Abstract
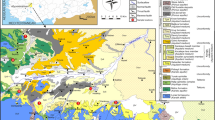
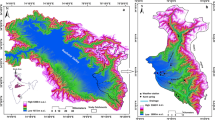
Widespread and intense zones of silicified, propylitic, and argillic alteration can be found in the Çan volcanics of Biga Peninsula, northwest Turkey. Most of the springs in the study area surface out from the boundary between fractured aquifer (silicified zone) and impervious boundary (argillic zone). This study focuses on two such springs in Kirazlı area (Kirazlı and Balaban springs) with a distinct quality pattern. Accordingly, field parameters (temperature, pH, and electrical conductivity), major anion and cation (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, bicarbonate, and sulfate), heavy metals (aluminum, arsenic, barium, chromium, cobalt, cupper, iron, lithium, manganese, nickel, lead, and zinc), and isotopes (oxygen-18, deuterium, and tritium) were determined in water samples taken from these springs during 2005 through 2007. The chemical analyses showed that aluminum concentrations were found to be two orders of magnitude greater in Kirazlı waters (mean value 13813.25 μg/L). The levels of this element exceeded the maximum allowable limits given in national and international standards for drinking-water quality. In addition, Balaban and Kirazlı springs are >55 years old according to their tritium levels; Kirazlı spring is older than Balaban spring. Kirazlı spring is also more enriched than Balaban spring based in oxygen-18 and deuterium values. Furthermore, Kirazlı spring water has been in contact with altered rocks longer than Balaban spring water, according to its relatively high chloride and electrical conductivity values.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arribas A Jr (1995) Characteristics of high-sulfidation epithermal deposits, and their relation to magmatic fluid. In: Thompson JFH (ed) Magmas, fluids and ore deposits [Shortcourse series 23]. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Canada, pp 419–454
Attendorn HG, Bowen R (1997) Radioactive and stable isotope geology. Chapman and Hall, London, 519 p
Baba A, Save D, Gunduz O, Gurdal G, Bozcu M, Sulun S et al (2009) The assessment of the mining activities in Çan Coal Basin from a medical geology perspective. Final report [in Turkish]. The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey Project No. ÇAYDAG-106Y041, Ankara, Turkey
Bau M, Usui A, Pracejus B, Mita N, Kanai Y, Irber W et al (1998) Geochemistry of low-temperature water–rock interaction: evidence from natural waters, andesite, and iron-oxyhydroxide precipitates at Nishiki–Numa iron-spring, Hokkaido, Japan. Chem Geol 151:293–307
Böhlke JK (1989) Comparison of metasomatic reactions between a common CO2-rich vein fluid and diverse wall rocks: intensive variables, mass transfers, and Au mineralization at Alleghany, California. Econ Geol 84:291–327
Ciftehan H (2006) Kirazlı property exploration 2004–2005 year end report [unpublished report]. Teckcominco Exploration and Mining Inc, Ankara, Turkey
Dessert C, Gaillardet J, Dupre B, Schott J, Pokrovsky O (2009) Fluxes of high- versus low-temperature water–rock interactions in aerial volcanic areas: example from the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:148–169
Environmental Protection Agency (2003) National primary drinking water standards. Office of Water, United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA 816-F-03-016
Finlow-Bates T, Stumpfl EF (1981) The behavior of so-called immobile elements in hydrothermally altered rocks associated with volcanogenic submarine-exhalative deposits. Min Deposit 16:319–328
General Directorate of Mineral Research, Exploration (2002) Geological map of Turkey, scale 1:500.000. MTA, Ankara, Turkey
Gislason SR, Arnorsson S, Armannsson H (1996) Chemical weathering of basalt in southwest Iceland: effects of runoff, age of rocks and vegetative/glacial cover. Am J Sci 296:837–907
Gunduz O, Baba A (2008) Fate of acidic mining lakes in Can Lignite District, Turkey. In Proceedings of the XXXVI IAH congress integrating groundwater science and human well-being, Proceedings CD-ROM, 26 October–1 November 2009, Toyoma, Japan
Gunduz O, Okumusoglu D, Baba A (2007) Acidic mining lakes and their influence on water quality: a case study from Can (Canakkale)—Turkey. In: Trefry MG (ed) Proceedings of the 6th groundwater quality conference (GW07: securing groundwater quality in urban and industrial environments), Fremantle, Western Australia
Hall G, Vaive JE, Beer R, Hoashi M (1996) Selective leaches revisited, with emphasis on the amorphous Fe oxyhydroxide phase extraction. J Geochem Explor 56:59–78
Hedenquist JW, Arribas A Jr (1999) Epithermal gold deposits: I. Hydrothermal processes in intrusion-related systems, and II. Characteristics, examples and origin of epithermal gold deposits. In: Molnar F, Lexa J, Hedenquist JW (eds) Epithermal mineralization of the Western Carpathians. Society of Economic Geologists, Guidebook Series Vol. 31, pp 13–63
Hedenquist JW, Richards JP (1998) The influence of geochemical techniques on the development of genetic models for porphyry copper deposits. In: Richards JP, Larsen PB (eds) Techniques in hydrothermal ore deposits geology. Reviews in economic geology, vol 10, pp 235–256
Heinrichs H, Herrmann AG (1990) Praktikum der Analytischen Geochemie. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp 352–355
Hemley JJ, Hostetler PB, Gude AJ, Mountjoy WT (1969) Some stability relations of alunite. Econ Geol 64:599–612
Henley RW, Truesdell AH, Barton PB Jr (1984) Fluid-mineral equilibria in hydrothermal systems: society of economic geologists reviews in economic geology, Robertson JM (series ed), vol 1. The Economic Geology Publishing Company, El Paso, TX, 267 p
Insani Tüketim Amaçlı Sular Hakkındaki Yönetmelik (ITASHY) (2005) Regulation on waters for human consumption [in Turkish]. Official Gazette dated 17/02/2005, No.25730, Ankara, Turkey
Karakaya N, Karakaya MÇ, Nalbantçılar MT, Yavuz F (2007) Relation between spring-water chemistry and hydrothermal alteration in the Şaplıca volcanic rocks, Şebinkarahisar (Giresun, Turkey). J Geochem Explor 93:35–46
Kerrich R, Fyfe WS (1981) The gold-carbonate association: source of CO2 and CO2-fixation reactions in Archean lode gold deposits. Chem Geol 33:265–294
Lerouge C, Flehos C, Kunov A, Hikov A, Georgieva S, Lescuyer JL et al (2004) Stable isotope study and origin of alunite from advanced argillic alteration systems in Bulgaria. In: Proceedings of Annual Scientific Conference of Bulgarian Geological Society, pp 16–17
Louvat P, Gislason SR, Allegre CJ (2008) Chemical and mechanical erosion rates in Iceland as deduced from river dissolved and solid material. Am J Sci 308:679–726
Lowell JD, Guilbert JM (1970) Lateral and vertical alteration—Mineralization zoning in porphyry copper deposits. Econ Geol 65:373–408
MacLean WH, Kranidiotis P (1987) Immobile elements as monitors of mass transfers in hydrothermal alteration: Phelps Dodge massive sulfide deposit, Matagami, Quebec. Econ Geol 82:951–962
Neall FB, Phillips GN (1987) Fluid-wall rock interaction in an Archean hydrothermal gold deposit: a thermodynamic model for the Hunt mine, Kambalda. Econ Geol 82:1679–1694
Nicholson K (1993) Geothermal fluids—Chemistry and exploration techniques. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany
Nieboer E, Gibson BL, Oxman AD, Kramer JR (1995) Health effects of aluminum: a critical review with emphasis on aluminum in drinking water. Environ Rev 3:29–81
Nordberg G (1998) Metals: chemical properties and toxicity, aluminum. In: Stellman JM (ed) Encyclopedia of occupational health and safety, vol III, 4th edn. International Labour Office, Geneva, pp 63.2–63.3
Pandarinath K, Dulski P, Torres-Alvarado IS, Verma SP (2008) Element mobility during the hydrothermal alteration of rhyolitic rocks of the Los Azufres geothermal field, Mexico. Geothermics 37:53–72
Piantone P, Wu X, Touray JC (1994) Zoned hydrothermal alteration and genesis of the gold deposit at Le Chatelet (French Massif Central). Econ Geol 89:757–777
Polizzi S, Pira E, Ferrara M, Bugiani M, Papaleo A, Albera R et al (2002) Neurotoxic effects of aluminum among foundry workers and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotoxicology 23:761–774
Seal RR II, Hammarstrom JM, Johnson AN, Piatak NM, Wandless GA (2008) Environmental geochemistry of a Kuroko-type massive sulfide deposit at the abandoned Valzinco mine, Virginia, USA. Appl Geochem 23:320–342
Thuy HT, Tobschall HJ, An PV (2000) Distribution of heavy metals in urban soils—A case study of Danang-Hoian area (Vietnam). Environ Geol 39:603–610
Verhagen BT, Geyh MA, Fröhlich K, With K (1991) Isotope hydrological methods for the quantitative evaluation of groundwater resources in arid and semi-arid areas. Research Reports of the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation of the Federal Republic of Germany, Bonn, Germany, pp 7–122
Verma SP, Torres-Alvarado IS, Satir M, Dobson PF (2005) Hydrothermal alteration effects in geochemistry and Sr, Nd, Pb, and O isotopes of magmas from the Los Azufres geothermal field (Mexico): a statistical approach. Geochem J 39:141–163
Zeien H, Brümmer GW (1989) Chemische Extraktion zur Bestimmung von Schwermetallbindungsformen in Böden. Mitteilgn Dtsch Bodenkundl Gesellsch 59:505–510
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Turkish Academy of Sciences and the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, A., Gunduz, O. Effect of Alteration Zones on Water Quality: A Case Study from Biga Peninsula, Turkey. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58, 499–513 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9406-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9406-8