Abstract
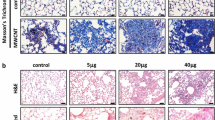
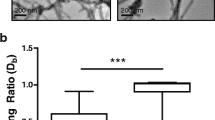
There is increasing concern about the toxicity of inhaled multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). Pulmonary macrophages represent the primary cell type involved in the clearance of inhaled particulate materials, and induction of apoptosis in these cells has been considered to contribute to the development of lung fibrosis. We have investigated the apoptotic, inflammogenic, and fibrogenic potential of two types of MWCNTs, characterised by a contrasting average tube length and entanglement/agglomeration. Both nanotube types triggered H2O2 formation by RAW 264.7 macrophages, but in vitro toxicity was exclusively seen with the longer MWCNT. Both types of nanotubes caused granuloma in the mouse lungs. However, the long MWCNT induced a more pronounced pro-fibrotic (mRNA expression of matrix metalloproteinase-8 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1) and inflammatory (serum level of monocyte chemotactic protein-1) response. Masson trichrome staining also revealed epithelial cell hyperplasia for this type of MWCNT. Enhanced apoptosis was detected by cleaved caspase 3 immunohistochemistry in lungs of mice treated with the long and rigid MWCNT and, to a lesser extent, with the shorter, highly agglomerated MWCNT. However, staining was merely localised to granulomatous foci, and neither of the MWCNTs induced apoptosis in vitro, evaluated by caspase 3/7 activity in RAW 264.7 cells. In addition, our study reveals that the inflammatory and pro-fibrotic effects of MWCNTs in the mouse lung can vary considerably depending on their composition. The in vitro analysis of macrophage apoptosis appears to be a poor predictor of their pulmonary hazard.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beamer CA, Holian A (2007) Antigen-presenting cell population dynamics during murine silicosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 37:729–738
Cho HY, Reddy SP, Kleeberger SR (2006) Nrf2 defends the lung from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:76–87
Clift MJ, Endes C, Vanhecke D, Wick P, Gehr P, Schins RP, Petri-Fink A, Rothen-Rutishauser B (2014) A comparative study of different in vitro lung cell culture systems to assess the most beneficial tool for screening the potential adverse effects of carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Sci 137:55–64
Davis JM, Ramakrishnan L (2009) The role of the granuloma in expansion and dissemination of early tuberculous infection. Cell 136:37–49
De Volder MF, Tawfick SH, Baughman RH, Hart AJ (2013) Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 339:535–539
Di Giorgio ML, Di Bucchianico S, Ragnelli AM, Aimola P, Santucci S, Poma A (2011) Effects of single and multi walled carbon nanotubes on macrophages: cyto and genotoxicity and electron microscopy. Mutat Res 722:20–31
Doll NJ, Stankus RP, Barkman HW (1983) Immunopathogenesis of asbestosis, silicosis, and coal workers’ pneumoconiosis. Clin Chest Med 4:3–14
Donaldson K (2000) Nonneoplastic lung responses induced in experimental animals by exposure to poorly soluble nonfibrous particles. Inhal Toxicol 12:121–139
Donaldson K, Aitken R, Tran L, Stone V, Duffin R, Forrest G, Alexander A (2006) Carbon nanotubes: a review of their properties in relation to pulmonary toxicology and workplace safety. Toxicol Sci 92:5–22
Donaldson K, Murphy FA, Duffin R, Poland CA (2010) Asbestos, carbon nanotubes and the pleural mesothelium: a review of the hypothesis regarding the role of long fibre retention in the parietal pleura, inflammation and mesothelioma. Particle Fibre Toxicol 7:5
Driscoll KE, Lindenschmidt RC, Maurer JK, Higgins JM, Ridder G (1990) Pulmonary response to silica or titanium dioxide: inflammatory cells, alveolar macrophage-derived cytokines, and histopathology. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2:381–390
Elgrabli D, Abella-Gallart S, Robidel F, Rogerieux F, Boczkowski J, Lacroix G (2008) Induction of apoptosis and absence of inflammation in rat lung after intratracheal instillation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Toxicology 253:131–136
Fairbairn IP (2004) Macrophage apoptosis in host immunity to mycobacterial infections. Biochem Soc Trans 32:496–498
Gasser M, Wick P, Clift MJ, Blank F, Diener L, Yan B, Gehr P, Krug HF, Rothen-Rutishauser B (2012) Pulmonary surfactant coating of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) influences their oxidative and pro-inflammatory potential in vitro. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:17
Hansen K, Mossman BT (1987) Generation of superoxide (O2–.) from alveolar macrophages exposed to asbestiform and nonfibrous particles. Cancer Res 47:1681–1686
Hirano S, Kanno S, Furuyama A (2008) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes injure the plasma membrane of macrophages. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 232:244–251
Jaurand MC, Renier A, Daubriac J (2009) Mesothelioma: do asbestos and carbon nanotubes pose the same health risk? Part Fibre Toxicol 6:16
Kane AB, MacDonald JL, Moalli PA (1986) Acute injury and regeneration of mesothelial cells produced by crocidolite asbestos fibers. Am Rev Respir Dis 133:A198
Kato T, Totsuka Y, Ishino K, Matsumoto Y, Tada Y, Nakae D, Goto S, Masuda S, Ogo S, Kawanishi M, Yagi T, Matsuda T, Watanabe M, Wakabayashi K (2013) Genotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in both in vitro and in vivo assay systems. Nanotoxicology 7:452–461
Kermanizadeh A, Pojana G, Gaiser BK, Birkedal R, Bilanicova D, Wallin H, Jensen KA, Sellergren B, Hutchison GR, Marcomini A, Stone V (2013) In vitro assessment of engineered nanomaterials using a hepatocyte cell line: cytotoxicity, pro-inflammatory cytokines and functional markers. Nanotoxicology 7:301–313
Kim JE, Lim HT, Minai-Tehrani A, Kwon JT, Shin JY, Woo CG, Choi M, Baek J, Jeong DH, Ha YC, Chae CH, Song KS, Ahn KH, Lee JH, Sung HJ, Yu IJ, Beck GR Jr, Cho MH (2010) Toxicity and clearance of intratracheally administered multiwalled carbon nanotubes from murine lung. J Toxicol Environ Health A 73:1530–1543
Kisin ER, Murray AR, Sargent L, Lowry D, Chirila M, Siegrist KJ, Schwegler-Berry D, Leonard S, Castranova V, Fadeel B, Kagan VE, Shvedova AA (2011) Genotoxicity of carbon nanofibers: are they potentially more or less dangerous than carbon nanotubes or asbestos? Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 252:1–10
Kobayashi N, Naya M, Ema M, Endoh S, Maru J, Mizuno K, Nakanishi J (2010) Biological response and morphological assessment of individually dispersed multi-wall carbon nanotubes in the lung after intratracheal instillation in rats. Toxicology 276:143–153
Koerten HK, Hazekamp J, Kroon M, Daems WT (1990) Asbestos body formation and iron accumulation in mouse peritoneal granulomas after the introduction of crocidolite asbestos fibers. Am J Pathol 136:141–157
Kuwano K, Miyazaki H, Hagimoto N, Kawasaki M, Fujita M, Kunitake R, Kaneko Y, Hara N (1999) The involvement of Fas–Fas ligand pathway in fibrosing lung diseases. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20:53–60
Leigh J, Wang H, Bonin A, Peters M, Ruan X (1997) Silica-induced apoptosis in alveolar and granulomatous cells in vivo. Environ Health Perspect 105(Suppl 5):1241–1245
Li JG, Li WX, Xu JY, Cai XQ, Liu RL, Li YJ, Zhao QF, Li QN (2007a) Comparative study of pathological lesions induced by multiwalled carbon nanotubes in lungs of mice by intratracheal instillation and inhalation. Environ Toxicol 22:415–421
Li Z, Hulderman T, Salmen R, Chapman R, Leonard SS, Young SH, Shvedova A, Luster MI, Simeonova PP (2007b) Cardiovascular effects of pulmonary exposure to single-wall carbon nanotubes. Environ Health Perspect 115:377–382
Liang J, Jung Y, Tighe RM, Xie T, Liu N, Leonard M, Gunn MD, Jiang D, Noble PW (2012) A macrophage subpopulation recruited by CC chemokine ligand-2 clears apoptotic cells in noninfectious lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 302:L933–L940
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Luo M, Deng X, Shen X, Dong L, Liu Y (2012) Comparison of cytotoxicity of pristine and covalently functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:274–283
Mariani TJ, Roby JD, Mecham RP, Parks WC, Crouch E, Pierce RA (1996) Localization of type I procollagen gene expression in silica-induced granulomatous lung disease and implication of transforming growth factor-beta as a mediator of fibrosis. Am J Pathol 148:151–164
Mercer RR, Hubbs AF, Scabilloni JF, Wang L, Battelli LA, Friend S, Castranova V, Porter DW (2011) Pulmonary fibrotic response to aspiration of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Particle Fibre Toxicol 8:21
Miller BG, Searl A, Davis JM, Donaldson K, Cullen RT, Bolton RE, Buchanan D, Soutar CA (1999) Influence of fibre length, dissolution and biopersistence on the production of mesothelioma in the rat peritoneal cavity. Ann Occup Hyg 43:155–166
Mitchell LA, Gao J, Wal RV, Gigliotti A, Burchiel SW, McDonald JD (2007) Pulmonary and systemic immune response to inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Sci 100:203–214
Moolgavkar SH, Brown RC, Turim J (2001) Biopersistence, fiber length, and cancer risk assessment for inhaled fibers. Inhal Toxicol 13:755–772
Mossman BT (2000) Mechanisms of action of poorly soluble particulates in overload-related lung pathology. Inhal Toxicol 12:141–148
Muhlfeld C, Poland CA, Duffin R, Brandenberger C, Murphy FA, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Gehr P, Donaldson K (2012) Differential effects of long and short carbon nanotubes on the gas-exchange region of the mouse lung. Nanotoxicology 6:867–879
Muller J, Huaux F, Moreau N, Misson P, Heilier JF, Delos M, Arras M, Fonseca A, Nagy JB, Lison D (2005) Respiratory toxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:221–231
Murphy FA, Schinwald A, Poland CA, Donaldson K (2012) The mechanism of pleural inflammation by long carbon nanotubes: interaction of long fibres with macrophages stimulates them to amplify pro-inflammatory responses in mesothelial cells. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:8
Nagatomo H, Morimoto Y, Oyabu T, Hirohashi M, Ogami A, Yamato H, Kuroda K, Higashi T, Tanaka I (2005) Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in the lungs of rats exposed to crocidolite asbestos. Inhal Toxicol 17:293–296
Niu J, Kolattukudy PE (2009) Role of MCP-1 in cardiovascular disease: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Clin Sci 117:95–109
Oberdorster G (1996) Evaluation and use of animal models to assess mechanisms of fibre carcinogenicity. IARC Sci Publ 140:107–125
Osmond-McLeod MJ, Poland CA, Murphy F, Waddington L, Morris H, Hawkins SC, Clark S, Aitken R, McCall MJ, Donaldson K (2011) Durability and inflammogenic impact of carbon nanotubes compared with asbestos fibres. Parti Fibre Toxicol 8:15
Pacurari M, Qian Y, Fu W, Schwegler-Berry D, Ding M, Castranova V, Guo NL (2012) Cell permeability, migration, and reactive oxygen species induced by multiwalled carbon nanotubes in human microvascular endothelial cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A 75:129–147
Poland CA, Duffin R, Kinloch I, Maynard A, Wallace WA, Seaton A, Stone V, Brown S, Macnee W, Donaldson K (2008) Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nat Nanotechnol 3:423–428
Porter DW, Ramsey D, Hubbs AF, Battelli L, Ma J, Barger M, Landsittel D, Robinson VA, McLaurin J, Khan A, Jones W, Teass A, Castranova V (2001) Time course of pulmonary response of rats to inhalation of crystalline silica: histological results and biochemical indices of damage, lipidosis, and fibrosis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 20(Suppl 1):1–14
Roda E, Coccini T, Acerbi D, Barni S, Vaccarone R, Manzo L (2011) Comparative pulmonary toxicity assessment of pristine and functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes intratracheally instilled in rats: morphohistochemical evaluations. Histol Histopathol 26:357–367
Sabo-Attwood T, Ramos-Nino M, Bond J, Butnor KJ, Heintz N, Gruber AD, Steele C, Taatjes DJ, Vacek P, Mossman BT (2005) Gene expression profiles reveal increased mClca3 (Gob5) expression and mucin production in a murine model of asbestos-induced fibrogenesis. Am J Pathol 167:1243–1256
Sato T, Takeno M, Honma K, Yamauchi H, Saito Y, Sasaki T, Morikubo H, Nagashima Y, Takagi S, Yamanaka K, Kaneko T, Ishigatsubo Y (2006) Heme oxygenase-1, a potential biomarker of chronic silicosis, attenuates silica-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:906–914
Schinwald A, Chernova T, Donaldson K (2012a) Use of silver nanowires to determine thresholds for fibre length-dependent pulmonary inflammation and inhibition of macrophage migration in vitro. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:47
Schinwald A, Murphy FA, Prina-Mello A, Poland CA, Byrne F, Movia D, Glass JR, Dickerson JC, Schultz DA, Jeffree CE, Macnee W, Donaldson K (2012b) The threshold length for fiber-induced acute pleural inflammation: shedding light on the early events in asbestos-induced mesothelioma. Toxicol Sci 128:461–470
Sohaebuddin SK, Thevenot PT, Baker D, Eaton JW, Tang L (2010) Nanomaterial cytotoxicity is composition, size, and cell type dependent. Part Fibre Toxicol 7:22
Stone V, Johnston H, Schins RP (2009) Development of in vitro systems for nanotoxicology: methodological considerations. Crit Rev Toxicol 39:613–626
Suga M, Iyonaga K, Ichiyasu H, Saita N, Yamasaki H, Ando M (1999) Clinical significance of MCP-1 levels in BALF and serum in patients with interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J 14:376–382
Takaya M, Serita F, Yamazaki K, Aiso S, Kubota H, Asakura M, Ikawa N, Nagano K, Arito H, Fukushima S (2010) Characteristics of multiwall carbon nanotubes for an intratracheal instillation study with rats. Ind Health 48:452–459
Tanaka T, Terada M, Ariyoshi K, Morimoto K (2010) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CC chemokine ligand 2 enhances apoptotic cell removal by macrophages through Rac1 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399:677–682
van Berlo D, Wessels A, Boots AW, Wilhelmi V, Scherbart AM, Gerloff K, van Schooten FJ, Albrecht C, Schins RP (2010) Neutrophil-derived ROS contribute to oxidative DNA damage induction by quartz particles. Free Radic Biol Med 49:1685–1693
van Berlo D, Clift MJ, Albrecht C, Schins RP (2012) Carbon nanotubes: an insight into the mechanisms of their potential genotoxicity. Swiss Med Wkly 142:w13698
Vietti G, Ibouraadaten S, Palmai-Pallag M, Yakoub Y, Bailly C, Fenoglio I, Marbaix E, Lison D, van den Brule S (2013) Towards predicting the lung fibrogenic activity of nanomaterials: experimental validation of an in vitro fibroblast proliferation assay. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:52
Wang X, Jia G, Wang H, Nie H, Yan L, Deng XY, Wang S (2009) Diameter effects on cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:3025–3033
Wang X, Katwa P, Podila R, Chen P, Ke PC, Rao AM, Walters DM, Wingard CJ, Brown JM (2011) Multi-walled carbon nanotube instillation impairs pulmonary function in C57BL/6 mice. Part Fibre Toxicol 8:24
Wang X, Guo J, Chen T, Nie H, Wang H, Zang J, Cui X, Jia G (2012) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes induce apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway and scavenger receptor. Toxicol In Vitro 26:799–806
Wilhelmi V, Fischer U, van Berlo D, Schulze-Osthoff K, Schins RP, Albrecht C (2012) Evaluation of apoptosis induced by nanoparticles and fine particles in RAW 264.7 macrophages: facts and artefacts. Toxicol In Vitro 26:323–334
Yao SQ, Rojanasakul LW, Chen ZY, Xu YJ, Bai YP, Chen G, Zhang XY, Zhang CM, Yu YQ, Shen FH, Yuan JX, Chen J, He QC (2011) Fas/FasL pathway-mediated alveolar macrophage apoptosis involved in human silicosis. Apoptosis 16:1195–1204
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Burkhard Stahlmecke (IUTA) for the electron microscopy characterisation of MWCNTs, and Christel Weishaupt and Petra Gross (IUF) for technical support. This study was financially supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and an ERS/Marie Curie Fellowship (awarded to AWB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
D. van Berlo and V. Wilhelmi have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Berlo, D., Wilhelmi, V., Boots, A.W. et al. Apoptotic, inflammatory, and fibrogenic effects of two different types of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in mouse lung. Arch Toxicol 88, 1725–1737 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1220-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1220-z