Abstract
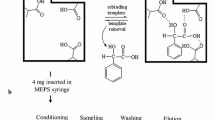
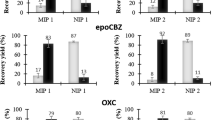
Diphenyl phosphate is a hydrolysis product and possible metabolite of the flame retardant and plasticiser additive triphenyl phosphate. A molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction (MISPE) method for extracting diphenyl phosphate from aqueous solutions has been developed and compared with SPE using a commercially available mixed-mode anion exchanger. The imprinted polymer was prepared using 2-vinylpyridine (2-Vpy) as the functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as the cross-linker, and a structural analogue of the analyte as the template molecule. The imprinted polymer was evaluated for use as a SPE sorbent, in tests with both aqueous standards and spiked urine samples, by comparing recovery and breakthrough data obtained using the imprinted form of the polymer and a non-imprinted form (NIP). Extraction from aqueous solutions resulted in more than 80% recovery. Adsorption by the molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was non-selective , but selectivity was achieved by selective desorption in the wash steps. Diphenyl phosphate could also be selectively extracted from urine samples, although the urine matrix reduced the capacity of the MISPE cartridges. Recoveries from urine extraction were higher than 70%. It was important to control pH during sample loading. The MISPE method was found to yield a less complex LC–ESI–MS chromatogram of the urine extracts compared with the mixed-mode anion-exchanger method. An LC–ESI–MS method using a Hypercarb LC column with a graphitised carbon stationary phase was also evaluated for organophosphate diesters. LC–ESI–MS using negative-ion detection in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode was shown to be linear for diphenyl phosphate in the range 0.08–20 ng μL−1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mosbach K (1994) Techniques 19:9–14
Sellergren B (1994) Anal Chem 66:1578–1582
Andersson LI, Paprica A, Arvidsson T (1997) Chromatographia 46:57–62
Andersson LI (2000) Analyst 125:1515–1517
Crescenzi C, Bayoudh S, Cormack PAG, Klein T, Ensing K (2001) Anal Chem 73:2171–2177
Brambilla G, Maurizio F, Rizzo B, Crescenzi V, Masci G (2001) J Chromatogr B 759:27–32
Bereczki A, Tolokán A, Horvai G, Horváth V, Lanza F, Hall AJ, Sellergren B (2001) J Chromatogr A 930:31–38
Blomgren A, Berggren C, Holmberg A, Larsson F, Sellergren B, Ensing K (2002) J Chromatogr A 975:157–164
Baggiani C, Giovannoli C, Anfossi L, Tozzi C (2001) J Chromatogr A 938:35–44
Koeber R, Fleischer C, Lanza F, Boos K-S, Sellergren B, Barceló D (2001) Anal Chem 73:2437–2444
Mena ML, Martínez-Ruiz P, Reviejo AJ, Pingarrón JM (2002) Anal Chim Acta 451:297–304
Caro E, Masqué N, Marcé RM, Borrull F, Cormack PAG, Sherrington DC (2002) J Chromatogr A 963:169–178
Pap T, Horváth V, Tolokán A, Horvai G, Sellergren B (2002) J Chromatogr A 973:1–12
Kubo T, Hosoya K, Watabe Y, Ikegami T, Tanaka N, Sano T, Kaya K (2003) J Chromatogr A 987:389–394
Lanza F, Sellergren B (2001) Chromatographia 53:599–611
Masqué N, Marcé RM, Borrull F (2001) Trends Anal Chem 20:477–486
Boos K-S, Fleischer CT (2001) Fresenius J Anal Chem 371:16–20
Carlsson H, Nilsson U, Östman C (2000) Environ Sci Technol 34:3885–3889
García AM, Sabater MC, Mendoza MT, Ballester F, Carrasco JM (2000) Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 65:764–771
Hardt J, Angered J (2000) J Anal Toxicol 24:678–684
Bravo R, Driskell WJ, Whitehead RD, Needham LL, Barr DB (2002) J Anal Toxicol 26:245–252
Möller K, Nilsson U, Crescenzi C (2001) J Chromatogr A 938:121–130
Sellergren B (2001) Techniques and instrumentation in analytical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Reemtsma T (2001) Trends Anal Chem 20:533–542
Choi BK, Hercules DM, Gusev AI (2001) J Chromatogr A 907:337–342
Knox JH, Ross P (1997) Adv Chromatogr 37:121–162
Acknowledgments
Dr Lars I. Andersson is thanked for helpful discussions. This investigation was financially supported by The Swedish Research Council (project no 621–2001–1482).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Möller, K., Crescenzi, C. & Nilsson, U. Determination of a flame retardant hydrolysis product in human urine by SPE and LC–MS. Comparison of molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction with a mixed-mode anion exchanger. Anal Bioanal Chem 378, 197–204 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-003-2267-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-003-2267-5