Abstract
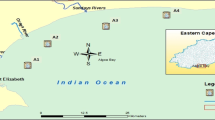
The first appraisal of butyltins (BT) contamination linked with imposex incidence in the Pacific coast of South America was performed in the current study. Imposex occurrence was analyzed in three muricid species (Thais biserialis, T. brevidentata, and T. kiosquiformis) distributed along 14 sites from the coastal areas of Ecuador. All studied muricids species showed imposex, which was observed in 11 out of 14 sites. The highest imposex levels were observed in T. kiosquiformis collected inside the Gulf of Guayaquil [relative penis length index (RPLI) 9.0–40.7], whereas RPLI values for T. biserialis and T. brevidentata ranged from 4.0 to 26.1 and 0.0 to 1.9, respectively. Additionally, BT compounds [tributyltin (TBT), dibutylin (DBT), and monobutylin (MBT)] were determined in surface sediments collected in 6 of the sites (main harbor areas), and values ranged between 12.7 and 99.5 ng Sn g−1 (dry weight) for TBT, 1.8 and 54.4 ng Sn g−1 for DBT, and 44 and 340 ng Sn g−1 for MBT. Although BT degradation indexes suggested an aged input of TBT, the high imposex levels detected in the current study suggest that international restrictions on TBT based antifouling paints were still not effective in Ecuador. Considering that the southern coast, especially nearby harbors inside the Gulf of Guayaquil, have shown to be contaminated by BTs, a combination of T. kiosquiformis and T. biserialis (the most sensitive species) can be used for future biomonitoring of Ecuador coastal areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre WE, Shervette VR (2005) Morphological diversity of the Cynoscion group (Perciformes: Sciaenidae) in the Gulf of Guayaquil Region, Ecuador: a comparative approach. Environ Biol Fish 73:403–413
Almeida E, Diamantino TC, de Sousa O (2007) Marine paints: the particular case of antifouling paints. Prog Org Coat 59:2–20
Bech M (1999) Sensitivity of different gastropod to tributyltin contamination. Phu Mar Biol Cent Spc Pub 19:1–6
Bech M (2002) A survey of imposex in muricids from 1996 to 2000 and identification of optimal indicators of tributyltin contamination along the East Coast of Phuket Island, Thailand. Mar Pollut Bull 44:887–896
Bigatti G, Primost MA, Cledón M, Averbuj A, Theobald N, Gerwinski W et al (2009) Biomonitoring of TBT contamination and imposex incidence along 4700 km of Argentinean shoreline (SW Atlantic: from 38S to 54S). Mar Pollut Bull 58:695–701
Blaber SJM (1970) The occurence of a penis-like out growth behind the right tentacle in spent females of Nucella Lapillus (L.). Proc Malacol Soc London 39:231–233
Bryan GW, Gibbs PE, Burt GR (1988) A comparison of the effectiveness of tri-n-butyltin chloride and 5 other organotin compounds in promoting the development of imposex in the dog-whelk, Nucella lapillus. J Mar Biol Ass U K 68:733–744
Bryant D, Rodenbur E, Cox T, Nielsen D (1995) Coastlines at risk: an index of potential development-related threats to coastal ecosystems [WRI Indicator Brief]. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC
Castro IB, Bemvenuti CE, Fillmann G (2007a) Preliminary appraisal of imposex in areas under the influence of southern Brazilian harbors. J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 2:73–79
Castro IB, Lima AFA, Braga ARC, Rocha-Barreira CA (2007b) Imposex in two muricid species (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from the northeastern Brazilian Coast. J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 2:81–91
Castro IB, de Meirelles CAO, Matthews-Cascon H, Rocha-Barreira CD, Penchaszadeh P, Bigatti G (2008) Imposex in endemic volutid from northeast Brazil (Mollusca: Gastropoda). Braz Arch Biol Technol 51:1065–1069
Castro IB, Perina FC, Fillmann G (2011) Review of organotin contamination in South America. Environ Monit Assess
Choi M, Moon HB, Yu J, Eom JY, Choi HG (2010) Temporal trend of butyltins in seawater, sediments, and mussels from Busan Harbor of Korea between 2002 and 2007: tracking the effectiveness of tributylin regulation. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:394–402
Clark EL, Sterrit RM, Lester JN (1988) The fate of tributyltin in the aquatic environment: a look at the data. Environ Sci Technol 22:600–604
Delucchi F, Tombesi NB, Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2006) Butyltin compounds in sediments of the Bahia Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 132:445–451
Díez S, Bayona JM (2009) Butyltin occurrence and risk assessment in sediments of the Iberian Peninsula. J Environ Manag 90:S25–S30
Díez S, Abalos M, Bayona JM (2002) Organotin contamination in sediments from western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Res 36:905–918
Díez S, Jover E, Albaiges J, Bayona JM (2006) Occurrence and degradation of butyltins and wastewater marker compounds in sediments from Barcelona Harbor, Spain. Environ Int 32:858–865
Evans SM (1999) Tributyltin pollution: the catastrophe that never happened. Mar Pollut Bull 38:629–636
Felizzola JF, Wagener AdLR, Almeida AC, Lin WO (2008) Butyltin speciation in sediments from Todos Os Santos Bay (Bahia, Brazil) by GC-PFPD. Quím Nova 31:89–93. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422008000100019
Fent K (2006) Worldwide occurrence of organotins from antifouling paints and effects in the aquatic environment. In: Konstantinou IK (ed) Handbook of environmental chemistry: antifouling paints biocides. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp 71–100
Fernandez MA, Wagener LR, Limaverde AM, Scofield AL, Pinheiro FM, Rodrigues E (2005) Imposex and surface sediment speciation: a combined approach to evaluate organotin contamination in Guanabara Bay, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil. Mar Environ Res 59:435–452
Galante-Oliveira S, Oliveira I, Jonkers N, Langston WJ, Pacheco M, Barroso CM (2009) Imposex levels and tributyltin pollution in Ria De Aveiro (NW Portugal) between 1997 and 2007: evaluation of legislation effectiveness. J Environ Monit 11:1405–1411
Gibbs PE, Bryan GM (1987) TBT paints and demise of the dog-whelk Nucella lapillus (Gastropoda). J Mar Biol Assess U K 68:1482–1487
Gibbs PE, Bryan GM, Pascoe PL, Burt GR (1987) The use of dog-whelk, Nucella lapillus, as an indicator of tributyltin (TBT) contamination. J Mar Biol Assess U K 67:507–523
Godoi AFL, Montone RC, Santiago-Silva M (2003) Determination of butyltin compounds in surface sediments from the Sao Paulo State coast (Brazil) by gas chromatography-pulsed flame photometric detection. J Chromatogr 985:205–210
Gooding M, Gallardo C, LeBlanc G (1999) Imposex in three marine gastropod species in Chile and potential impact on muriciculture. Mar Pollut Bull 38:1227–1231
Gravel P, Johanning K, McLachlan J, Vargas JA, Oberdorster E (2006) Imposex in the intertidal snail Thais brevidentata (Gastropoda: Muricidae) from the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Rev Biol Trop 54:21–26
Gray JS (1981) The ecology of marine sediments. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY
Horiguchi T (2009) The endocrine-disrupting effect of organotin compounds for aquatic organisms. In: Arai T, Harino H, Ohji M, Langston WJ (eds) Ecotoxicology of antifouling biocides. Springer, Tokyo, Japan, pp 125–146
Horiguchi T, Shiraishi H, Shimizu M, Morita M (1997) Effects of triphenyltin chloride and five other organotin compounds on the development of imposex in the rock shell, Thais clavigera. Environ Pollut 95:85–91
Huaquin LG, Osorio C, Verdugo R, Collado G (2004) Morphological changes in the reproductive system of females Acanthina monodon (Pallas 1774) (Gastropoda: Muricidae) affected by imposex from the coast of Central Chile. Invertebr Reprod Dev 46:111–117
International Maritime Organization (2008) Summary of the status of conventions as of 31 May 2007. http://www.imo.org/
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2002) Analytical, Applied, clinical, inorganic, and physical chemistry divisions interdivisional working party for harmonization of quality assurance schemes for analytical laboratories. Pure App Chem 74:835–855
Lahbib Y, Abidli S, Chiffoleau JF, Averty B, El Menif NT (2009) First record of butyltin body burden and imposex status in Hexaplex trunculus (L.) along the Tunisian coast. J Environ Monit 11:1253–1258
Lahbib Y, Abidli S, Chiffoleau JF, Averty B, Menif NTE (2010) Imposex and butyltin concentrations in snails from the Lagoon of Bizerta (Northern Tunisia). Mar Biol Res 6:600–607
Langston WJ, Harino H, Pope ND (2009) Behaviour of organotins in the coastal environment. In: Arai T, Harino H, Ohji M, Langston WJ (eds) Ecotoxicology of antifouling biocides. Springer, Tokyo, Japan, pp 75–94
Li C, Collin R (2009) Imposex in one of the world’s busiest shipping zones. Smithson Contrib Mar Sci 38:189–196
Maguire RJ (1984) Butyltin compounds and inorganic tin in sediments in Ontario. Environ Sci Techol 18:291–294
Matthiessen P, Gibbs PE (1998) Critical appraisal of the evidence for tributyltin-mediated endocrine disruption in mollusks. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:37–43
Miloslavich P, Penchaszadeh PE, Bigatti G (2007) Imposex in gastropods from Venezuela. Cienc Mar 33:319–324
Mora SJ, Phillips DR (1997) Tributyltin (TBT) pollution in riverine sediments following a spill from a timber treatment facility in Henderson, New Zealand. Environ Technol 18:1187–1193
Morabito R, Massanisso P, Quevauviller P (2000) Derivatization methods for the determination of organotin compounds in environmental samples. Trends Anal Chem 19:113–119
Oehlmann J, Stroben E, Schulte Oehlmann U, Bauer B, Fioroni P, Markert B (1996) Tributyltin biomonitoring using prosobranchs as sentinel organisms. Frenesius J Anal Chem 354:540–545
Oliveira CR, Santos DM, Santos Madureira LA, Marchi MRR (2010) Speciation of butyltin derivatives in surface sediments of three southern Brazilian harbors. J Hazard Mater 181:851–856
Osorio MFA (2009) Imposex en muricideos (Mollusca: Gastropoda) del perfil costero ecuatoriano: Una indicación de contaminación por compuestos organoestañosos. Universidad de Guayaquil
Pinochet H, Tessini C, Bravo M, Quiroz W, De Gregori I (2009) Butyltin compounds and their relation with organic matter in marine sediments from San Vicente Bay, Chile. Environ Monit Assess 155:341–353
Porte C, Janer G, Lorusso LC, Ortiz-Zarragoitia M, Cajaraville MP, Fossi MC et al (2006) Endocrine disruptors in marine organisms: approaches and perspectives. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 143:303–315
Quintela M, Barreiro R, Ruiz JM (2000) The use of Nucella lapillus (L.) transplanted in cages to monitor tributyltin (TBT) pollution. Sci Total Environ 247:227–237
Ramasamy MS, Murugan A (2002) Imposex in muricid gastropod Thais biserialis (Mollusca: Neogastropoda: Muricidae) from Tuticorin Harbour, southeast coast of India. Indian J Mar Sci 31:243–245
Ruiz JM, Bachelet G, Caumette P, Donard OFX (1996) Three decades of tributyltin in the coastal environmental with emphasis on Archacon Bay, France. Environ Pollut 93:195–203
Ruiz JM, Díaz J, Albaina N, Couceiro L, Irabien A, Barreiro R (2010) Decade-long monitoring reveals a transient distortion of baseline butyltin bioaccumulation pattern in gastropods. Mar Pollut Bull 60:931–934
Sakami T, Fujioka Y, Shimoda T (2008) Comparison of microbial community structures in intensive and extensive shrimp culture ponds and a mangrove area in Thailand. Fish Sci 74:889–898
Santos DM, Araújo IP, Machado EC, Carvalho-Filho MAS, Fernandez MA, Marchi MRR et al (2009) Organotin compounds in the Paranaguá estuarine complex, Paraná, Brazil: evaluation of biological effects, surface sediment, and suspended particulate matter. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1926–1931
Shi HH, Huang CJ, Zhu XS, Yu XJ, Xie WY (2005) Generalized system of imposex and reproductive failure in female gastropods of coastal waters of mainland China. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 304:179–189
Shim WJ, Oh JR, Kahng SH, Shim JH, Lee SH (1999) Horizontal distribution of butyltins in surface sediments from an enclosed bay system, Korea. Environ Pollut 106:351–357
Sousa A, Laranjeiro F, Takahashi S, Tanabe S, Barroso CM (2009) Imposex and organotin prevalence in a European post-legislative scenario: temporal trends from 2003 to 2008. Chemosphere 77:566–573
Sternberg R, Gooding M, Hotchkiss A, LeBlanc G (2010) Environmental endocrine control of reproductive maturation in gastropods: implications for the mechanism of tributyltin-induced imposex in prosobranchs. Ecotoxicology 19:4–23
Stewart C, Demora SJ, Jones MRL, Miller MC (1992) Imposex in New Zealand neogastropods. Mar Pollut Bull 24:204–209
Stroben E, Oehlmann J, Fioroni P (1992) The morphological expression of imposex in Hinia reticulata (Gastropoda, Buccinidae)—a potential indicator of tributyltin pollution. Mar Biol 113:625–636
Town RM, Filella M (2002) Implications of natural organic matter binding heterogeneity on understanding lead(II) complexation in aquatic systems. Sci Total Environ 300:143–154
Vasconcelos P, Gaspar MB, Barroso CM (2010) Imposex in Bolinus brandaris from the Ria Formosa Lagoon (Southern Portugal): usefulness of "single-site baselines" for environmental monitoring. J Environ Monit 12:1823–1832
Yamamoto J, Yonezawa Y, Nakata K, Horiguchi F (2009) Ecological risk assessment of TBT in Ise Bay. J Environ Manag 90:S41–S50
Acknowledgments
I. B. de Castro (doctoral Grant No. 141550/2007) and G. Fillmann (PQ 311459/2006-4 and 314335/2009-9) were sponsored by CNPq (Brazilian National Research Council). The authors are grateful for the Universidade de Guayaquil support. We also thank René Oscar Rodríguez Grimón for helping during sampling and Instituto Proficere (www.proficere.com.br) for grammatical revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, Í.B., Arroyo, M.F., Costa, P.G. et al. Butyltin Compounds and Imposex Levels in Ecuador. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62, 68–77 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9670-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9670-2