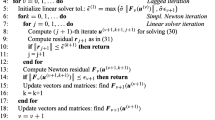Abstract
In this work we design and analyze an efficient numerical method to solve two dimensional initial-boundary value reaction–diffusion problems, for which the diffusion parameter can be very small with respect to the reaction term. The method is defined by combining the Peaceman and Rachford alternating direction method to discretize in time, together with a HODIE finite difference scheme constructed on a tailored mesh. We prove that the resulting scheme is ε-uniformly convergent of second order in time and of third order in spatial variables. Some numerical examples illustrate the efficiency of the method and the orders of uniform convergence proved theoretically. We also show that it is easy to avoid the well-known order reduction phenomenon, which is usually produced in the time integration process when the boundary conditions are time dependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Mallo I., Cano B. and Jorge J.C. (2004). Spectral-fractional step Runge–Kutta discretizations for initial boundary value problems with time dependent boundary conditions. Math. Comput. 73: 1801–1825
Clavero C. and Gracia J.L. (2005). High order methods for elliptic and time dependent reaction–diffusion singularly perturbed problemsms. Appl. Math. Comput. 168: 1109–1127
Clavero C., Gracia J.L. and Jorge J.C. (2006). A uniformly convergent alternating direction HODIE finite difference scheme for 2D time dependent convection-diffusion problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 26: 155–172
Clavero C., Jorge J.C., Lisbona F. and Shishkin G.I. (1998). A fractional step method on a special mesh for the resolution of multidimensional evolutionary convection–diffusion prolems. Appl. Numer. Math. 27: 211–231
Clavero C., Jorge J.C., Lisbona F. and Shishkin G.I. (2000). An alternating direction scheme on a nonuniform mesh for reaction–difusion parabolic problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 20: 263–280
Farrell P.A., Hegarty A.F., Miller J.J.H., O‘Riordan E. and Shishkin G.I. (2000). Robust Computational Techniques for Boundary Layers. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton
Han H. and Kellogg R.B. (1990). Differentiability properties of solutions of the equation \(-\varepsilon^{2}\delta u +ru=f(x,y)\) in a square. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 21: 394–408
Hemker P.W., Shishkin G.I. and Shishkina L.P. (1997). The use of defect correction for the solution of parabolic singular perturbation problems. ZAMM 77: 59–74
Hemker P.W., Shishkin G.I. and Shishkina L.P. (2000). ε-uniform schemes with high-order time-accuracy for parabolic singular perurbation problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 20: 99–121
Kopteva N. (2003). Error expansion for an upwind scheme applied to a two dimensional convection-diffusion problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41: 1851–1869
Ladyzhenskaja, O.A., Solonnikov, V.A., Ural’tseva, N.N.: Linear and quasilinear equations of parabolic type. Translations of Mathematical Monographs, 23, AMS, Providence, RI (1968)
Linß T. and Stynes M. (2001). Asymptotic analysis and Shishkin-type decomposition for an elliptic convection-diffusion problem. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 261: 604–632
Linß T. (2003). Layer-adapted meshes for convection–diffusion problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192: 1061–1105
Miller J.J.H., O’Riordan E. and Shishkin G.I. (1996). Fitted Numerical Methods for Singular Perturbation Problems. World-Scientific, Singapore
Miller J.J.H., O’Riordan E., Shishkin G.I. and Shishkina L.P. (1998). Fitted mesh methods for problems with parabolic boundary layers. Mathematical Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy 98A: 173–190
Palencia C. (1993). A stability result for sectorial operators in Banach spaces. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 30: 1373–1384
Peaceman D. and Rachford H. (1955). The numerical solution of elliptic and parabolic differential equations. J. SIAM 3: 28–41
Roos H.G., Stynes M. and Tobiska L. (1996). Numerical Methods for Singularly Perturbed Differential Equations, Convection–Diffusion and Flow Problems. Springer, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research has been partially supported by the project MEC/FEDER MTM2004-01905 and the Diputación General de Aragón.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bujanda, B., Clavero, C., Gracia, J.L. et al. A high order uniformly convergent alternating direction scheme for time dependent reaction–diffusion singularly perturbed problems. Numer. Math. 107, 1–25 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-007-0083-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-007-0083-0