Abstract.
This paper describes the analytical methods (thermal ionization mass spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, and alpha spectrometry) that have been developed for determination of the age of uranium and discusses their advantages and limitations. With regard to potential application of the methods (e.g. Fissile Material Cut-off Treaty), the discussion focuses on highly enriched uranium, because this seems to be of highest strategic relevance.
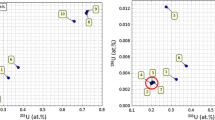
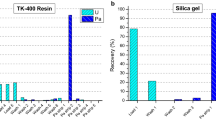
The different analytical methods were tested and validated by use of uranium reference materials of different 235U isotope abundance and of known ages. The results show that thermal ionization mass spectrometry and alpha spectrometry are both very accurate and precise techniques for this application. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, on the other hand, although less precise, because of the different approach to the analytical problem, is still sufficiently accurate to be used as a rapid screening method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallenius, .M., Morgenstern, .A., Apostolidis, .C. et al. Determination of the age of highly enriched uranium. Anal Bioanal Chem 374, 379–384 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-002-1555-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-002-1555-9