Abstract
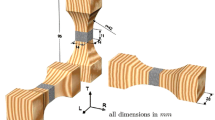
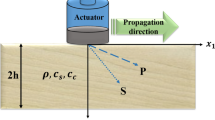
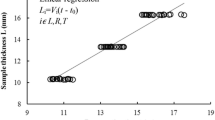
The present study investigates the influence of moisture content on the elastic characteristics of beech wood (Fagus sylvatica L.) by means of ultrasonic waves. A set of elastic engineering parameters (i.e. three Young’s moduli, three shear moduli and six Poisson’s ratios) is determined at four specific moisture contents. The results reveal the significant influence of the moisture content on the elastic behaviour of beech wood. With the exception of some Poisson’s ratios, the engineering parameters decrease with increasing moisture content, indicating a decline in stiffness at higher moisture contents. At the same time, wood anisotropy, displayed by the two-dimensional representation of the velocity surface, remains almost unchanged. The results prove that the ultrasonic technique is suitable for determining the elastic moduli. However, non-diagonal terms of the stiffness matrix must be considered when calculating the Young’s moduli. This is shown experimentally by comparing the ultrasonic Young’s moduli calculated without, and allowing for, the non-diagonal terms. While the ultrasonic technique is found to be reliable to measure the elastic moduli, based on the measured values, its eligibility to measure the Poisson’s ratios remains uncertain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashman RB, Cowin SC, Van Buskirk WC, Rice JC (1984) A continuous wave technique for the measurement of the elastic properties of cortical bone. J Biomech 17(5):349–361
Bodig J, Jayne BA (1993) Mechanics of wood and wood composites. Krieger Publishing Company, Malabar
Bucur V (2006) Acoustics of wood. Springer, Berlin
Bucur V, Archer RR (1984) Elastic constants for wood by an ultrasonic method. Wood Sci Technol 18:255–265
Carrington H (1922) The elastic constants of spruce as influenced by moisture. Aeronautical J 26:462–477
Carrington H (1923) The elastic constants of spruce. Philos Mag 45:1055–1057
EN12668-1 (2010) Non-destructive testing—characterization and verification of ultrasonic examination equipment—part 1: instruments
Gonçalves R, Trinca AJ, Cerri DGP (2011) Comparison of elastic constants of wood determined by ultrasonic wave propagation and static compression testing. Wood Fiber Sci 43(1):64–75
Hearmon RFS, Barkas WW (1941) The effect of grain direction on the Young’s moduli and rigidity moduli of beech and sitka spruce. In: Proceedings of the Physical Society 53(6):674–680
Hering S, Keunecke D, Niemz P (2012) Moisture-dependent orthotropic elasticity of beech wood. Wood Sci Technol 46(5):927–938. doi:10.1007/s00226-011-0449-4
Hörig H (1935) Anwendung der Elastizitätstheorie anisotroper Körper auf Messungen an Holz. Arch Appl Mech 6(1):8–14
Keunecke D, Sonderegger W, Pereteanu K, Lüthi T, Niemz P (2007) Determination of Young’s and shear moduli of common yew and Norway spruce by means of ultrasonic waves. Wood Sci Technol 41(4):309–327
Keunecke D, Hering S, Niemz P (2008) Three-dimensional elastic behaviour of common yew and Norway spruce. Wood Sci Technol 42(8):633–647
Keylwerth R (1951) Die anisotrope Elastizität des Holzes und der Lagenhölzer. Verlag des Vereins Deutscher Ingenieure—VDI-Forschungsheft 430
Kriz RD, Stinchcomb WW (1979) Elastic moduli of transversely isotropic graphite fibers and their composites. Exp Mech 19(2):41–49
McBurney RS, Drow JT (1962) The elastic properties of wood : Young’s moduli and Poisson’s ratios of Douglas-fir and their relations to moisture content Forest Product Laboratory Report No. 1528-D. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory Madison, Wisconsin
Molinski W, Fabisiak E (2001) Velocity of ultrasound propagation in the beech (Fagus sylvatica L) tension wood. Folia Forestalia Polonica B 32:75–81
Neuhaus FH (1983) Über das elastische Verhalten von Fichtenholz in Abhängigkeit von der Holzfeuchtigkeit. Holz Roh-Werkst 41:21–25
Niemz P, Caduff D (2008) Research into determination of the Poisson ratio of spruce wood. Holz Roh-Werkst 66(1):1–4
Oliveira FGR, Campos JAO, Pletz E, Sales A (2002) Nondestructive evaluation of wood using ultrasonic technique. Maderas Ciencia y tecnología 4(2):133–139
Oliveira FGR, Candian M, Lucchette FF, Luis Salgon JL, Sales A (2005) A technical note on the relationship between ultrasonic velocity and moisture content of Brazilian hardwood (Goupia glabra). Build Environ 40(2):297–300
Saadat-Nia MA, Brancheriau L, Gallet P, Enayati AA, Pourtahmasi K, Honarvar F (2011) Ultrasonic wave parameter changes during propagation through poplar and spruce reaction wood. BioResources 6(2):1172–1185
Sakai H, Minamisawa A, Takagi K (1990) Effect of moisture content on ultrasonic velocity and attenuation in woods. Ultrasonics 28:382–385
Sandoz JL (1993) Moisture content and temperature effect on ultrasound timber grading. Wood Sci Technol 27(5):337–380
Schniewind AP, Barrett JD (1972) Wood as a linear orthotropic viscoelastic material. Wood Sci Technol 6:43–57
Stamer J, Sieglerschmidt H (1933) Elastische Formänderung der Hölzer. Z Ver Dtsch Ing 77(19):503–505
Tiemann HD (1906) Effect of moisture upon the strength and stiffness of wood. Bulletin of United States Forest Service, United States Government Printing Office, Washington
Ting TCT, Chen T (2005) Poisson’s ratio for anisotropic elastic materials can have no bounds. Quart J Mech Appl Math 58(1):73–82
Truell R, Elbaum C, Chick BB (1969) Ultrasonic methods in solid state physics. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozyhar, T., Hering, S., Sanabria, S.J. et al. Determining moisture-dependent elastic characteristics of beech wood by means of ultrasonic waves. Wood Sci Technol 47, 329–341 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-012-0499-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-012-0499-2