Abstract
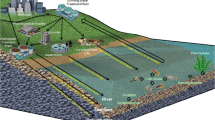
The estrogens estrone (E1), 17α-estradiol (E2α), 17β-estradiol (E2β), and estriol (E3) are natural sex hormones produced by humans and animals. In addition, there are some synthetic estrogens, such as 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2), used for contraception purposes. These compounds are able to produce endocrine disruption in living organisms at nanogram-per-liter levels. In both humans and animals, estrogens are excreted in urine and feces, reaching the natural environment through discharge from sewage treatment plants (STP) and manure disposal units. In STPs, hormone removal depends on the type of treatment process and on different parameters such as the hydraulic and sludge retention times. Thus, hormone elimination rates vary from 0% to 90% in different STPs. Animals are also an important source of estrogens in the environment. Indeed, animals produce high concentrations of hormones which will end up in manure which is typically spread on land. Hence, waste-borne animal hormones may transfer these pollutants to the soil. The purpose of this review is to highlight the significance for both health and the environment of pollution by estrogens and critically review the existing knowledge on their fate and removal in different treatment processes. Relevant information on the microbial degradation of hormones and metabolic pathways is also included.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler P, Steger-Hartmann T, Kalbfus W (2001) Distribution of natural and synthetic estrogenic steroid hormones in water samples from Southern and Middle Germany. Act Hydrochim Hydrobiol 29:227–241
Aerni HR, Kobler B, Rutishauser BV, Wettstein FE, Fischer R, Giger W, Hungerbuhler A, Marazuela MD, Peter A, Schonenberger R, Vogeli AC, Suter MJF, Eggen RIL (2004) Combined biological and chemical assessment of estrogenic activities in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:688–696
Andersen HR, Andersson AM, Arnold SF, Autrup H, Barfoed M, Beresford NA, Bjerregaard P, Christiansen LB, Gissel B, Hummel R, Jorgensen EB, Korsgaard B, Le Guevel R, Leffers H, McLachlan J, Moller A, Nielsen JB, Olea N, Oles-Karasko A, Pakdel F, Pedersen KL, Perez P, Skakkeboek NE, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM, Sumpter JP, Thorpe SM, Grandjean P (1999) Comparison of short-term estrogenicity tests for identification of hormone-disrupting chemicals. Environ Health Perspect 107:89–108
Andersen H, Siegrist H, Halling-Sorensen B, Ternes TA (2003a) Fate of estrogens in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 37:4021–4026
Andersen L, Holbech H, Gessbo A, Norrgren L, Petersen GI (2003b) Effects of exposure to 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol during early development on sexual differentiation and induction of vitellogenin in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Physiol C-Toxicol Pharmacol 134:365–374
Andersen HR, Hansen M, Kjolholt J, Stuer-Lauridsen F, Ternes T, Halling-Sorensen B (2005) Assessment of the importance of sorption for steroid estrogens removal during activated sludge treatment. Chemosphere 61:139–146
Andreolini F, Borra C, Caccamo F, Dicorcia A, Samperi R (1987) Estrogen conjugates in late-pregnancy fluids—extraction and group separation by a graphitized carbon-black cartridge and quantification by high-performance liquid-chromatography. Anal Chem 59:1720–1725
Atienzar FA, Billinghurst Z, Depledge MH (2002) 4-n-Nonylphenol and 17-beta estradiol may induce common DNA effects in developing barnacle larvae. Environ Poll 120:735–738
Balaguer P, Francois F, Comunale F, Fenet H, Boussioux AM, Pons M, Nicolas JC, Casellas C (1999) Reporter cell lines to study the estrogenic effects of xenoestrogens. Sci Total Environ 233:47–56
Baronti C, Curini R, D'Ascenzo G, Di Corcia A, Gentili A, Samperi R (2000) Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environ Sci Technol 34:5059–5066
Belfroid AC, Van des Horst A, Vethaak AD, Schäfer AJ, Rijs GBJ, Wegener J, Cofino WP (1999) Analysis and occurrence of estrogenic hormones and their glucuronides in surface water and waste water in The Netherlands. Sci Total Environ 225:101–108
Billinghurst Z, Clare AS, Matsumura K, Depledge MH (2000) Induction of cypris major protein in barnacle larvae by exposure to 4-n-nonylphenol and 17 beta-oestradiol. Aquat Toxicol 47:203–212
Bovee TFH, Helsdingen RJR, Rietjens I, Keijer J, Hoogenboom R (2004) Rapid yeast estrogen bioassays stably expressing human estrogen receptors alpha and beta, and green fluorescent protein: a comparison of different compounds with both receptor types. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 91:99–109
Bradford SA, Segal E, Zheng W, Wang QQ, Hutchins SR (2008) Reuse of concentrated animal feeding operation wastewater on agricultural lands. J Environ Qual 37:S97–S115
Braga O, Smythe GA, Schafer AI, Feitz AJ (2005a) Fate of steroid estrogens in Australian inland and coastal wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 39:3351–3358
Braga O, Smythe GA, Schafer AI, Feltz AJ (2005b) Steroid estrogens in primary and tertiary wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci Technol 52:273–278
Brody JG, Rudel RA (2003) Environmental pollutants and breast cancer. Environ Health Perspect 111:1007–1019
Burnison BK, Hartmann A, Lister A, Servos MR, Ternes T, Van Der Kraak G (2003) A toxicity identification evaluation approach to studying estrogenic substances in hog manure and agricultural runoff. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2243–2250
Burton CH, Turner C (2003) Manure management, treatment strategies for sustainable agriculture. Silsoe Research Institute, Bedford
Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM, Llompart M, Garcia-Jares C, Rodriguez I, Gomez M, Ternes T (2004) Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Res 38:2918–2926
Carballa M, Omil F, Alder AC, Lema JM (2006) Comparison between the conventional anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and its combination with a chemical or thermal pre-treatment concerning the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Water Sci Technol 53:109–117
Cargouet M, Perdiz D, Mouatassim-Souali A, Tamisier-Karolak S, Levi Y (2004) Assessment of river contamination by estrogenic compounds in Paris area (France). Sci Total Environ 324:55–66
Clara M, Kreuzinger N, Strenn B, Gans O, Kroiss H (2005) The solids retention time: a suitable design parameter to evaluate the capacity of wastewater treatment plants to remove micropollutants. Water Res 39:97–106
Czajka CP, Londry KL (2006) Anaerobic biotransformation of estrogens. Sci Total Environ 367:932–941
D'Ascenzo G, Di Corcia A, Gentili A, Mancini R, Mastropasqua R, Nazzari M, Samperi R (2003) Fate of natural estrogen conjugates in municipal sewage transport and treatment facilities. Sci Total Environ 302:199–209
Daston GP, Cook JC, Kavlock RJ (2003) Uncertainties for endocrine disrupters: our view on progress. Toxicol Sci 74:245–252
de Mes T, Zeeman G, Lettinga G (2005) Occurrence and fate of estrone, 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol in STPs for domestic wastewater. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol 4:275–311
de Mes T, Kujawa-Roeleveld K, Zeeman G, Lettinga G (2008) Anaerobic biodegradation of estrogens—hard to digest. Water Sci Technol 57:1177–1182
Della Greca M, Pinto G, Pistillo P, Pollio A, Previtera L, Temussi F (2008) Biotransformation of ethinylestradiol by microalgae. Chemosphere 70:2047–2053
Desbrow C, Routledge EJ, Brighty GC, Sumpter JP, Waldock M (1998) Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environ Sci Technol 32:1549–1558
Dray J, Dray F, Tiller F, Ulman A (1972) Hydrolysis of urine metabolites of different steroid hormones by β-glucuronidase of Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur 123:853–857
Duong CN, Schlenk D, Chang NI, Kim SD (2009) The effect of particle size on the bioavailability of estrogenic chemicals from sediments. Chemosphere 76:395–401
Dytczak MA, Londry KL, Oleszkiewicz JA (2008) Biotransformation of estrogens in nitrifying activated sludge under aerobic and alternating anoxic/aerobic conditions. Water Environ Res 80:47–52
Ermawati R, Morimura S, Tang YQ, Liu K, Kida K (2007) Degradation and behavior of natural steroid hormones in cow manure waste during biological treatments and ozone oxidation. J Biosci and Bioeng 103:27–31
Fahrbach M, Kuever J, Meinke R, Kampfer P, Hollender J (2006) Denitratisoma oestradiolicum gen. nov., sp nov., a 17 beta-oestradiol-degrading, denitrifying betaproteobacterium. Int J System Evol Microbiol 56:1547–1552
Fahrbach M, Kuever J, Remesch M, Huber BE, Kampfer P, Dott W, Hollender J (2008) Steroidobacter denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov., a steroidal hormone-degrading gammaproteobacterium. J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2215–2223
Fernandez MP, Noguerol TN, Lacorte S, Buchanan I, Pina B (2009) Toxicity identification fractionation of environmental estrogens in waste water and sludge using gas and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry and recombinant yeast assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:957–968
Fine DD, Breidenbach GP, Price TL, Hutchins SR (2003) Quantitation of estrogens in ground water and swine lagoon samples using solid-phase extraction, pentafluorobenzyl/trimethylsilyl derivatizations and gas chromatography-negative ion chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1017:167–185
Fujii K, Kikuchi S, Satomi M, Ushio-Sata N, Morita N (2002) Degradation of 17β-estradiol by a gram-negative bacterium isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan. App Environ Microbiol 68:2057–2060
Furuichi T, Kannan K, Suzuki K, Tanaka S, Giesy JP, Masunaga S (2006) Occurrence of estrogenic compounds in and removal by a swine farm waste treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 40:7896–7902
Gabet-Giraud V, Miege C, Herbreteau B, Hernandez-Raquet G, Coquery M (2010) Development and validation of an analytical method by LC-MSMS for the quantification of estrogens in sewage sludge. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:1841–1851. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-3428-y
Gaulke LS, Strand SE, Kalhorn TF, Stensel HD (2008) 17alpha-Ethinylestradiol transformation via abiotic nitration in the presence of ammonia oxidizing bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42:7622–7627
Geuns JMC (1978) Steroid-hormones and plant-growth and development. Phytochemistry 17:1–14
Gomes RL, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2009) Fate of conjugated natural and synthetic steroid estrogens in crude sewage and activated sludge batch studies. Environ Sci Technol 43:3612–3618
Haiyan R, Shulan J, Dao W, Ahmad N (2007) Degradation characteristics and metabolic pathway of 17α-ethynylestradiol by Sphingobacterium sp. JCR5. Chemosphere 66:340–346
Hanselman TA, Graetz DA, Wilkie AC (2003) Manure-borne estrogens as potential environmental contaminants: a review. Environ Sci Technol 37:5471–5478
Hanselman TA, Graetz DA, Wilkie AC, Szabo NJ, Diaz CS (2006) Determination of steroidal estrogens in flushed dairy manure wastewater by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Environ Qual 35:695–700
Hemmings SNJ, Hartel PG (2006) Mineralization of hormones in breeder and broiler litters at different water potentials and temperatures. J Environ Qual 35:701–706
Holbrook RD, Novak JT, Grizzard TJ, Love NG (2002) Estrogen receptor agonist fate during wastewater and biosolids treatment processes: a mass balance analysis. Environ Sci Technol 36:4533–4539
Holbrook RD, Love NG, Novak JT (2004) Sorption of 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol by colloidal organic carbon derived from biological wastewater treatment systems. Environ Sci Technol 38:3322–3329
Hutchins SR, White MV, Hudson FM, Fine DD (2007) Analysis of lagoon samples from different concentrated animal feeding operations for estrogens and estrogen conjugates. Environ Sci Technol 41:738–744
Ivanov V, Lim JJW, Stabnikova O, Gin KYH (2010) Biodegradation of estrogens by facultative anaerobic iron-reducing bacteria. Process Biochem 45:284–287
Ivashechkin P, Corvini PFX, Dohmann M (2004) Behaviour of endocrine disrupting chemicals during the treatment of municipal sewage sludge. Water Sci Technol 50:133–140
Jarvenpaa P, Kosunen T, Fotsis T, Adlercreutz H (1980) In vitro metabolism of estrogens by isolated intestinal microorganisms and by human fecal microflora. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 13:345–349
Jiang L, Yang J, Chen J (2010) Isolation and characteristics of 17 β-estradiol-degrading Bacillus spp. strains from activated sludge. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-010-9338-z
Jobling S, Casey D, Rodgers-Gray T, Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Pawlowski S, Baunbeck T, Turner AP, Tyler CR (2003) Comparative responses of molluscs and fish to environmental estrogens and an estrogenic effluent. Aquat Toxicol 65:205–220
Johnson AC, Sumpter JP (2001) Removal of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in activated sludge treatment works. Environ Sci Technol 35:4697–4703
Johnson AC, Williams RJ (2004) A model to estimate influent and effluent concentrations of estradiol, estrone, and ethinylestradiol at sewage treatment works. Environ Sci Technol 38:3649–3658
Johnson AC, Belfroid A, Di Corcia A (2000) Estimating steroid oestrogen inputs into activated sludge treatment works and observations on their removal from the effluent. Sci Total Environ 256:163–173
Johnson AC, Aerni HR, Gerritsen A, Gibert M, Giger W, Hylland K, Jurgens M, Nakari T, Pickering A, Suter MJF, Svenson A, Wettstein FE (2005) Comparing steroid estrogen, and nonylphenol content across a range of European sewage plants with different treatment and management practices. Water Res 39:47–58
Johnson AC, Williams RJ, Simpson P, Kanda R (2007) What difference might sewage treatment performance make to endocrine disruption in rivers? Environ Poll 147:194–202
Jones OAH, Green PG, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2007) Questioning the excessive use of advanced treatment to remove organic micropollutants from wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 41:5085–5089
Joss A, Andersen H, Ternes T, Richle PR, Siegrist H (2004) Removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater treatment under aerobic and anaerobic conditions: consequences for plant optimization. Environ Sci Technol 38:3047–3055
Jurgens MD, Holthaus KIE, Johnson AC, Smith JJL, Hetheridge M, Williams RJ (2002) The potential for estradiol and ethinylestradiol degradation in English rivers. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:480–488
Ke JX, Zhuang WQ, Gin KYH, Reinhard M, Hoon LT, Tay JH (2007) Characterization of estrogen-degrading bacteria isolated from an artificial sandy aquifer with ultrafiltered secondary effluent as the medium. App Microbiol Biotechnol 75:1163–1171
Koh YKK, Chiu TY, Boobis AR, Scrimshaw MD, Bagnall JP, Soares A, Pollard S, Cartmell E, Lester JN (2009) Influence of operating parameters on the biodegradation of steroid estrogens and nonylphenolic compounds during biological wastewater treatment processes. Environ Sci Technol 43:6646–6654
Körner W, Bolz U, Sussmuth W, Hiller G, Schuller W, Hanf V, Hagenmaier H (2000) Input/output balance of estrogenic active compounds in a major municipal sewage plant in Germany. Chemosphere 40:1131–1142
Kuster M, Lopez MJ, de Alda MJL, Barcelo D (2004) Analysis and distribution of estrogens and progestogens in sewage sludge, soils and sediments. Trends Anal Chem 23:790–798
Lai KM, Johnson KL, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2000) Binding of waterborne steroid estrogens to solid phases in river and estuarine systems. Environ Sci Technol 34:3890–3894
Lai KM, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2002) Biotransformation and bioconcentration of steroid estrogens by Chlorella vulgaris. App Environ Microbiol 68:859–864
Lange R, Hutchinson TH, Croudace CP, Siegmund F, Schweinfurth H, Hampe P, Panter GH, Sumpter JP (2001) Effects of the synthetic estrogen 17α-ethinylestradiol on the life-cycle of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1216–1227
Lange IG, Daxenberger A, Schiffer B, Witters H, Ibarreta D, Meyer HHD (2002) Sex hormones originating from different livestock production systems: fate and potential disrupting activity in the environment. Anal Chim Acta 473:27–37
Layton AC, Gregory BW, Seward JR, Schultz TW, Sayler GS (2000) Mineralization of steroidal hormones by biosolids in wastewater treatment systems in Tennessee U.S.A. Environ Sci Technol 34:3925–3931
Lee HB, Liu D (2002) Degradation of 17β-estradiol and its metabolites by sewage bacteria. Water Air Soil Poll 134:353–368
Lee HB, Peart TE, Chan J, Gris G (2004) Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in sewage and sludge samples in Toronto, Canada. Water Qual Res J Can 39:57–63
Leusch FDL, Chapman HF, van den Heuvel MR, Tan BLL, Gooneratne SR, Tremblay LA (2006) Bioassay-derived androgenic and estrogenic activity in municipal sewage in Australia and New Zealand. Ecotox Environ Saf 65:403–411
Liu ZH, Kanjo Y, Mizutani S (2009) Removal mechanisms for endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in wastewater treatment—physical means, biodegradation, and chemical advanced oxidation: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:731–748
Lorenzen A, Hendel JG, Conn KL, Bittman S, Kwabiah AB, Lazarovitz G, Masse D, McAllister TA, Topp E (2004) Survey of hormone activities in municipal biosolids and animal manures. Environ Toxicol 19:216–225
Matsui S, Takigami H, Matsuda T, Taniguchi N, Adachi J, Kawami H, Shimizu Y (2000) Estrogen and estrogen mimics contamination in water and the role of sewage treatment. Water Sci Technol 42:173–179
Muller M, Rabenoelina F, Balaguer P, Patureau D, Lemenach K, Budzinski H, Barcelo D, De Alda ML, Kuster M, Delgenes JP, Hernandez-Raquet G (2008) Chemical and biological analysis of endocrine-disrupting hormones and estrogenic activity in an advanced sewage treatment plant. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1649–1658
Muller M, Patureau D, Godon JJ, Delgenes JP, Hernandez-Raquet G (2010) Molecular and kinetics characterisation of mixed cultures degrading natural and synthetic estrogens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:691–701
Murkies AL, Wilcox G, Davis SR (1998) Clinical review 92—phytoestrogens. J Clin Endocrin Metabol 83:297–303
Nakada N, Tanishima T, Shinohara H, Kiri K, Takada H (2006) Pharmaceutical chemicals and endocrine disrupters in municipal wastewater in Tokyo and their removal during activated sludge treatment. Water Res 40:3297–3303
Nash JP, Kime DE, Van der Ven LTM, Wester PW, Brion F, Maack G, Stahlschmidt-Allner P, Tyler CR (2004) Long-term exposure to environmental concentrations of the pharmaceutical ethynylestradiol causes reproductive failure in fish. Environ Health Perspect 112:1725–1733
Nieto A, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Marce RM (2008) Determination of natural and synthetic estrogens and their conjugates in sewage sludge by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1213:224–230
Panter GH, Thompson RS, Beresford N, Sumpter JP (1999) Transformation of a non-oestrogenic steroid metabolite to an oestrogenically active substance by minimal bacterial activity. Chemosphere 38:3579–3596
Pauwels B, Wille K, Noppe H, De Brabander H, van de Wiele T, Verstraete W, Boon N (2008) 17 alpha-Ethinylestradiol cometabolism by bacteria degrading estrone, 17β-estradiol and estriol. Biodegradation 19:683–693
Payne DW, Talalay P (1985) Isolation of novel microbial 3α-, 3β-, and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Purification, characterisation, and analytical applications of a 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Algaligenes sp. J Biol Chem 260:13648–13655
Pillon A, Servant N, Vignon F, Balaguer P, Nicolas JC (2005) In vivo bioluminescence imaging to evaluate estrogenic activities of endocrine disrupters. Anal Biochem 340:295–302
Raman DR, Layton AC, Moody LB, Easter JP, Sayler GS, Burns RT, Mullen MD (2001) Degradation of estrogens in dairy waste solids: effects of acidification and temperature. Trans ASAE 44:1881–1888
Raman DR, Williams EL, Layton AC, Burns RT, Easter JP, Daugherty AS, Mullen MD, Sayler GS (2004) Estrogen content of dairy and swine wastes. Environ Sci Technol 38:3567–3573
Sandor T, Mehdi AZ (1979) Steroids and evolution. In: Barrington EJW (ed) Hormones and evolution. Academic, New York, pp 1–72
Sarmah AK, Northcott GL, Leusch FDL, Tremblay LA (2006) A survey of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in municipal sewage and animal waste effluents in the Waikato region of New Zealand. Sci Total Environ 355:135–144
Scholz S, Gutzeit HO (2000) 17alpha-Ethinylestradiol affects reproduction, sexual differentiation and aromatase gene expression of the medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 50:363–373
Servos MR, Bennie DT, Burnison BK, Jurkovic A, McInnis R, Neheli T, Schnell A, Seto P, Smyth SA, Ternes TA (2005) Distribution of estrogens, 17β-estradiol and estrone, in Canadian municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 336:155–170
Shappell NW, Billey LO, Forbes D, Matheny TA, Poach ME, Reddy GB, Hunt PG (2007) Estrogenic activity and steroid hormones in swine wastewater through a lagoon constructed-wetland system. Environ Sci Technol 41:444–450
Sharpe RM, Irvine DS (2004) How strong is the evidence of a link between environmental chemicals and adverse effects on human reproductive health? British Med J 328:447–451
Shi JH, Suzuki Y, Lee BD, Nakai S, Hosomi M (2002) Isolation and characterization of the ethynylestradiol-biodegrading microorganism Fusarium proliferatum strain HNS-1. Water Sci Technol 45:175–179
Shi J, Fujisawa S, Nakai S, Hosomi M (2004) Biodegradation of natural and synthetic estrogens by nitrifying activated sludge and ammonia-oxidising bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Water Res 38:2323–2330
Shore LS, Shemesh M (2003) Naturally produced steroid hormones and their release into the environment. Pure Appl Chem 75:1859–1871
Shore LS, Kapulnik Y, Ben-Dor B, Fridman Y, Wininger S, Shemesh M (1992) Effects of estrone and 17β-estradiol on vegetative growth of Medicago sativa. Physiol Plantarum 84:217–222
Shore LS, Kapulnik Y, Gurevich M, Wininger S, Badamy H, Shemesh M (1995) Induction of phytoestrogen production in Medicago sativa leaves by irrigation with sewage water. Environ Experiment Botany 35:363–369
Snyder SA, Villeneuve DL, Snyder EM, Giesy JP (2001) Identification and quantification of estrogen receptor agonists in wastewater effluents. Environ Sci Technol 35:3620–3625
Song H, Nakano K, Taniguchi T, Nomura M, Nishimura O (2009) Estrogen removal from treated municipal effluent in small-scale constructed wetland with different depth. Bioresource Technol 100:2945–2951
Stuer-Lauridsen F, Kjolholt J (2000) Identification of selected hydrophobic organic contaminants in wastewater with semipermeable membrane devices (SPMDS). Water Res 34:3478–3482
Sumpter JP (1998) Reproductive effects from oestrogen activity in polluted water. Arch Toxicol Suppl 20:143–150
Sun WL, Ni JR, Xu N, Sun LY (2007) Fluorescence of sediment humic substance and its effect on the sorption of selected endocrine disruptors. Chemosphere 66:700–707
Suzuki Y, Kubota A, Furukawa T, Sugamoto K, Asano Y, Takahashi H, Sekito T, Dote Y, Sugimoto Y (2009) Residual of 17 β-estradiol in digestion liquid generated from a biogas plant using livestock waste. J Hazard Mat 165:677–682
Svenson A, Allard AS, Ek M (2003) Removal of estrogenicity in Swedish municipal sewage treatment plants. Water Res 37:4433–4443
Ternes TA, Kreckel P, Mueller J (1999) Behaviour and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants—II. Aerobic batch experiments with activated sludge. Sci Total Environ 225:91–99
Ternes TA, Andersen H, Gilberg D, Bonerz M (2002) Determination of estrogens in sludge and sediments by liquid extraction and GC/MS/MS. Anal Chem 74:3498–3504
Vader JS, Ginkel CG, Sperling FMGM, Jong J, Boer W, Graaf JS, Most M, Stokman PGW (2000) Degradation of ethinylestradiol by nitrifying activated sludge. Chemosphere 41:1239–1243
Watts MM, Pascoe D, Carroll K (2002) Population responses of the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex (L.) to an environmental estrogen, 17 α-ethinylestradiol. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:445–450
Webb S, Ternes T, Gibert M, Olejniczak K (2003) Indirect human exposure to pharmaceuticals via drinking water. Toxicol Lett 142:157–167
Weber S, Leuschner P, Kampfer P, Dott W, Hollender J (2005) Degradation of estradiol and ethinylestradiol by activated sludge and by a defined mixed culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:106–112
Weber S, Khan S, Hollender J (2006) Human risk assessment of organic contaminants in reclaimed wastewater used for irrigation. Desalination 187:53–64
Wiart J, Duvaud E, Mugnier E, Gazzo A, Aubain P (1999) Disposal and recycling of sewage sludge in Europe and other countries. ADEME, France
Williams EL (2002) Survey of estrogens concentrations in dairy and swine waste holding and treatment structures in and around Tennessee. M.S thesis, University of Tennessee, Knoxville
Xu N, Johnson AC, Jürgens MD, Llewellyn NR, Hankins NP, Darton RC (2009) Estrogen concentration affects its biodegradation rate in activated sludge. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2263–2270
Yang W, Cicek N (2008) Treatment of swine wastewater by submerged membrane bioreactors with consideration of estrogenic activity removal. Desalination 231:200–208
Yi T, Harper WF Jr (2007) The effect of biomass characteristics on the partitioning and sorption hysteresis of 17 α-ethinylestradiol. Water Res 41:1543–1553
Ying GG, Kookana RS (2003) Degradation of five selected endocrine-disrupting chemicals in seawater and marine sediment. Environ Sci Technol 37:1256–1260
Yoshimoto T, Nagai F, Fujimoto J, Watanabe K, Mizukoshi H, Makino T, Kimura K, Saino H, Sawada H, Omura H (2004) Degradation of estrogens by Rhodococcus zopfii and Rhodococcus equi isolates from activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5283–5289
Yu ZQ, Huang WL (2005) Competitive sorption between 17α-ethinylestradiol and naphthalene/phenanthrene by sediments. Environ Sci Technol 39:4878–4885
Yu CP, Roh H, Chu KH (2007) 17 beta-Estradiol-degrading bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Environ Sci Technol 41:486–492
Zeng QL, Li YM, Gu GW, Zhao JM, Zhang CJ, Luan JF (2009) Sorption and biodegradation of 17β-estradiol by acclimated aerobic activated sludge and isolation of the bacterial strain. Environ Engineer Sci 26:783–790
Zheng W, Yates SR, Bradford SA (2008) Analysis of steroid hormones in a typical airy waste disposal system. Environ Sci Technol 42:530–535
Zhou JL, Liu R, Wilding A, Hibberd A (2007) Sorption of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals to different aquatic colloids. Environ Sci Technol 41:206–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Combalbert, S., Hernandez-Raquet, G. Occurrence, fate, and biodegradation of estrogens in sewage and manure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1671–1692 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2547-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2547-x