Abstract
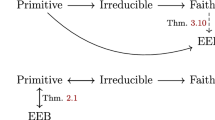
Completely positive, trace preserving (CPT) maps and Lindblad master equations are both widely used to describe the dynamics of open quantum systems. The connection between these two descriptions is a classic topic in mathematical physics. One direction was solved by the now famous result due to Lindblad, Kossakowski, Gorini and Sudarshan, who gave a complete characterisation of the master equations that generate completely positive semi-groups. However, the other direction has remained open: given a CPT map, is there a Lindblad master equation that generates it (and if so, can we find its form)? This is sometimes known as the Markovianity problem. Physically, it is asking how one can deduce underlying physical processes from experimental observations.
We give a complexity theoretic answer to this problem: it is NP-hard. We also give an explicit algorithm that reduces the problem to integer semi-definite programming, a well-known NP problem. Together, these results imply that resolving the question of which CPT maps can be generated by master equations is tantamount to solving P = NP: any efficiently computable criterion for Markovianity would imply P = NP; whereas a proof that P = NP would imply that our algorithm already gives an efficiently computable criterion. Thus, unless P does equal NP, there cannot exist any simple criterion for determining when a CPT map has a master equation description.
However, we also show that if the system dimension is fixed (relevant for current quantum process tomography experiments), then our algorithm scales efficiently in the required precision, allowing an underlying Lindblad master equation to be determined efficiently from even a single snapshot in this case.
Our work also leads to similar complexity-theoretic answers to a related long-standing open problem in probability theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen M.A., Chuang I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (2000)
Carmichael H.J.: Statistical Methods in Quantum Optics, Volume 1. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer, 2003
Weiss, U.: Quantum dissipative systems. Series in Modern Condensed Matter Physics. River Edge, NJ: World Scientific, 1999
Lindblad G.: On the generators of quantum dynamical semigroups. Commun. Math. Phys. 48, 119 (1976)
Gorini V., Kossakowski A., Sudarshan E.C.G.: Completely positive dynamical semigroups of N-level systems. J. Math. Phys. 17, 821 (1976)
Holevo A.S.: Statistical structure of quantum theory. Berlin-Heidelberg-New, York: Springer (2001)
Wolf M.M., Eisert J., Cubitt T.S., Cirac J.I.: Assessing non-Markovian quantum dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 150402 (2008)
Boulant, N., Havel, T.F., Pravia, M.A., Cory, D.G.: Robust method for estimating the Lindblad operators of a dissipative quantum process from measurements of the density operator at multiple time points. Phys. Rev. A 67 042322 (2003)
Boulant N., Emerson J., Havel T.F., Cory D.G.: Incoherent noise and quantum information processing. J. Chem. Phys. 121(7), 2955 (2004)
Howard M. et al.: Quantum process tomography and linblad estimation of a solid-state qubit. New J. Phys 8, 33 (2006)
Weinstein Y.S. et al.: Quantum process tomography of the quantum fourier transform. J. Chem. Phys 121, 6117 (2004)
Lidar D.A., Bihary Z., Whaley K.B.: From completely positive maps to the quantum Markovian semigroup master equation. Chem. Phys 268, 35 (2001)
Papadimitriou, C.H.: Computational Complexity. Reading, MA: Addison Wesley (1993)
Garey, M.R., Johnson D.S.: Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. Sanfrancisco, CA: W.H. Freeman (1979)
Norris J.R.: Markov Chains. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1997)
Elfving, G.: Zur theorie der Markoffschen ketten. Acta Soc. Sei. Fennicae. 2(8) (1937)
Kingman J.F.C.: The imbedding problem for finite Markov chains. Z. Wahr 1, 14 (1962)
Kingman J.F.C., Williams D.: The combinatorial structure of non-homogeneous Markov chains. Z. Wahr 26, 77 (1973)
Fuglede B.: On the imbedding problem for stochastic and doubly stochastic matrices. Probab. Th. Rel. Fields, 80, 241 (1988)
Mukherjea A.: The role of nonnegative idempotent matrices in certain problems in probability. In: Charles R. Johnson, ed., Matrix theory and applications. Providence, RI: Amer. Math. Soc., 1990
Cubitt, T.S.: The embedding problem for stochastic matrices is NP-hard. Manuscript in preparation
Nielsen M.A., Knill E., Laflamme R.: Complete quantum teleportation using nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature 396, 52 (1998)
Vandersypen L.M.K., Chuang I.L.: NMR techniques for quantum control and computation. Rev. Mod. Phys 76, 1037 (2004)
Emerson J. et al.: Symmetrized characterization of noisy quantum processes. Science, 317, 1893 (2007)
Riebe M. et al.: Process tomography of ion trap quantum gates. Phys. Rev. Lett 97, 220407 (2006)
Monz T. et al.: Realization of the quantum Toffoli gate with trapped ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 040501 (2009)
O’Brien J.L. et al.: Quantum process tomography of a controlled-not gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 080502 (2004)
Lundeen J.S. et al.: Tomography of quantum detectors. Nature Phys 5, 27 (2009)
Howard M. et al.: Quantum process tomography and Linblad estimation of a solid-state qubit. New J. Phys 8, 33 (2006)
Choi M.D.: Completely positive linear maps on complex matrices. Lin. Alg. Appl 10, 285 (1975)
Jamiolkowski A.: Linear transformations which preserve trace and positive semidefiniteness of operators. Rep. Math. Phys. 3, 275 (1972)
Wolf M.M., Cirac J.I.: Dividing quantum channels. Commun. Math. Phys. 279, 147 (2008)
Denisov L.V.: Infinitely divisible markov mappings in quantum probability theory. Th. Prob. Appl 33, 392 (1988)
Gurvits, L.: Classical deterministic complexity of Edmonds problem and quantum entanglement. In: Proceedings of the thirty-fifth ACM symposium on Theory of computing. New York: ACM Press, 2003, pp. 10–19
Ioannou L.M.: Computational complexity of the quantum separability problem. Quant. Inf. Comp. 7(4), 335–370 (2007)
Vandenberghe L., Boyd S.: Semidefinite programming. SIAM Rev. 38(1), 49–95 (1996)
Horn R.A., Johnson C.R.: Topics in Matrix Analysis. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1994)
Kato, T.: Perturbation Theory for Linear Operators. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer, Second edition, 1976
Weilenmann J.: Continuity properties of fractional powers, of the logarithm, and of holomorphic semigroups. J. Func. Anal. 27, 1–20 (1978)
Moler C., Van Loan C.: Nineteen dubious ways to compute the exponential of a matrix, twenty-five years later. SIAM Rev. 45, 3–49 (2003)
Schaefer, T.J.: The complexity of satisfiability problems. In: Proceedings of the 10th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC’78), New York:ACM Press, 1978, p. 216
Stewart G.W.: Error and perturbation bounds for subspaces associated with certain eigenvalue problems. SIAM Rev. 15(4), 727–764 (1973)
Golub, G.H., van Loan, C.F.: Matrix Computations. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, Third edition, 1996
Horn R.A., Johnson C.R.: Matrix Analysis. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1990)
Schrijver A.: Theory of Linear and Integer Programming. Wiley, New York (1986)
Porkolab, L., Khachiyan, L.: Computing integral points in convex semi-algebraic sets. In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS ’97), Discataway, NJ: IEEE 1997, p. 162
Porkolab, L.: On the Complexity of Real and Integer Semidefinite Programming. PhD thesis, Rutgers, (1996)
Cuthbert J.R.: The logarithm function for finite-state Markov semi-groups. J. London Math. Soc. 6(2), 524 (1973)
Johansen S.: Some results on the imbedding problem for finite markov chains. J. London Math. Soc. 8(2), 345 (1974)
Carette, P.: Characterizations of embeddable 3x3 stochastic matrices with a negative eigenvalue. New York J. Math. 1, 120 (1995)
Cuthbert J.R.: On uniqueness of the logarithm for Markov semi-groups. J. London Math. Soc. 4(2), 623 (1972)
Davies E.B.: Embeddable Markov matrices. Electronic J. Prob 15, 1474 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. B. Ruskai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cubitt, T.S., Eisert, J. & Wolf, M.M. The Complexity of Relating Quantum Channels to Master Equations. Commun. Math. Phys. 310, 383–418 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00220-011-1402-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00220-011-1402-y