Abstract
The implementation of the Chemical Weapon Convention (CWC), prohibiting the development, production, storage and use of chemical weapons by 192 nations and the ban of highly toxic OP pesticides, especially class I pesticides according to the WHO classification, by many countries constitutes a great success of the international community. However, the increased interest of terrorist groups in toxic chemicals and chemical warfare agents presents new challenges to our societies. Almost seven decades of research on organophosphorus compound (OP) toxicology was mainly focused on a small number of OP nerve agents despite the fact that a huge number of OP analogues, many of these agents having comparable toxicity to classical nerve agents, were synthesized and published. Only limited physicochemical, toxicological and medical information on nerve agent analogues is available in the open literature. This implies potential gaps of our capabilities to detect, to decontaminate and to treat patients if nerve agent analogues are disseminated and may result in inadequate effectiveness of newly developed countermeasures. In summary, our societies may face new, up to now disregarded, threats by toxic OP which calls for increased awareness and appropriate preparedness of military and civilian CBRN defense, a broader approach for new physical and medical countermeasures and an integrated system of effective detection, decontamination, physical protection and treatment.




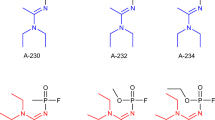
Data are from Aurbek et al. (2006, 2010), Worek et al. (2007), Bartling et al. (2007), Worek et al. (2004, 2009) and from unpublished data. The respective second-order inhibition rate constants, k i, were referred to sarin (k i 4 × 107 M−1min−1; set at 1). The inset presents the relation between the in vitro inhibitory potency and human toxicity estimates referred to sarin (cf. Table 6). GA tabun, GB sarin, GD soman, GF cyclosarin

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Donia MB (1981) Organophosphorus ester-delayed neurotoxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 21:511–548
Aldridge WN, Reiner E (1972) Enzyme inhibitors as substrates—interactions of esterases with esters of organophosphorus and carbamic acids. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam
Aquilonius SM, Fredriksson SA, Sundwall A (1964) Studies on phosphorylated thiocholine and choline derivatives. I. General toxicology and pharmacology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 6:269–279
Aurbek N, Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Worek F (2006) Analysis of inhibition, reactivation and aging kinetics of highly toxic organophosphorus compounds with human and pig acetylcholinesterase. Toxicology 224:91–99
Aurbek N, Herkert NM, Koller M, Thiermann H, Worek F (2010) Kinetic analysis of interactions of different sarin and tabun analogues with human acetylcholinesterase and oximes: is there a structure-activity relationship? Chem Biol Interact 187:215–219
Baldit GL (1958) Amiton-a new acaricide and scalicide. J Sci Food Agr 9:516–524
Ballantyne B, Marrs TC (1992) Overview of the biological and clinical aspects of organophosphates and carbamates. In: Ballantyne B, Marrs T (eds) Clinical and experimental toxicology of organophosphates and carbamates. Butterworth & Heinemann, Oxford, pp 3–14
Bartling A, Worek F, Szinicz L, Thiermann H (2007) Enzyme-kinetic investigation of different sarin analogues reacting with human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Toxicology 233:166–172
Benschop HP, de Jong L (2001) Toxicokinetics of nerve agents. In: Somani S, Romano J (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicity at low levels. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 25–81
Berry WK, Davies DR (1966) Factors influencing the rate of ‘aging’ in a series of alkyl methylphosphonyl-acetylcholinesterases. Biochem J 100:572–576
Bertolote JM, Fleischmann A, Eddleston M, Gunnell D (2006) Deaths from pesticide poisoning: a global response. Br J Psychiatr 189:201–203
Bhattacharjee AK, Marek E, Le HT, Ratcliffe R, DeMar JC, Pervitsky D, Gordon RK (2015) Discovery of non-oxime reactivators using an in silico pharmacophore model of reactivators for DFP-inhibited acetylcholinesterase. Eur J Med Chem 90:209–220
Bierwisch A, Wille T, Thiermann H, Worek F (2016) Kinetic analysis of interactions of amodiaquine with human cholinesterases and organophosphorus compounds. Toxicol Lett 246:49–56
Binenfeld Z (1966) Novi nervni bojni otrovi. Voj Preg 23:40–45
Bjarnason S, Mikler J, Hill I, Tenn C, Garrett M, Caddy N, Sawyer TW (2008) Comparison of selected skin decontaminant products and regimens against VX in domestic swine. Hum Exp Toxicol 27:253–261
Black R (2016) Development, historical use and properties of chemical warfare agents. In: Worek F, Jenner J, Thiermann H (eds) Chemical warfare toxicology, vol 1., Fundamental aspects. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 1–28
Black RM, Harrison JM (1996) The chemistry of organophosphorus chemical warfare agents. In: Hartley F (ed) The chemistry of organophosphorus compounds. Wiley, Chichester, pp 781–840
Black RM, Clarke RJ, Read RW, Reid M (1994) Application of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry to the analysis of chemical warfare samples, found to contain residues of the nerve agent sarin, sulphur mustard and their degredation products. J Chromatogr A 662:301–321
Bouchard M, Gosselin NH, Brunet RC, Samuel O, Dumoulin MJ, Carrier G (2003) A toxicokinetic model of malathion and its metabolites as a tool to assess human exposure and risk through measurements of urinary biomarkers. Toxicol Sci 73:182–194
Braue EH, Smith KH, Doxzon BF, Lumpkin HL, Clarkson ED (2011) Efficacy studies of Reactive Skin Decontamination Lotion, M291 Skin Decontamination Kit, 0.5% bleach, 1% soapy water, and Skin Exposure Reduction Paste against chemical warfare agents, part 1: guinea pigs challenged with VX. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 30:15–28
Busker RW, Zijlstra JJ, van der Wiel HJ, Melchers B, van Helden H (1991) Organophosphate poisoning: a method to test therapeutic effects of oximes other than acetylcholinesterase reactivation in the rat. Toxicology 69:331–344
Casida JE (1956) Metabolism of organophosphorus insecticides in relation to their antiesterase activity, stability, and residual properties. J Agric Food Chem 4:772–785
Casida JE, Durkin KA (2013) Anticholinesterase insecticide retrospective. Chem Biol Interact 203:221–225
CBC News (2015) U.S.: Tests show mustard gas traces in ISIS attack. http://www.cbsnews.com/news/ustests-mustard-gas-traces-isis-attack-kurdish-forces-iraq/. Accessed 18 Apr 2016
Chang SS, Lu TH, Eddleston M, Konradsen F, Sterne J, Lin JJ, Gunnell D (2012) Factors associated with the decline in suicide by pesticide poisoning in Taiwan: a time trend analysis, 1987–2010. Clin Toxicol 50:471–480
Cherny I, Greisen P, Ashani Y, Khare SD, Oberdorfer G, Leader H, Baker D, Tawfik DS (2013) Engineering V-type nerve agents detoxifying enzymes using computationally focused libraries. ACS Chem Biol 8:2394–2403
Chilcott RP (2007) Dermal aspects of chemical warfare agents. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 409–422
Cohen O, Kronman C, Chitlaru T, Ordentlich A, Velan B, Shafferman A (2001) Effect of chemical modification of recombinant human acetylcholinesterase by polyethylene glycol on its circulatory longevity. Biochem J 357:795–802
Covington TR, Lumley LA, Ruark CD, Clarkson ED, Whalley CE, Gearhart JM (2016) Modeling of organophosphorus chemical warfare nerve agents: a physiologically based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PBPK-PD) model of VX. In: Worek F, Jenner J, Thiermann H (eds) Chemical warfare toxicology, vol 1., Fundamental aspects. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 213–263
Dacre JC (1984) Toxicology of some anticholinesterases used as chemical warfare agents—a review. In: Brzin M (ed) Cholinesterases. Walter de Gruyter & Co, Berlin, pp 415–426
Daczkowski CM, Pegan SD, Harvey SP (2015) Engineering the organophosphorus acid anhydrolase enzyme for increased catalytic efficiency and broadened stereospecificity on Russian VX. Biochemistry 54:6423–6433
De Clermont P (1854) Chimie organique - note sur la preparation de quelques ethers. Compt Rend Acad Sci 39:338–341
De Clermont P (1855) Mémoire sur les éthers phosphoriques. Ann Chim Phys 44:330–336
De Jong L, Benschop HP (1988) Biochemical and toxicological implications of chirality in anticholinesterase organophosphates. In: Ariens E, van Rensen J, Welling W (eds) Stereoselectivity of pesticides—biological and chemical problems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 109–149
Eddleston M, Karalliedde L, Buckley N, Fernando R, Hutchinson G, Isbister G, Konradsen F, Murray D, Piola JC, Senanayake N, Sheriff R, Singh S, Siwach SB, Smit L (2002) Pesticide poisoning in the developing world—a minimum pesticides list. Lancet 360:1163–1167
Eddleston M, Eyer P, Worek F, Juszczak E, Alder N, Mohamed F, Senarathna L, Hittarage A, Azher S, Jeganathan K, Jayamanne S, von Meyer L, Dawson AH, Sheriff M, Buckley NA (2009) Pralidoxime in acute organophosphorus insecticide poisoning—a randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med 6:e1000104
Eddleston M, Street JM, Self I, Thompson A, King T, Williams N, Naredo G, Dissanayake K, Yu LM, Worek F, John H, Smith S, Thiermann H, Harris JB, Clutton RE (2012) A role for solvents in the toxicity of agricultural organophosphorus pesticides. Toxicology 294:94–103
Eto M (1974) Organophosphorus pesticides: organic and biological chemistry. CRC Press, Cleveland
European Parliamentary Research Service (2015) ISIL/Da’esh and ‘non-conventional’ weapons of terror. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2015/572806/EPRS_BRI(2015)572806_EN.pdf. Accessed 18 Apr 2016
Eyer P (1995) Neuropsychopathological changes by organophosphorus compounds—a review. Hum Exp Toxicol 14:857–864
Eyer P, Worek F (2007) Oximes. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 305–329
FAO Statistics Division (2013) Pesticide use. http://faostat3.fao.org. Accessed 05 May 2016
Feldmann RJ, Maibach HI (1974) Percutaneous penetration of some pesticides and herbicides in man. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 28:126–132
Foxenberg RJ, McGarrigle BP, Knaak JB, Kostyniak PJ, Olson JR (2007) Human hepatic cytochrome P450-specific metabolism of parathion and chlorpyrifos. Drug Metab Dispos 35:189–193
Gaines TB (1969) Acute toxicity of pesticides. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 14:515–534
Garner F, Jones K (2014) Biological monitoring for exposure to methamidophos: a human oral dosing study. Toxicol Lett 231:277–281
Ghosh R, Newman JF (1955) A new group of organophosphorus pesticides. Chem Ind 11
Goel A, Aggarwal P (2007) Pesticide poisoning. Natl Med J India 20:182–191
Goldsmith M, Eckstein S, Ashani Y, Greisen P, Leader H, Sussman JL, Aggarwal N, Ovchinnikov S, Tawfik DS, Baker D, Thiermann H, Worek F (2016) Catalytic efficiencies of directly evolved phosphotriesterase variants with structurally different organophosphorus compounds in vitro. Arch Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1626-2
Gunnell D, Eddleston M, Phillips MR, Konradsen F (2007) The global distribution of fatal pesticide self-poisoning: systematic review. BMC Public Health 7:357
Hall CR, Inch TD, Inns RH, Muir AW, Sellers DJ, Smith AP (1977) Differences between some biological properties of enantiomers of alkyl S-alkyl methylphosphonothioates. J Pharm Pharmacol 29:574–576
Hamilton MG, Hill I, Conley J, Sawyer TW, Caneva DC, Lundy PM (2004) Clinical aspects of percutaneous poisoning by the chemical warfare agent VX: effects of application site and decontamination. Mil Med 169:856–862
Hayes WJ (1971) Studies on exposure during the use of anticholinesterase pesticides. Bull World Health Organ 44:277–288
Hoette TM (2012) Systems analysis of past, present, and future chemical terrorism scenarios. SAND2012-1468, Sandia National Laboratories
Holmstedt B (1951) Synthesis and pharmacology of dimethylamido-ethoxy-phosphoryl cyanide (Tabun) together with a description of some allied anticholinesterase compounds containing the N–P bond. Acta Physiol Scand 25(Suppl. 90):1–120
Holmstedt B (1959) Pharmacology of organophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev 11:567–688
Holmstedt B (1963) Structure-activity relationship of organophosphorus anticholinesterase agents. In: Koelle G (ed) Cholinesterases and anticholinesterase agents. Springer, Berlin, pp 428–485
Hummel S (2016) The Islamic State and WMD: assessing the future threat. CTC Sentinel 9:18–21
International Programme on Chemical Safety (2010) The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification 2009. World Health Organisation, Geneva
Jackson CJ, Carville A, Ward J, Mansfield K, Ollis DL, Khurana T, Bird SB (2014) Use of OpdA, an organophosphorus (OP) hydrolase, prevents lethality in an African green monkey model of acute OP poisoning. Toxicology 317:1–5
Jandorf BJ, Michel HO, Schaffer NK, Egan R, Summerson WH (1955) The mechanism of reaction between esterases and phosphorus-containing anti-esterases. Disc Faraday Soc 20:134–142
John H, Balszuweit F, Kehe K, Worek F, Thiermann H (2015) Toxicokinetic aspects of nerve agents and vesicants. In: Gupta RC (ed) Handbook of toxicology of chemical warfare agents. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 817–856
Joosen M, van der Schans MJ, Kuijpers WC, van Helden H, Noort D (2013) Timing of decontamination and treatment in case of percutaneous VX poisoning: a mini review. Chem Biol Interact 203:149–153
Jose A, Selvakumar R, Peter JV, Karthik G, Fleming DH, Fleming JJ (2015) Estimation of monocrotophos renal elimination half-life in humans. Clin Toxicol 53:629–632
Kabachnik MI, Brestkin AP, Godovikov NN, Michelson MJ, Rozengart EV, Rozengart VI (1970) Hydrophobic areas on the active surface of cholinesterases. Pharmacol Rev 22:355–388
Kadivar H, Adams SC (1991) Treatment of chemical and biological warfare injuries: insights derived from the 1984 Iraqi attack on Majnoon island. Mil Med 156:171–177
Kalasz H, Nurulain SM, Veress G, Antus S, Darvas F, Adeghate E, Adem A, Hashemi F, Tekes K (2015) Mini review on blood–brain barrier penetration of pyridinium aldoximes. J Appl Toxicol 35:116–123
Katz FS, Pecic S, Tran TH, Trakht I, Schneider L, Zhu Z, Ton-That L, Luzac M, Zlatanic V, Damera S, Macdonald J, Landry DW, Tong L, Stojanovic MN (2015) Discovery of new classes of compounds that reactivate acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphates. ChemBioChem 16:2205–2215
Knipe DW, Metcalfe C, Fernando R, Pearson M, Konradsen F, Eddleston M, Gunnell D (2014) Suicide in Sri Lanka 1975–2012: age, period and cohort analysis of police and hospital data. BMC Public Health 14:839
Koelle GB (1992) Pharmacology and toxicology of organophosphates. In: Ballantyne B, Marrs T (eds) Clinical and experimental toxicology of organophosphates and carbamates. Butterworth and Heinemann, Oxford, pp 35–39
Kovarik Z, Katalinic M, Sinko G, Binder J, Holas O, Jung YS, Musilova L, Jun D, Kuca K (2010) Pseudo-catalytic scavenging: searching for a suitable reactivator of phosphorylated butyrylcholinesterase. Chem Biol Interact 187:167–171
Krieger R (2010) Hayes’ handbook of pesticide toxicology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lange W, von Krueger G (1932) Über Ester der Monofluorphosphorsäure. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges 65:1598–1601
Lee EC (2003) Clinical manifestations of sarin nerve gas exposure. JAMA 290:659–662
Lenz DE, Yeung D, Smith JR, Sweeney RE, Lumley LA, Cerasoli DM (2007) Stoichiometric and catalytic scavengers as protection against nerve agent toxicity: a mini review. Toxicology 233:31–39
Letort S, Balieu S, Erb W, Gouhier G, Estour F (2016) Interactions of cyclodextrins and their derivatives with toxic organophosphorus compounds. Beilstein J Org Chem 12:204–228
Lohs KH (1975) Delayed toxic effects of chemical warfare agents. SIPRI Monograph. Almqvist & Wiksell, Stockholm
Lotti M, Moretto A (2005) Organophosphate-induced delayed polyneuropathy. Toxicol Rev 24:37–49
MacIlwain C (1993) Study proves Iraq used nerve gas. Nature 363:3
Mäkinen MA, Anttalainen OA, Sillinpää M (2010) Ion mobility spectrometry and its applications in detection of chemical warfare agents. Anal Chem 82:9594–9600
Marrs TC (2007) Toxicology of organophosphate nerve agents. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 191–221
Masson P (2015) Catalytic bioscavengers: the new generation of bioscavenger-based medical countermeasures. In: Gupta RC (ed) Handbook of toxicology of chemical warfare agents. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1107–1123
Masson P (2016) Nerve agents: catalytic scavengers as an alternative approach for medical countermeasures. In: Worek F, Jenner J, Thiermann H (eds) Chemical warfare toxicology, vol 2., Management of poisoning. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 43–81
Masson P, Carletti E, Nachon F (2009) Structure, activities and biomedical applications of human butyrylcholinesterase. Protein Peptide Lett 16:1215–1224
Maxwell DM (1992) The specificity of carboxylesterase protection against the toxicity of organophosphorus compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 114:306–312
Maxwell DM, Brecht KM, O’Neill BL (1987) The effect of carboxylesterase inhibition on interspecies differences in soman toxicity. Toxicol Lett 39:35–42
Maxwell DM, Brecht KM, Koplovitz I (1997) Characterization and treatment of the toxicity of O-isobutyl S-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]methylphosphonothioate, a structural isomer of VX, in guinea pigs. J Am Coll Toxicol 15(Suppl 2):S78–S88
Maynard RL, Beswick FW (1992) Organophosphorus compounds as chemical warfare agents. In: Ballantyne B, Marrs T (eds) Clinical and experimental toxicology of organophosphates and carbamates. Butterworth and Heinemann, Oxford, pp 373–385
McDonough JH (2002) Performance impacts of nerve agents and their pharmacological countermeasures. Mil Psychol 14:93–119
McDonough JH, Shih TM (2007) Atropine and other anticholinergic drugs. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 287–303
McKone TE, Huey BM, Downing E, Duffy LM (2000) Strategies to protect the health of deployed U.S. Forces: detecting, characterizing, and documenting exposures. National Academic Press, Washington, DC
Mercey G, Verdelet T, Renou J, Kliachyna M, Baati R, Nachon F, Jean L, Renard PY (2012) Reactivators of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents. Acc Chem Res 45:756–766
Michaelis C (1903) Über die organischen Verbindungen des Phosphors mit Stickstoff. Liebigs Ann Chem 326:129–258
Mikler J, Tenn C, Worek F, Reiter G, Thiermann H, Garrett M, Bohnert S, Sawyer TW (2011) Immobilization of Russian VX skin depots by localized cooling: implications for decontamination and medical countermeasures. Toxicol Lett 206:47–53
Moralev SN, Rozengart EV (2007) Comparative enzymology of cholinesterases. International University Line, La Jolla
Morita H, Yanagisawa N, Nakajima T, Shimizu M, Hirabayashi H, Okudera H, Nohara M, Midorikawa Y, Mimura S (1995) Sarin poisoning in Matsumoto, Japan. Lancet 346:290–293
Mumford H, Price ME, Wetherell JR (2008) A novel approach to assessing percutaneous VX poisoning in the conscious guinea-pig. J Appl Toxicol 28:694–702
Mumford H, Price ME, Lenz DE, Cerasoli DM (2011) Post-exposure therapy with human butyrylcholinesterase following percutaneous VX challenge in guinea pigs. Clin Toxicol 49:287–297
Mumford H, Docx CJ, Price ME, Green AC, Tattersall J, Armstrong SJ (2013) Human plasma-derived BuChE as a stoichiometric bioscavenger for treatment of nerve agent poisoning. Chem Biol Interact 203:160–166
Musilek K, Dolezal M, Gunn-Moore F, Kuca K (2011) Design, evaluation and structure–activity relationship studies of the AChE reactivators against organophosphorus pesticides. Med Res Rev 31:548–575
Mutch E, Williams FM (2006) Diazinon, chlorpyrifos and parathion are metabolised by multiple cytochromes P450 in human liver. Toxicology 224:22–32
Myhrer T, Mariussen E, Enger S, Aas P (2015) Supralethal poisoning by any of the classical nerve agents is effectively counteracted by procyclidine regimens in rats. Neurotoxicology 50:142–148
Nachon F, Brazzolotto X, Trovaslet M, Masson P (2013) Progress in the development of enzyme-based nerve agent bioscavengers. Chem Biol Interact 206:536–544
National Research Council—Committee on Toxicology (1997) Review of acute human-toxicity estimates for selected chemical-warfare agents
Nozaki H, Aikawa N, Fujishima S, Suzuki M, Shinozawa Y, Hori S, Nogawa S (1995a) A case of VX poisoning and the difference from sarin. Lancet 346:698–699
Nozaki H, Aikawa N, Shinozawa Y, Hori S, Fujishima S, Takuma K, Sagoh M (1995b) Sarin poisoning in Tokyo subway. Lancet 345:980–981
O’Brien RD (1960) Toxic phosphorus esters—chemistry, metabolism, and biological effects. Academic Press, New York
Okumura T, Takasu N, Ishimatsu S, Miyanoki S, Mitsuhashi A, Kumuda K, Tanaka K, Hinohara S (1996) Report of 640 victims of the Tokyo subway sarin attack. Ann Emerg Med 28:129–135
OPCW Technical Secretariat (2015) Report of the OPCW fact-finding mission in Syria regarding alleged incidents in Marea, Syrian Arab Republic, August 2015
Peter JV, Sudarsan TI, Moran JL (2014) Clinical features of organophosphate poisoning: a review of different classification systems and approaches. Ind J Crit Care Med 18:735–745
Pita R, Anadon A (2015) Chemical weapons of mass destruction and terrorism: a threat analysis. In: Gupta RC (ed) Handbook of toxicology of chemical warfare agents. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 55–65
Pita R, Domingo J (2014) The use of chemical weapons in the Syrian conflict. Toxics 2:391–402
Price ME, Docx CJ, Rice H, Fairhall SJ, Poole S, Bird M, Whiley L, Flint DP, Green AC, Timperley CM, Tattersall JE (2016) Pharmacokinetic profile and quantitation of protection against soman poisoning by the antinicotinic compound MB327 in the guinea-pig. Toxicol Lett 244:154–160
Prinz HJ (1969) Eine schwere percutane Vergiftung mit Parathion (E605®). Arch Toxikol 25:318–328
Reiter G, Koller M, Thiermann H, Dorandeu F, Mikler J, Worek F (2007) Development and application of procedures for the highly sensitive quantification of cyclosarin enantiomers in hemolysed swine blood samples. J Chromatogr B 859:9–15
Reiter G, Mikler J, Hill I, Weatherby K, Thiermann H, Worek F (2008) Chromatographic resolution, characterisation and quantification of VX enantiomers in hemolysed swine blood samples. J Chromatogr B 873:86–94
Reiter G, Müller S, Hill I, Weatherby K, Thiermann H, Worek F, Mikler J (2015) In vitro and in vivo toxicological studies of V nerve agents: molecular and stereoselective aspects. Toxicol Lett 232:438–448
Rengstorff RH (1994) Vision and ocular changes following accidental exposure to organophosphates. J Appl Toxicol 14:115–118
Rice H (2016) Toxicology of organophosphorus nerve agents. In: Worek F, Jenner J, Thiermann H (eds) Chemical warfare toxicology, vol 1., Fundamental aspects. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 81–116
Rice H, Dalton CH, Price ME, Graham SJ, Green AC, Jenner J, Groombridge HJ, Timperley CM (2015) Toxicity and medical countermeasure studies on the organophosphorus nerve agents VM and VX. Proc R Soc A 471:20140891
Rider JA, Moeller HC, Puletti EJ, Swader JI (1969) Toxicity of parathion, systox, octamethyl pyrophosphoramide, and methyl parathion in man. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 14:603–611
Ring A, Strom BO, Turner SR, Timperley CM, Bird M, Green AC, Chad JE, Worek F, Tattersall J (2015) Bispyridinium compounds inhibit both muscle and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in human cell lines. PLoS ONE 10:e0135811
Roberts G, Maynard RL (2007) Responding to chemical terrorism: operational planning and decontamination. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 175–190
Rochu D, Chabriere E, Masson P (2007) Human paraoxonase: a promising approach for pre-treatment and therapy of organophosphorus poisoning. Toxicology 233:47–59
Sartori MF (1951) New developments in the chemistry of war gases. Chem Rev 48:225–257
Saunders BC (1957) Some aspects of the chemistry and toxic action of organic compounds containing phosphorus and fluorine. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Schrader G (1951) Die Entwicklung neuer Insektizide auf Grundlage organischer Fluor- und Phosphor-Verbindungen. Monogr Angew Chemie 62:1–62
Schrader G (1963) Die Entwicklung neuer insektizider Phosphorsäure-Ester. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Scott L (2007) Nerve agents: low-dose effects. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 241–248
Seeger T, Eichhorn M, Lindner M, Niessen KV, Tattersall J, Timperley CM, Bird M, Green AC, Thiermann H, Worek F (2012) Restoration of soman-blocked neuromuscular transmission in human and rat muscle by the bispyridinium non-oxime MB327 in vitro. Toxicology 294:80–84
Shafferman A, Ordentlich A, Barak D, Stein D, Ariel N, Velan B (1996) Aging of phosphylated human acetylcholinesterase: catalytic processes mediated by aromatic and polar residues of the active centre. Biochem J 318:833–840
Shih TM, Rowland TC, McDonough JH (2007) Anticonvulsants for nerve agent-induced seizures: the influence of the therapeutic dose of atropine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:154–161
Sidell FR (1974) Soman and sarin: clinical manifestations and treatment of accidental poisoning by organophosphates. Clin Toxicol 7:1–17
Sidell FR (1997) Nerve agents. In: Sidell F, Takafuji E, Franz D (eds) Medical aspects of chemical and biological warfare. Borden Institute, Washington, DC, pp 129–179
Sidell FR (2007) A history of human studies with nerve agents by the UK and USA. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 223–239
Sit RK, Radic Z, Gerardi V, Zhang L, Garcia E, Katalinic M, Amitai G, Kovarik Z, Fokin VV, Sharpless KB, Taylor P (2011) New structural scaffolds for centrally acting oxime reactivators of phosphylated cholinesterases. J Biol Chem 286:19422–19430
Sit RK, Fokin VV, Amitai G, Sharpless KB, Taylor P, Radic Z (2014) Imidazole aldoximes effective in assisting butyrylcholinesterase catalysis of organophosphate detoxification. J Med Chem 57:1378–1389
Sweeney RE, Langenberg JP, Maxwell DM (2006) A physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PB/PK) model for multiple exposure routes of soman in multiple species. Arch Toxicol 80:719–731
Szinicz L (2005) History of chemical and biological warfare agents. Toxicology 214:167–181
Tammelin LE (1958) Organophosphorylcholines and cholinesterases. Ark Kemi 12:287–298
Tenberken O, Mikler J, Hill I, Weatherby K, Thiermann H, Worek F, Reiter G (2010) Toxicokinetics of tabun enantiomers in anaesthetized swine after intravenous tabun administration. Toxicol Lett 198:177–181
Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Felgenhauer N, Zilker T, Worek F (2007) Lessons to be learnt from organophosphorus pesticide poisoning for the treatment of nerve agent poisoning. Toxicology 233:145–154
Thiermann H, Steinritz D, Worek F, Radtke M, Eyer P, Eyer F, Felgenhauer N, Zilker T (2011) Atropine maintenance dosage in patients with severe organophosphate pesticide poisoning. Toxicol Lett 206:77–83
Thiermann H, Aurbek N, Worek F (2016) Treatment of nerve agent poisoning. In: Worek F, Jenner J, Thiermann H (eds) Chemical warfare toxicology, vol 2., Management of poisoning. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 1–42
Timchalk C, Busby A, Campbell JA, Needham LL, Barr DB (2007) Comparative pharmacokinetics of the organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos and its major metabolites diethylphosphate, diethylthiophosphate and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in the rat. Toxicology 237:145–157
Timperley CM (2015) Best synthetic methods: organophosphorus (V) chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam
United Nations Treaty Collection (1997) Convention on the prohibition of the development, production, stockpiling and use of chemical weapons and on their destruction. https://treaties.un.org/pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-3&chapter=26&lang=en. Accessed 18 Apr 2016
U.S. Army Chemical School (2005) Potential military chemical/biological agents and compounds. Field Manual 3-11.9. U.S. Army Chemical School, Ft. Leonard Wood, Mo. USA
Vale JA, Rice P, Marrs TC (2007) Managing civilian casualties affected by nerve agents. In: Marrs T, Maynard R, Sidell F (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicology and treatment. Wiley, Chichester, pp 249–260
van der Schans MJ, Lander BJ, van der Wiel H, Langenberg JP, Benschop HP (2003) Toxicokinetics of the nerve agent (±)-VX in anesthetized and atropinized hairless guinea pigs and marmosets after intravenous and percutaneous administration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 191:48–62
Veterans Today (2015) ISIS stole sarin gas from Lybia & has already used it, Gaddafi's cousin. http://www.veteranstoday.com/2015/12/19/isis-stole-sarin-gas-from-libya-stores-has-already-used-itgaddafis-cousin/. Accessed 18 Apr 2016
Watson A, Opresko D, Young RA, Hauschild V, King J, Bakshi K (2015) Organophosphate nerve agents. In: Gupta RC (ed) Handbook of toxicology of chemical warfare agents. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 87–109
Weimaster JF, Beaudry WT, Bossle PC, Ellzy MW, Janes LG, Johnson DW, Lochner JM, Pleva SG, Reeder JH, Rohrbaugh DK, Rosso TE, Szafraniec LJ, Szafraniec LL, Albro TG, Creasey WR, Stuff JR, Smiths PB, Stewart IR (1995) Chemical analysis of environmental samples collected in Iraq: analysis for the presence of chemical warfare agents. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 64:115–128
Weissman BA, Raveh L (2008) Therapy against organophosphate poisoning: the importance of anticholinergic drugs with antiglutamatergic properties. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 232:351–358
Wester RC, Maibach HI, Bucks AW, Guy RH (1983) Malathion percutaneous absorption after repeated administration to man. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 68:116–119
Worek F, Thiermann H (2013) The value of novel oximes for treatment of poisoning by organophosphorus compounds. Pharmacol Ther 139:249–259
Worek F, Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P (2004) Kinetic analysis of interactions between human acetylcholinesterase, structurally different organophosphorus compounds and oximes. Biochem Pharmacol 68:2237–2248
Worek F, Aurbek N, Koller M, Becker C, Eyer P, Thiermann H (2007) Kinetic analysis of reactivation and aging of human acetylcholinesterase inhibited by different phosphoramidates. Biochem Pharmacol 73:1807–1817
Worek F, Herkert NM, Koller M, Aurbek N, Thiermann H (2009) Interaction of pentylsarin analogues with human acetylcholinesterase: a kinetic study. Toxicol Lett 187:119–123
Worek F, Seeger T, Goldsmith M, Ashani Y, Leader H, Sussman JL, Tawfik D, Thiermann H, Wille T (2014a) Efficacy of the rePON1 mutant IIG1 to prevent cyclosarin toxicity in vivo and to detoxify structurally different nerve agents in vitro. Arch Toxicol 88:1257–1266
Worek F, Seeger T, Reiter G, Goldsmith M, Ashani Y, Leader H, Sussman JL, Aggarwal N, Thiermann H, Tawfik D (2014b) Post-exposure treatment of VX poisoned guinea pigs with the engineered phosphotriesterase mutant C23: a proof-of-concept study. Toxicol Lett 231:45–54
Worek F, Seeger T, Zengerle M, Kubik S, Thiermann H, Wille T (2014c) Effectiveness of a substituted β-cyclodextrin to prevent cyclosarin toxicity in vivo. Toxicol Lett 226:222–227
Worek F, Herkert NM, Koller M, Thiermann H, Wille T (2015) Application of a dynamic in vitro model with real-time determination of acetylcholinesterase activity for the investigation of tabun analogues and oximes. Toxicol In Vitro 30:514–520
Zilker T (2005) Medical management of incidents with chemical warfare agents. Toxicology 214:221–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worek, F., Wille, T., Koller, M. et al. Toxicology of organophosphorus compounds in view of an increasing terrorist threat. Arch Toxicol 90, 2131–2145 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1772-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1772-1