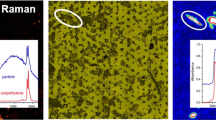
Abstract
The presence of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems is a topical problem and leads to the need of appropriate and reliable analytical methods to distinctly identify and to quantify these particles in environmental samples. As an example transmission, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) imaging can be used to analyze samples directly on filters without any visual presorting, when the environmental sample was afore extracted, purified, and filtered. However, this analytical approach is strongly restricted by the limited IR transparency of conventional filter materials. Within this study, we describe a novel silicon (Si) filter substrate produced by photolithographic microstructuring, which guarantees sufficient transparency for the broad mid-infrared region of 4000–600 cm-1. This filter type features holes with a diameter of 10 μm and exhibits adequate mechanical stability. Furthermore, it will be shown that our Si filter substrate allows a distinct identification of the most common microplastics, polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP), in the characteristic fingerprint region (1400–600 cm-1). Moreover, using the Si filter substrate, a differentiation of microparticles of polyesters having quite similar chemical structure, like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), is now possible, which facilitates a visualization of their distribution within a microplastic sample by FTIR imaging. Finally, this Si filter can also be used as substrate for Raman microscopy—a second complementary spectroscopic technique—to identify microplastic samples.

Optical and FTIR images of a microplastic model sample of PET and PBT on the novel Si filter substrate. The distribution of this quite similar polymers within a microplastic sample is visible by choosing a band region of 1060–1033 cm-1 for PET and of 955–925 cm-1 for PBT











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1596–1605
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46:3060–3075
Frias JPGL, Otero V, Sobral P (2014) Evidence of microplastics in samples of zooplankton from Portuguese coastal waters. Mar Environ Res 95:89–95
Song YK, Hong SH, Jang M, Kang J-H, Kwon OY, Han GM, Shim WJ (2014) Large accumulation of micro-sized synthetic polymer particles in the sea surface microlayer. Environ Sci Technol 48:9014–9021
Carpenter EJ, Anderson SJ, Harvey GR, Miklas HP, Peck BB (1972) Polystyrene spherules in coastal waters. Science 178:749–750
Lattin GL, Moore CJ, Zellers AF, Moore SL, Weisberg SB (2004) A comparison of neustonic plastic and zooplankton at different depths near the southern California shore. Mar Pollut Bull 49:291–294
Doyle MJ, Watson W, Bowlin NM, Sheavly SB (2011) Plastic particles in coastal pelagic ecosystems of the northeast Pacific Ocean. Mar Environ Res 71:41–52
Dekiff JH, Remy D, Klasmeier J, Fries E (2014) Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ Pollut 186:248–256
Van Cauwenberghe L, Claessens M, Vandegehuchte MB, Mees J, Janssen CR (2013) Assessment of marine debris on the Belgian Continental Shelf. Mar Pollut Bull 73:161–169
Van Cauwenberghe L, Vanreusel A, Mees J, Janssen CR (2013) Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ Pollut 182:495–499
Lechner A, Keckeis H, Lumesberger-Loisl F, Zens B, Krusch R, Tritthart M, Glas M, Schludermann E (2014) The Danube so colourful: a potpourri of plastic litter outnumbers fish larvae in Europe’s second largest river. Environ Pollut 188:177–181
Zbyszewski M, Corcoran PL (2011) Distribution and degradation of fresh water plastic particles along the beaches of Lake Huron, Canada. Water Air Soil Pollut 220:365–372
Imhof HK, Ivleva NP, Schmid J, Niessner R, Laforsch C (2013) Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr Biol 23:R867–R868
Free CM, Jensen OP, Mason SA, Eriksen M, Williamson NJ, Boldgiv B (2014) High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar Pollut Bull 85:156–163
Rillig MC (2012) Microplastic in terrestrial ecosystems and the soil? Environ Sci Technol 46:6453–6454
Fendall LS, Sewell MA (2009) Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1225–1228
Gregory MR (1996) Plastic “scrubbers” in hand cleansers: a further (and minor) source for marine pollution identified. Mar Pollut Bull 32:867–871
Hintersteiner I, Himmelsbach M, Buchberger WW (2015) Characterization and quantitation of polyolefin microplastics in personal-care products using high-temperature gel-permeation chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:1253–1259
Derraik JG (2002) The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 44:842–852
Cole M, Lindeque P, Halsband C, Galloway TS (2011) Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2588–2597
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347:768–771
Ivar do Sul JA, Costa MF (2014) The present and future of microplastic pollution in the marine environment. Environ Pollut 185:352–364
Setälä O, Fleming-Lehtinen V, Lehtiniemi M (2014) Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ Pollut 185:77–83
Lee K-W, Shim WJ, Kwon OY, Kang J-H (2013) Size-dependent effects of micro polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ Sci Technol 47:11278–11283
Van Cauwenberghe L, Janssen CR (2014) Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ Pollut 193:65–70
Lusher AL, McHugh M, Thompson RC (2013) Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar Pollut Bull 67:94–99
Foekema EM, De Gruijter C, Mergia MT, van Franeker JA, Murk AJ, Koelmans AA (2013) Plastic in north sea fish. Environ Sci Technol 47:8818–8824
Wright SL, Thompson RC, Galloway TS (2013) The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: a review. Environ Pollut 178:483–492
Rios LM, Jones PR, Moore C, Narayan UV (2010) Quantitation of persistent organic pollutants adsorbed on plastic debris from the Northern Pacific Gyre’s “eastern garbage patch”. J Environ Monit 12:2226–2236
Endo S, Takizawa R, Okuda K, Takada H, Chiba K, Kanehiro H, Ogi H, Yamashita R, Date T (2005) Concentration of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in beached resin pellets: variability among individual particles and regional differences. Mar Pollut Bull 50:1103–1114
Zettler ER, Mincer TJ, Amaral-Zettler LA (2013) Life in the “plastisphere”: microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ Sci Technol 47:7137–7146
Harrison JP, Schratzberger M, Sapp M, Osborn AM (2014) Rapid bacterial colonization of low-density polyethylene microplastics in coastal sediment microcosms. BMC Microbiol 14:232
Masó M, Garcés E, Pagès F, Camp J (2003) Drifting plastic debris as a potential vector for dispersing harmful algal bloom ((HAB)) species. Sci Mar 67:107–111
Oberbeckmann S, Loeder MGJ, Gerdts G, Mark Osborn A (2014) Spatial and seasonal variation in diversity and structure of microbial biofilms on marine plastics in northern European waters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90:478–492
Löder MGJ, Kuczera M, Mintenig S, Lorenz C, Gerdts G (2015) FPA-based micro-FTIR imaging for the analysis of microplastics in environmental samples. Environ Chem. doi:10.1071/EN14205
Fries E, Dekiff JH, Willmeyer J, Nuelle M-T, Ebert M, Remy D (2013) Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:1949–1956
Imhof HK, Schmid J, Niessner R, Ivleva NP, Laforsch C (2012) A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 10:524–537
Harrison JP, Ojeda JJ, Romero-González ME (2012) The applicability of reflectance micro-Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy for the detection of synthetic microplastics in marine sediments. Sci Total Environ 416:455–463
Günzler H, Heise HM (1996) IR-Spektroskopie: Eine Einführung. VCH, Weinheim
Laermer F, Schilp A (1996) U.S. Patent 5501893, 26.03.1996: method of anisotropically etching silicon
Jansen H, de Boer M, Otter B, Elwenspoek M (1995) The black silicon method IV: the fabrication of three-dimensional structures in silicon with high aspect ratios for scanning probe microscopy and other applications. Proc Micro Electromech Syst. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.1995.472548
Jansen H, de Boer M, Elwenspoek M (1996) The black silicon method VI: high aspect ratio trench etching for MEMS applications. Proc Ninth Int Work Micro Electromech Syst. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.1996.493989
Kenoyer L, Oxford R, Moll A (2003) Optimization of Bosch etch process for through wafer interconnects. Proc. 15th Bienn Univ Microelectron Symp :338–339
Kumagai M, Uchiyama N, Ohmura E, Sugiura R, Atsumi K, Fukumitsu K (2007) Advanced dicing technology for semiconductor wafer—stealth dicing. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 20:259–265
Krcho D (1997) FTIR spectroscopy for silicon solar cell characterisation. Proc Aust New Zeal Sol Energy Soc Solar 1997, pp. 117/1-117/7, presented at ANZSES Solar `97: Sustainable Energy, Canberra, Australian National University, 1 - 3 December 1997
Vidrine DW (1980) Room temperature carbon and oxygen determination in single-crystal silicon. Anal Chem 52:92–96
Hummel DO, Scholl F (1988) Atlas der Polymer- und Kunststoffanalyse, Band 2 Kunststoff, Fasern, Kautschuk, Harze, Ausgangs- und Hilfsstoffe, Abbauprodukte - Teil b/I. VCH, Weinheim
Olabisi O (1997) Handbook of thermoplastics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Schmidt PG (1963) Polyethylene terephthalate structural studies. J Polym Sci 1:1271–1292
Menzheres GY, Moisya EG, Miks R (1984) IR spectra and structure of polybutylene terephthalate. Theor Exp Chem 20:222–226
Acknowledgments
We thank Vincent Körber (IPF) and the construction team for technical support and Dr. Cordelia Zimmerer (IPF) for helpful discussion regarding FTIR imaging. The authors also would like to thank Rene Puschmann, Michael Lorenz, Tina Klembt, and Dr. Frank Menzel from Fraunhofer IZM-ASSID for assistance with manufacturing of the Si filter substrate. We are also grateful to Dr. Sonja Oberbeckmann (Leibniz IOW), Dr. Gunnar Gerdts (AWI, Helgoland), and Prof. Christian Laforsch (University of Bayreuth) for helpful discussion. Finally, we thank the Leibniz Association for financial support of the project “MikrOMIK.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Käppler, A., Windrich, F., Löder, M.G.J. et al. Identification of microplastics by FTIR and Raman microscopy: a novel silicon filter substrate opens the important spectral range below 1300 cm−1 for FTIR transmission measurements. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 6791–6801 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8850-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8850-8