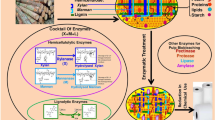
Abstract
Pitch control is an important aspect in pulp and paper manufacture, and the first example where microbial biotechnology provided successful solutions in this industrial sector. Triglycerides cause deposits in softwood mechanical pulping, and both microbial and enzymatic products have been commercialized to be applied on wood and pulp, respectively. The former are based on colorless strains of sapstain fungi. The latter are improved lipases, including thermostable variants from directed evolution. These enzymes are among the additives of choice in pulping of high-resin-content softwoods. However, lipases are not useful when pitch originates from other lipids, such as steroids and terpenes, and the sapstain inocula are also only partially effective. In the search for stronger biocatalysts to degrade recalcitrant lipids, the potential of white-rot fungi and their enzymes has been demonstrated. When inocula of these fungi are used, wood treatment must be controlled to avoid cellulose degradation. However, the efficiency and selectivity of the laccase-mediator system permits its integration as an additional bleaching stage. A double benefit can be obtained from these treatments since pitch is controlled at the same time that residual lignin is removed facilitating the implementation of totally chlorine free pulp bleaching.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar M, Scott GM, Swaney RE, Shipley DF (2000) Biomechanical pulping: a mill-scale evaluation. Resour Conserv Recycl 28:241–252
Allen LH (2000a) Pitch control in paper mills. In: Back EL, Allen LH (eds) Pitch control wood resin and deresination. TAPPI, Atlanta, pp 307–328
Allen LH (2000b) Pitch control in pulp mills. In: Back EL, Allen LH (eds) Pitch control wood resin and deresination. TAPPI, Atlanta, pp 265–288
Back EL (2000) The location and morphology of resin components in the wood. In: Back EL, Allen LH (eds) Pitch control wood resin and deresination. Tappi, Atlanta, pp 1–35
Back EL, Allen LH (2000) Pitch control wood resin and deresination. TAPPI, Atlanta
Bajpai P, Bajpai PK, Akhtar M, Jauhari MB (2001) Biokraft pulping of eucalyptus with selected lignin-degrading fungi. J Pulp Paper Sci 27:235–239
Bergelin E, Holmbom B (2003) Deresination of birch kraft pulp in bleaching. J Pulp Paper Sci 29:29–34
Bergelin E, Moller R, Holmbom B (2005) Analysis of pitch and deposit samples in kraft pulp production. Pap Puu-Pap Tim 87:399–403
Blanchette RA (1995) Degradation of the lignocellulose complex in wood. Can J Bot 73:S999–S1010
Borch K, Franks N, Lund H, Xu H, Luo J (2003) Oxidizing enzymes in the manufacturing of paper materials. Patent (USA) US 2003/0124710 A1
Bornscheuer U, Bessler C, Srinivas R, Hari KS (2002) Optimizing lipases and related enzymes for efficient application. Trends Biotechnol 20:433–437
Bourbonnais R, Paice MG (1990) Oxidation of non-phenolic substrates. An expanded role for laccase in lignin biodegradation. FEBS Lett 267:99–102
Bourbonnais R, Paice MG (1996) Enzymatic delignification of kraft pulp using laccase and a mediator. Tappi J 79:199–204
Brash AR (1999) Lipoxygenases: occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate. J Biol Chem 274:23679–23682
Brush T, Farrell RL, Ho C (1994) Biodegradation of wood extractives from Southern and Yellow pine by Ophiostoma piliferum. Tappi J 77:155–159
Buchert J, Mustranta A, Tamminen T, Spetz P, Holmbom B (2002) Modification of spruce lignans with Trametes hirsuta laccase. Holzforschung 56:579–584
Burnes TA, Blanchette RA, Farrell RL (2000) Bacterial biodegradation of extractives and patterns of bordered pit membrane attack in pine wood. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5201–5205
Calero-Rueda O, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Prieto A, Plou FJ, Ballesteros A, Martínez AT, Martínez MJ (2004) Hydrolysis of sterol esters by an esterase from Ophiostoma piceae: application for pitch control in pulping of Eucalyptus globulus wood. Intern J Biotechnol 6:367–375
Call H-P (1994) Verfahren zur Veränderung, Abbau oder Bleichen von Lignin, ligninhaltigen Materialien oder ähnlichen Stoffen. Patent (International) WO 94/29510
Camarero S, García O, Vidal T, Colom J, del Río JC, Gutiérrez A, Gras JM, Monje R, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (2004) Efficient bleaching of non-wood high-quality paper pulp using laccase-mediator system. Enzyme Microb Technol 35:113–120
Camarero S, Ibarra D, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (2005) Lignin-derived compounds as efficient laccase mediators for decolorization of different types of recalcitrant dyes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1775–1784
Chen T, Wang Z, Gao Y, Breuil C, Hatton JV (1994) Wood extractives and pitch problems: analysis and partial removal by biological treatment. Appita 47:463–466
Chen T, Wang Z, Zhou Y, Breuil C, Aschim OK, Yee E, Nadeau L (1995) Using solid-phase extraction to assess why aspen causes more pitch problems than softwoods in kraft pulping. Tappi J 78:143–149
Chen S, Lin Y, Zhang Y, Wang XH, Yang JL (2001) Enzymatic pitch control at Nanping paper mill. Tappi J 84:44–47
del Río JC, Gutiérrez A (2006) Chemical composition of abaca (Musa textilis) leaf fibers used for manufacturing of high quality paper Pulps. J Agric Food Chem 54:4600–4610
del Río JC, Gutiérrez A, González-Vila FJ, Martín F, Romero J (1998) Characterization of organic deposits produced in the Kraft pulping of Eucalyptus globulus wood. J Chromatogr 823:457–465
del Río JC, Gutiérrez A, González-Vila FJ (1999) Analysis of impurities occurring in a totally-chlorine free-bleached Kraft pulp. J Chromatogr 830:227–232
del Río JC, Romero J, Gutiérrez A (2000) Analysis of pitch deposits produced in Kraft pulp mills using a totally chlorine free bleaching sequence. J Chromatogr A 874:235–245
Dorado J, Claassen FW, Lenon G, van Beek TA, Wijnberg JBPA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2000a) Degradation and detoxification of softwood extractives by sapstain fungi. Bioresource Technol 71:13–20
Dorado J, Claassen FW, van Beek TA, Lenon G, Wijnberg JBPA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2000b) Elimination and detoxification of softwood extractives by white-rot fungi. J Biotechnol 80:231–240
Dorado J, van Beek TA, Claassen FW, Sierra-Alvarez R (2001) Degradation of lipophilic wood extractive constituents in Pinus sylvestris by the white-rot fungi Bjerkandera sp. and Trametes versicolor. Wood Sci Technol 35:117–125
Dubé E, Shareck F, Hurtubise Y, Beauregard M, Daneault C (2008) Enzyme-based approaches for pitch control in thermomechanical pulping of softwood and pitch removal in process water. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:1261–1266
Eberhardt TL, Han JS, Micales JA, Young RA (1994) Decay resistance in conifer seed cones—role of resin acids as inhibitors of decomposition by white-rot fungi. Holzforschung 48:278–284
Eggert C, Temp U, Dean JFD, Eriksson K-EL (1996) A fungal metabolite mediates degradation of non-phenolic lignin structures and synthetic lignin by laccase. FEBS Lett 391:144–148
Ekman R (2000) Resin during storage and its biological treatment. In: Back EL, Allen LH (eds) Pitch control wood resin and deresination. Tappi, Atlanta, pp 185–204
Ekman R, Holmbom B (2000) The chemistry of wood resin. In: Back EL, Allen LH (eds) Pitch control wood resin and deresination. TAPPI, Atlanta, pp 37–76
Farrell RL (2007) Cartapip/SylvanexTM: Ophiostoma fungal product for commercial pulp and paper and solid wood applications. Proc 10 Intern Congr Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry, Madison, 10–14 June 63–64
Farrell RL, Blanchette RA, Brush TS, Hadar Y, Iverson S, Krisa K, Wendler PA, Zimmerman W (1993) Cartapip™: a biopulping product for control of pitch and resin acid problems in pulp mills. J Biotechnol 30:115–122
Fengel D, Wegener G (1984) Wood: Chemistry, ultrastructure reactions. De Gruyter, Berlin
Fischer K, Messner K (1992a) Adsorption of lipase on pulp fibers during biological pitch control in paper industry. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:470–473
Fischer K, Messner K (1992b) Biological pitch reduction of sulfite pulp on pilot scale. In: Kuwahara M, Shimada M (eds) Biotechnology in the pulp and paper industry. UNI, Kyoto, pp 169–174
Fischer K, Puchinger L, Schloffer K (1993) Enzymatic pitch control of sulfite pulp on pilot scale. J Biotechnol 27:341–348
Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP (2002) Identification of new hydroxy fatty acids and ferulic acid esters in the wood of Eucalyptus globulus. Holzforschung 56:143–149
Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP (2005) Lipophilic extractives in Eucalyptus globulus kraft pulps. Behavior during ECF bleaching. J Wood Chem Technol 25:67–80
Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP, Evtuguin DV (2006) Effect of oxygen, ozone and hydrogen peroxide bleaching stages on the contents and composition of extractives of Eucalyptus globulus kraft pulps. Bioresource Technol 97:420–428
Fujita Y, Awaji H, Matsukura M, Hata K (1991) Enzymic pitch control in papermaking process. Kami Pa Gikyoshi 45:905–921
Fujita Y, Awaji H, Taneda H, Matsukura M, Hata K, Shimoto H, Sharyo M, Sakaguchi H, Gibson K (1992) Recent advances in enzymic pitch control. Tappi J 75(4):117–122
González-Vila FJ, Gutiérrez A, Martín F, Verdejo T (1997) Application of analytical pyrolysis to the characterization of Eucalyptus extractives and pitch deposits from a pulp mill. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 40–41:501–510
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC (2001) Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry demonstration of steryl glycosides in eucalypt wood, kraft pulp and process liquids. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15:2515–2520
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC (2003a) Lipids from flax fibers and their fate in alkaline pulping. J Agric Food Chem 51:4965–4971
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC (2003b) Lipids from flax fibers and their fate in alkaline pulping (Vol 51, pg 4965, 2003). J Agric Food Chem 51:6911–6914
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC (2005) Chemical characterization of pitch deposits produced in the manufacturing of high-quality paper pulps from hemp fibers. Bioresource Technol 96:1445–1450
Gutiérrez A, Caramelo L, Prieto A, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (1994) Anisaldehyde production and aryl-alcohol oxidase and dehydrogenase activities in ligninolytic fungi from the genus Pleurotus. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1783–1788
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, González-Vila FJ, Romero J (1998) Variation in the composition of wood extractives from Eucalyptus globulus during seasoning. J Wood Chem Technol 18:439–446
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, González-Vila FJ, Martín F (1999a) Chemical composition of lipophilic extractives from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. wood. Holzforschung 53:481–486
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (1999b) Fungal degradation of lipophilic extractives in Eucalyptus globulus wood. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1367–1371
Gutiérrez A, Martínez MJ, del Río JC, Romero J, Canaval J, Lenon G, Martínez AT (2000) Fungal pretreatment of Eucalyptus wood can strongly decrease the amount of lipophilic extractives during chlorine-free kraft pulping. Environ Sci Technol 34:3705–3709
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (2001a) The biotechnological control of pitch in paper pulp manufacturing. Trends Biotechnol 19:340–348
Gutiérrez A, Romero J, del Río JC (2001b) Lipophilic extractives from Eucalyptus globulus pulp during kraft cooking followed by TCF and ECF bleaching. Holzforschung 55:260–264
Gutiérrez A, Romero J, del Río JC (2001c) Lipophilic extractives in process waters during manufacturing of totally chlorine free kraft pulp from eucalypt wood. Chemosphere 44:1237–1242
Gutiérrez A, Rodríguez IM, del Río JC (2004) Chemical characterization of lignin and lipid fractions in kenaf bast fibers used for manufacturing high-quality papers. J Agric Food Chem 52:4764–4773
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Ibarra D, Rencoret J, Romero J, Speranza M, Camarero S, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (2006a) Enzymatic removal of free and conjugated sterols forming pitch deposits in environmentally sound bleaching of eucalypt paper pulp. Environ Sci Technol 40:3416–3422
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Rencoret J, Ibarra D, Martínez AT (2006b) Main lipophilic extractives in different paper pulp types can be removed using the laccase-mediator system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:845–851
Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Rencoret J, Ibarra D, Speranza AM, Camarero S, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (2006c) Sistema enzima-mediador para el control de los depósitos de pitch en la fabricación de pasta y papel. Patent (International) PCT/ES06/070091
Gutiérrez A, Rodríguez IM, del Río JC (2006d) Chemical characterization of lignin and lipid fractions in industrial hemp bast fibers used for manufacturing high-quality paper pulps. J Agric Food Chem 54:2138–2144
Gutiérrez A, Rencoret J, Ibarra D, Molina S, Camarero S, Romero J, del Río JC, Martínez AT (2007) Removal of lipophilic extractives from paper pulp by laccase and lignin-derived phenols as natural mediators. Environ Sci Technol 41:4124–4129
Gutiérrez A, Rodríguez IM, del Río JC (2008) Chemical composition of lipophilic extractives from sisal (Agave sisalana) fibers. Ind Crops Prod 28:81–87
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:235–251
Hata K, Matsukura M, Taneda H, Fujita Y (1996) Mill-scale application of enzymatic pitch control during paper production. In: Viikari L, Jeffries TW (eds) Enzymes for pulp and paper processing. ACS, Washington, pp 280–296
Hata K, Matsukura M, Fujita Y, Toyota K, Taneda H (1998) Biodegradation of resin acids in pulp and paper industry: application of microorganisms and their enzymes. ACS Sym Ser 687:27–40
Held BW, Thwaites JM, Farrell RL, Blanchette RA (2003) Albino strains of Ophiostoma species for biological control of sapstaining fungi. Holzforschung 57:237–242
Ibarra D, Chávez MI, Rencoret J, del Río JC, Gutiérrez A, Romero J, Camarero S, Martínez MJ, Jimenez-Barbero J, Martínez AT (2007) Structural modification of eucalypt pulp lignin in a totally chlorine free bleaching sequence including a laccase-mediator stage. Holzforschung 61:634–646
Jansson MB, Wormald P, Dahlman O (1995) Reactions of wood extractives during ECF and TCF bleaching of kraft pulp. Pulp Paper Can 96:T134–T137
Josefsson P, Nilsson F, Sundstrom L, Norberg C, Lie E, Jansson MB, Henriksson G (2006) Controlled seasoning of Scots pine chips using an albino strain of Ophiostoma. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 45:2374–2380
Kallioinen A, Vaari A, Ratto M, Konn J, Siikaaho M, Viikari L (2003) Effects of bacterial treatments on wood extractives. J Biotechnol 103:67–76
Karlsson S, Holmbom B, Spetz P, Mustranta A, Buchert J (2001) Reactivity of Trametes laccases with fatty and resin acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:317–320
Kontkanen H, Tenkanen M, Fagerstrom R, Reinikainen T (2004) Characterisation of steryl esterase activities in commercial lipase preparations. J Biotechnol 108:51–59
Kontkanen H, Saloheimo M, Pere J, Miettinen-Oinonen A, Reinikainen T (2006a) Characterization of Melanocarpus albomyces steryl esterase produced in Trichoderma reesei and modification of fibre products with the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:696–704
Kontkanen H, Tenkanen M, Reinikainen T (2006b) Purification and characterisation of a novel steryl esterase from Melanocarpus albomyces. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:265–273
Leach JM, Thakore AN (1976) Toxic constituents in mechanical pulping effluents. Tappi 59:129–132
Leone R, Breuil C (1998) Filamentous fungi can degrade aspen steryl esters and waxes. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 41:133–137
Liss SN, Bicho PA, Saddler JN (1997) Microbiology and biodegradation of resin acids in pulp mill effluents: a minireview. Can J Microbiol 43:599–611
Mancheno JM, Pernas MA, Martinez MJ, Ochoa B, Rua ML, Hermoso JA (2003) Structural insights into the lipase/esterase behavior in the Candida rugosa lipases family: crystal structure of the lipase 2 isoenzyme at 1.97A resolution. J Mol Biol 332:1059–1069
Marsheck WJ, Kraychy S, Muir RD (1972) Microbial degradation of sterols. Appl Microbiol 23:72–77
Martínez MJ, Barrasa JM, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Martínez AT (1999) Fungal screening for biological removal of extractives from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. wood. Can J Bot 77:1513–1522
Martínez AT, Speranza M, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Ferreira P, Camarero S, Guillén F, Martínez MJ, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC (2005) Biodegradation of lignocellulosics: microbiological, chemical and enzymatic aspects of fungal attack to lignin. Intern Microbiol 8:195–204
Martínez-Íñigo MJ, Immerzeel P, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Sierra-Alvarez R (1999) Biodegradability of extractives in sapwood and heartwood from Scots pine by sapstain and white-rot fungi. Holzforschung 53:247–252
Martínez-Íñigo MJ, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (2000) Time course of fungal removal of lipophilic extractives from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. wood. J Biotechnol 84:119–126
Matsukura M, Fujita Y, Sakaguchi H (1990) On the use of Resinase™ A for pitch control. Novo A-6122:1-7
Mayer AM, Staples RC (2002) Laccase: new functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry 60:551–565
Molina S, Rencoret J, del Río JC, Lomascolo A, Record E, Martínez AT, Gutiérrez A (2008) Oxidative degradation of model lipids representative for main paper pulp lipophilic extractives by the laccase-mediator system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:211–222
Morrison WHI, Akin DE (2001) Chemical composition of components comprising bast tissue in flax. J Agric Food Chem 49:2333–2338
Nguyen D, Zhang X, Paice MG, Tsang A, Renaud S (2007) Microplate enzyme assay for screening lipoxygenases to degrade wood extractives. Biocatal Biotransform 25:202–210
Otero D, Sundberg K, Blanco A, Negro C, Holmbom B (2000) Effect of wood polysaccharides on the depositability of wood pitch. Nordic Pulp Paper Res J 15:607–613
Paice MG, Bourbonnais R, Reid ID, Archibald FS, Jurasek L (1995) Oxidative bleaching enzymes: a review. J Pulp Paper Sci 21:J280–J284
Panda T, Gowrishankar BS (2005) Production and applications of esterases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:160–169
Piontek K, Antorini M, Choinowski T (2002) Crystal structure of a laccase from the fungus Trametes versicolor at 1.90-Å resolution containing a full complement of coppers. J Biol Chem 277:37663–37669
Poppius-Levlin K, Wang W, Tamminen T, Hortling B, Viikari L, Niku-Paavola M-L (1999) Effects of laccase/HBT treatment on pulp and lignin structures. J Pulp Paper Sci 25:90–94
Qin M, Hannuksela T, Holmbom B (2003) Physico-chemical characterization of TMP resin and related model mixtures. Colloids Surfaces A 221:243–254
Qin M, Hannuksela T, Holmbom B (2004) Deposition tendency of TMP resin and related model mixtures. J Pulp Paper Sci 30:279–283
Rencoret J, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC (2007) Lipid and lignin composition of woods from different eucalypt species. Holzforschung 61:165–174
Riva S (2006) Laccases: blue enzymes for green chemistry. Trends Biotechnol 24:219–226
Rocheleau MJ, Sitholé BB, Allen LH, Noel Y (1999) Fungal treatment of aspen for wood resin reduction: effect on aged aspen wood chips at room temperature and at 5°C. Holzforschung 53:16–20
Rodríguez Couto S, Toca Herrera JL (2006) Industrial and biotechnologcial applications of laccases: a review. Biotechnol Adv 24:500–513
Saam J, Ivanov I, Walther M, Holzhutter HG, Kuhn H (2007) Molecular dioxygen enters the active site of 12/15-lipoxygenase via dynamic oxygen access channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13319–13324
Sealey J, Ragauskas AJ, Elder TJ (1999) Investigations into laccase-mediator delignification of kraft pulps. Holzforschung 53:498–502
Silvério FO, Barbosa LCA, Maltha CRA, Fidêncio PH, Cruz MP, Veloso DP, Milanez AF (2008) Effect of storage time on the composition and content of wood extractives in Eucalyptus cultivated in Brazil. Biores Technol 99:4878–4886
Silvestre AJD, Pereira CCL, Pascoal Neto C, Evtuguin DV, Duarte AC, Cavaleiro JAS, Furtado FP (1999) Chemical composition of pitch deposits from ECF Eucalyptus globulus bleached kraft pulp mill: Its relationship with wood extractives and additives in process streams. Appita J 52:375–382
Su Y, Wang EI, Farrell R, Ho C-I, Chang H-M (2004) Screening of fungi for removal of wood extractives. Proc 58th Appita Ann Conf Exhibit, Canberra, 19-24 April 27-34
van Beek TA, Kuster B, Claassen FW, Tienvieri T, Bertaud F, Lenon G, Petit-Conil M, Sierra-Alvarez R (2007) Fungal bio-treatment of spruce wood with Trametes versicolor for pitch control: Influence on extractive contents, pulping process parameters, paper quality and effluent toxicity. Bioresource Technol 98:302–311
Widsten P, Kandelbauer A (2008) Laccase application in the forest processing industries: a review. Enzyme Microb Technol 42:293–307
Zhang X, Stebbing DW, Saddler JN, Beatson RP, Kruus K (2000) Enzyme treatments of the dissolved and colloidal substances present in mill white water and the effects on the resulting paper properties. J Wood Chem Technol 20:321–335
Zhang X, Eigendorf G, Stebbing DW, Mansfield SD, Saddler JN (2002) Degradation of trilinolein by laccase enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys 405:44–54
Zhang X, Renaud S, Paice M (2005) The potential of laccase to remove extractives present in pulp and white water from TMP newsprint mills. J Pulp Paper Sci 31:175–180
Zhang X, Nguyen D, Paice MG, Tsang A, Renaud S (2007) Degradation of wood extractives in thermo-mechanical pulp by soybean lipoxygenase. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:866–873
Zimmerman WC, Blanchette RA, Burnes TA, Farrell RL (1995) Melanin and perithecial development in Ophiostoma piliferum. Mycologia 87:857–863
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish projects AGL2008-00709, BIO2005-03569 and BIO2008-01533, and the BIORENEW project of the European Union (contract NMP2-CT-2006-026456).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez, A., del Río, J.C. & Martínez, A.T. Microbial and enzymatic control of pitch in the pulp and paper industry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82, 1005–1018 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1905-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1905-z