Abstract
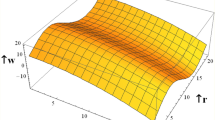
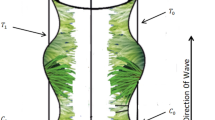
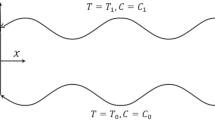
The present analysis discusses the peristaltic flow of a nanofluid in a diverging tube. This is the first article on the peristaltic flow in nanofluids. The governing equations for nanofluid are modelled in cylindrical coordinates system. The flow is investigated in a wave frame of reference moving with velocity of the wave c. Temperature and nanoparticle equations are coupled so Homotopy perturbation method is used to calculate the solutions of temperature and nanoparticle equations, while exact solutions have been calculated for velocity profile and pressure gradient. The solution depends on Brownian motion number N b , thermophoresis number N t , local temperature Grashof number B r and local nanoparticle Grashof number G r . The effects of various emerging parameters are investigated for five different peristaltic waves. It is observed that the pressure rise decreases with the increase in thermophoresis number N t . Increase in the Brownian motion parameter N b and the thermophoresis parameter N t temperature profile increases. Streamlines have been plotted at the end of the article.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
Specific heat
- b :
-
Wave amplitude
- N b :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- N t :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- λ:
-
Wave length
- c 1 :
-
Wave speed
- B r :
-
Local temperature Grashof
- c :
-
Volumetric volume expansion coefficient
- σ:
-
Nano particle phenomena
- G r :
-
Local nano particle Grashof number
- D B :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- K T :
-
Thermal—diffusion ratio
- \( D_{{\bar{T}}} \) :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- \( \bar{C} \) :
-
Nano particle phenomena
- F :
-
Frictional forces
- \( \bar{T} \) :
-
Temperature
- T m :
-
Temperature of the medium
- u :
-
Velocity component in r-direction
- w :
-
Velocity component in z-direction
- μ:
-
Viscosity
- ρ p :
-
Density of the particle
- ρ:
-
Density of the fluid
- ν:
-
Kinematic viscosity
- φ:
-
Wave amplitude
References
Latham TW (1966) Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump, MS. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Mekheimer KS, Abd elmaboud Y (2008) Influence of heat transfer and magnetic field on peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in a vertical annulus. Application of an endoscope. Phys Lett A 372:1657–1665
Nadeem S, Akbar NS (2010) Series solutions for the peristaltic flow of a Tangent hyperbolic fluid in a uniform inclined tube. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung 65a:887–895
Nadeem S, Akbar NS, Bibi N, Ashiq S (2010) Influence of heat and mass transfer on peristaltic flow of a third order fluid in a diverging tube. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numerical Simul 15:2916–2931
Mekheimer KS (2008) Effect of the induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of a couple stress fluid. Phys Lett A 372:4271–4278
Srinivas S, Gayathri R (2009) Peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in a vertical asymmetric channel with heat transfer and porous medium. Appl Math Comput 215:185–196
Srinivas S, Kothandapani M (2009) The influence of heat and mass transfer on MHD peristaltic flow through a porous space with compliant walls. Appl Math Comput 213:197–208
Srinivas S, Kothandapani M (2008) Peristaltic transport in an asymmetric channel with heat transfer. A note. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35:514–522
Nadeem S, Akbar NS (2009) Effects of heat transfer on the peristaltic transport of MHD Newtonian fluid with variable viscosity: application of Adomian decomposition method. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numerical Simul 14:3844–3855
Nadeem S, Akbar NS (2009) Influence of heat transfer on a peristaltic transport of Herschel–Bulkley fluid in a non-uniform inclined tube. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numerical Simul 14:4100–4113
Mekheimer KS, Abd elmaboud Y (2008) The influence of heat transfer and magnetic field on peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in a vertical annulus: application of an endoscope. Phys A 372:1657–1665
Srinivas S, Gayathri R, Kothandapani M (2009) The influence of slip conditions, wall properties and heat transfer on MHD peristaltic transport. Comput Phys Commun 180:2115–2122
Khan WA, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:2477–2483
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: Siginer DA, Wang HP (eds) Developments and applications of Non-Newtonian flows, vol 66. ASME, New York, pp 99–105
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transf 128:240–250
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M (2003) Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:3639–3653
Das SK, Putra N, Roetzel W (2003) Pool boiling of nano-fluids on horizontal narrow tubes. Int J Multiph Flow 29:1237–1247
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2010) Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int J Therm Sci 49:243–247
He JH (1998) Approximate analytical solution for seepage flow with fractional derivatives in porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 167:57–68
He JH (2005) Application of homotopy perturbation method to nonlinear wave equations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 26:695–700
He JH (1999) Homotopy perturbation technique. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 178:257–262
Acknowledgments
Third author as a visiting Professor thanks the partial support of Global Research Network for Computational Mathematics and King Saud University for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0929-y.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbar, N.S., Nadeem, S., Hayat, T. et al. Peristaltic flow of a nanofluid in a non-uniform tube. Heat Mass Transfer 48, 451–459 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0892-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0892-7