Abstract
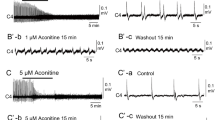
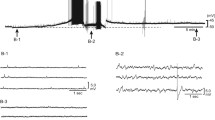
We analysed the modulation of respiratory neurons by adrenaline or noradrenaline (NA) in a newborn rat brainstem-spinal cord preparation. Adrenaline or NA caused a dose-dependent depression of the respiratory rhythm and induced C4 spinal tonic discharges. The inhibitory effect of adrenaline (ED50=0.5 μM) on the respiratory rhythm was stronger than NA (ED50=5 μM). The adrenaline respiratory rhythm depression was partially blocked by the α1-antagonist prazosin or by the α2-antagonist yohimbine. The C4 tonic discharge elicited by adrenaline was blocked by the α1-antagonist prazosin. The direct effects of adrenaline on pre-inspiratory (Pre-I) neurons were examined in a synaptic blockade solution (low Ca), and fifty-six percent of Pre-I neurons were found to continue firing. In low-Ca solution, Pre-I neurons were excited (n=29 of 39) or depressed (n=5 of 39) by adrenaline, and excited by α1-agonist phenylephrine or depressed by α2-agonist clonidine. These results suggest that the respiratory rhythm depression under intact network conditions is mediated by some other inhibitory system. The inhibitory effect of adrenaline on the respiratory rhythm was partially blocked by the GABAA-antagonists bicuculline or picrotoxin, but not by the GABAB-antagonist phaclofen. The present results suggest that: (1) respiratory rhythm generation is more sensitive to adrenaline than NA through α-adrenergic action of adrenaline; (2) the activity of Pre-I neurons could be directly regulated by excitation via α1-receptors and inhibition via α2-receptors; and (3) the depression of the respiratory rhythm by adrenaline is partly mediated by GABAAergic neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 April 1997 / Accepted: 6 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arata, A., Onimaru, H. & Homma, I. The adrenergic modulation of firings of respiratory rhythm-generating neurons in medulla-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Exp Brain Res 119, 399–408 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050355