Abstract
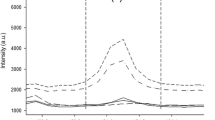
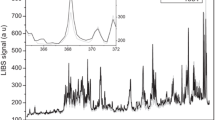
Laser-induced breakdown spectrometry (LIBS) has been applied to spatially locate several atomic species in speleothems taken from the Nerja’s Cave (Málaga, Spain). Spatial distribution profiles of Mg at 285.21 nm and Sr at 407.77 nm were obtained while the laser was rastered through different paths along the sample. These elements were selected due to their importance as palaeoclimatic indicators. The 532 nm output of a Nd:YAG laser was used to irradiate the samples and generate the plasma that was spectrally analyzed and detected by using an intensified CCD detector. The signals were normalized to the Ca line to minimize pulse-to-pulse fluctuations in the laser source. Several studies were carried out to check for the point-to-point heterogeneity of the natural speleothem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 August 1997 / Revised: 23 October 1997 / Accepted: 30 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vadillo, J., Vadillo, I., Carrasco, F. et al. Spatial distribution profiles of magnesium and strontium in speleothems using laser-induced breakdown spectrometry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 361, 119–123 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050846
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050846