in vitro comparison. J Med Microbiol 55(1):59–63
Kim S, Choi JE, Choi J, Chung KH, Park K, Yi J, Ryu DY (2009) Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23(6):1076–1084
Kweon MH, Adhami VM, Lee JS, Mukhtar H (2006) Constitutive overexpression of Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 in A549 cells contributes to resistance to apoptosis induced by epigallocatechin 3-gallate. J Biol Chem 281(44):33761–33772
Limbach LK, Wick P, Manser P, Grass RN, Bruinink A, Stark WJ (2007) Exposure of engineered nanoparticles to human lung epithelial cells: influence of chemical composition and catalytic activity on oxidative stress. Environ Sci Technol 41(11):4158–4163
Lorenzen A, Kennedy SW (1993) A fluorescence-based protein assay for use with a microplate reader. Anal Biochem 214(1):346–348
Melaiye A, Sun Z, Hindi K, Milsted A, Ely D, Reneker DH, Tessier CA, Youngs WJ (2005) Silver(I)-imidazole cyclophane gem-diol complexes encapsulated by electrospun tecophilic nanofibers: formation of nanosilver particles and antimicrobial activity. J Am Chem Soc 127(7):2285–2291
Miura N, Shinohara Y (2009) Cytotoxic effect and apoptosis induction by silver nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390(3):733–737
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8959–8964
Nielsen PS, de Peter N, Okkels H, Autrup H (1996) Environmental air pollution and DNA adducts in Copenhagen bus drivers—effect of GSTM1 and NAT2 genotypes on adduct levels. Carcinogenesis 17(5):1021–1027
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 12(5):913–922
Pavanello S, Kapka L, Siwinska E, Mielzynska D, Bolognesi C, Clonfero E (2008) Micronuclei related to anti-B[a]PDE-DNA adduct in peripheral blood lymphocytes of heavily polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-exposed nonsmoking coke-oven workers and controls. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17(10):2795–2799
Randerath K, Li DH, Randerath E (1990) Age-related DNA modifications (I-compounds): modulation by physiological and pathological processes. Mutat Res 238(3):245–253
Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle L, Schlager JJ, Dai L, Hussain SM (2008) Can silver nanoparticles be useful as potential biological labels? Nanotechnology 19:235104
Smith LE, Denissenko MF, Bennett WP, Li H, Amin S, Tang M, Pfeifer GP (2000) Targeting of lung cancer mutational hotspots by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(10):803–811
Sorensen M, Autrup H, Moller P, Hertel O, Jensen SS, Vinzents P, Knudsen LE, Loft S (2003) Linking exposure to environmental pollutants with biological effects. Mutat Res 544(2–3):255–271
Suzuki H, Toyooka T, Ibuki Y (2007) Simple and easy method to evaluate uptake potential of nanoparticles in mammalian cells using a flow cytometric light scatter analysis. Environ Sci Technol 41(8):3018–3024
Ueda S, Masutani H, Nakamura H, Tanaka T, Ueno M, Yodoi J (2002) Redox control of cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 4(3):405–414
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reutelingsperger CP (1996) A novel assay to measure loss of plasma membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent cells in culture. Cytometry 24(2):131–139
Wijnhoven SWP, Peijnenburg WJGM, Herberts CA, Hagens WI, Oomen AG, Heugens EHW, Roszek B, Bisschops J, Gosens I, Van De Meent D, Dekkers S, De Jong WH, van Zijverden M, Sips ANJAM, Geertsma RE (2009) Nano-silver—a review of available data and knowledge gaps in human and environmental risk assessment. Nanotoxicology 3(2):109–138
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Madler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, Yeh JI, Zink JI, Nel AE (2008) Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2(10):2121–2134
Xia T, Li N, Nel AE (2009) Potential health impact of nanoparticles. Annu Rev Public Health 30(1):137–150
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Erik Baatrup, Institute of Biology, Aarhus University for conducting AAS measurements. The SUNANO project was granted by the Danish Strategic Research Council, NABIIT2006-06-0015.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foldbjerg, R., Dang, D.A. & Autrup, H. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in the human lung cancer cell line, A549. Arch Toxicol 85, 743–750 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0545-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0545-5