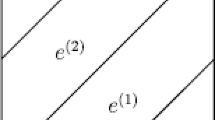Abstract
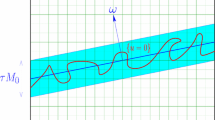
In this paper we investigate the cubic-to-orthorhombic phase transition in the framework of linear elasticity. Using convex integration techniques, we prove that this phase transition represents one of the simplest three-dimensional examples in which already the linearised theory of elasticity displays non-rigidity properties. As a complementary result, we demonstrate that surface energy constraints rule out such highly oscillatory behaviour. We give a full characterization of all possibly emerging patterns for generic material parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, J.M., James, R.D.: Fine phase mixtures as minimizers of energy. Analysis and Continuum Mechanics. Springer, New York, 647–686, 1989
Bhattacharya, K.: Microstructure of martensite: why it forms and how it gives rise to the shape-memory effect. Oxford Series on Materials Modeling. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003
Bhattacharya K., Kohn R.V.: Elastic energy minimization and the recoverable strains of polycrystalline shape-memory materials. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal., 139(2), 99–180 (1997)
Capella, A., Otto, F.: A quantitative rigidity result for the cubic-to-tetragonal phase transition in the geometrically linear theory with interfacial energy. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A Math. 142, 273–327 (2012). doi:10.1017/S0308210510000478
Conti S.: Quasiconvex functions incorporating volumetric constraints are rank-one convex. J. Math. Pures Appl. 90(1), 15–30 (2008)
Conti S., Dolzmann G., Kirchheim B.: Existence of Lipschitz minimizers for the three-well problem in solid–solid phase transitions. Ann. de l’Inst. Henri Poincare (C) Non Linear Anal. 24(6), 953–962 (2007)
Conti, S., Dolzmann, G., Müller, S.: Korn’s second inequality and geometric rigidity with mixed growth conditions. Calc. Var. Partial Differ. Equ. 1–18 (2012)
Dacorogna B.: Direct Methods in the Calculus of Variations, Vol. 78. Springer, New York (2007)
De Lellis, C., Székelyhidi, L., Jr.: The Euler equations as a differential inclusion. Ann. Math. 1417–1436 (2009)
Dolzmann, G., Kirchheim, B., Müller, S., Šverák, V.: The two-well problem in three dimensions. Calc. Var. Partial Differ. Equ. 10, 21–40 (2000). doi:10.1007/PL00013455
Dolzmann, G., Müller, S.: The influence of surface energy on stress-free microstructures in shape memory alloys. Meccanica 30, 527–539 (1995). doi:10.1007/BF01557083
Dolzmann G., Müller S.: Microstructures with finite surface energy: the two-well problem. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 132, 101–141 (1995)
Kirchheim, B.: Lipschitz minimizers of the 3-well problem having gradients of bounded variation (1998). (MPI preprint)
Kirchheim, B.: Rigidity and geometry of microstructures. MPI-MIS Lecture Notes, 2007
Kirchheim, B., Spadaro, E., Székelyhidi, L. Jr.: Equidimensional isometric maps (2014). arXiv:1408.6737
Kohn R.V., Müller S.: Surface energy and microstructure in coherent phase transitions. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 47(4), 405–435 (1994)
Kondrat’ev V.A., Oleinik O.A.: Boundary-value problems for the system of elasticity theory in unbounded domains. Korn’s inequalities. Russ. Math. Surv. 43(5), 65–119 (1988)
Müller, S., Šverák, V.: Convex integration with constraints and applications to phase transitions and partial differential equations. J. Eur. Math. Soc. 1, 393–422 (1999). doi:10.1007/s100970050012
Rüland, A.: Rigidity properties of the cubic-to-orthorhombic phase transition in the linear theory of elasticity with surface energy. Diploma Thesis, 2010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Šverák
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rüland, A. The Cubic-to-Orthorhombic Phase Transition: Rigidity and Non-Rigidity Properties in the Linear Theory of Elasticity. Arch Rational Mech Anal 221, 23–106 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00205-016-0971-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00205-016-0971-5