Abstract
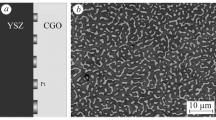
The high-temperature solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is suited for the environmentally acceptable and efficient conversion of chemical into electric energy. A prerequisite for introducing this technology on the market is the controlled formation of the interface between electrodes and the electrolyte. In the case of using an electrolyte based on LaGaO3 the formation of third phases and the diffusion of individual metallic cations from and to the electrolyte was investigated with the aid of point analyses on micrographs of the environment of the interface using quantitative EDS analysis. In case of an anode of Ni-CeO2 cermet the mixed oxide SrLaGa3O7 is formed and, in addition, a relatively pronounced transport of La from the electrolyte into the CeO2 phase was observed. A relatively strong diffusion of Mn and an even stronger diffusion of Co into the electrolyte took place between the cathode of, e.g., La0.75Sr0.2Mn0.8Co0.2O3 and the La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O3 electrolyte, whereas a weak transport of Ga to the cathode was identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 September 1998 / Revised: 7 April 1999 / Accepted: 11 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naoumidis, A., Ahmad-Khanlou, A., Samardzija, Z. et al. Chemical interaction and diffusion on interface cathode/electrolyte of SOFC. Fresenius J Anal Chem 365, 277–281 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051488
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051488