Abstract
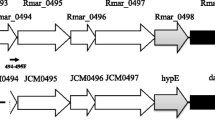
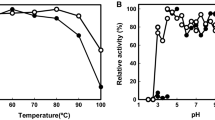
The activity of a dye-linked l-proline dehydrogenase (dye-l-proDH) was found in the crude extract of an aerobic hyperthermophilic archaeon, Pyrobaculum calidifontis JCM 11548, and was purified 163-fold through four sequential chromatography steps. The enzyme has a molecular mass of about 108 kDa and is a homodimer with a subunit molecular mass of about 46 kDa. The enzyme retained more than 90% of its activity after incubation at 100 °C for 120 min (pH 7.5) or after incubation at pHs 4.5–9.0 for 30 min at 50 °C. The enzyme catalyzed l-proline dehydrogenation to Δ1-pyroline-5-carboxylate using 2,6-dichloroindophenol (DCIP) as the electron acceptor and the Michaelis constants for l-proline and DCIP were 1.67 and 0.026 mM, respectively. The prosthetic group on the enzyme was identified as flavin adenine dinucleotide by high-performance liquid chromatography. The subunit N-terminal amino acid sequence was MYDYVVVGAG. Using that sequence and previously reported genome information, the gene encoding the enzyme (Pcal_1655) was identified. The gene was then cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli and found to encode a polypeptide of 415 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 46,259. The dye-l-proDH gene cluster in P. calidifontis inherently differs from those in the other hyperthermophiles reported so far.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Amo T, Paje ML, Inagaki A, Ezaki S, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2002) Pyrobaculum calidifontis sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic archaeon that grows in atmospheric air. Archaea 1:113–121
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis—2. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann NY Acad Sci 121:404–427
Frew JE, Hill HA (1987) Electrochemical biosensors. Anal Chem 59:933A–944A
Kawakami R, Sakuraba H, Ohshima T (2004) Gene and primary structures of dye-linked L-proline dehydrogenase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus profundus show the presence of a novel heterotetrameric amino acid dehydrogenase complex. Extremophiles 8:99–108
Kawakami R, Sakuraba H, Ohshima T (2005) A second novel dye-linked L-proline dehydrogenase complex is present in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii OT-3. FEBS J 272:4044–4054
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the bacteriophase T4. Nature 227:680–685
Meister A (1954) The alpha-keto analogues of arginine, ornithine, and lysine. J Biol Chem 206:577–585
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Ohshima T, Ishida M (1992) A large-scale preparative electrophoretic method for the purification of pyridine nucleotide-linked dehydrogenases. Protein Expr Purif 3:121–125
Ohshima T, Tanaka S (1993) Dye-linked L-malate dehydrogenase from thermophilic Bacillus species DSM 465, purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem 214:37–42
Sakuraba H, Takamatsu Y, Satomura T, Kawakami R, Ohshima T (2001) Purification, characterization, and application of a novel dye-linked L-proline dehydrogenase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon, Thermococcus profundus. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1470–1475
Satomura T, Kawakami R, Sakuraba H, Ohshima T (2002) Dye-linked D-proline dehydrogenase from hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrobaculum islandicum is a novel FAD-dependent amino acid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 277:12861–12867
Satomura T, Kawakami R, Sakuraba H, Ohshima T (2008) A novel flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) containing D-lactate dehydrogenase from the thermoacidophilic crenarchaeota Sulfolobus tokodaii strain 7: purification, characterization and expression in Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 106:16–21
Tani Y, Tanaka K, Yabutani T, Mishima Y, Sakuraba H, Ohshima T, Motonaka J (2008) Development of a D-amino acids electrochemical sensor based on immobilization of thermostable D-proline dehydrogenase within agar gel membrane. Anal Chim Acta 619:215–220
Tani Y, Itoyama Y, Nishi K, Wada C, Shoda Y, Satomura T, Sakuraba H, Ohshima T, Hayashi Y, Yabutani T, Motonaka J (2009) An amperometric D-amino acid biosensor prepared with the a thermostable D-proline dehydrogenase and carbon nanotube-ionic liquid gel. Anal Sci 25:919–923
Trickey P, Wagner MA, Jorns MS, Mathews FS (1999) Monomeric sarcosine oxidase: structure of a covalently flavinylated amine oxidizing enzyme. Structure 7:331–345
Tuge H, Kawakami R, Sakuraba H, Ago H, Miyano M, Aki K, Katunuma N, Ohshima T (2005) Crystal structure of a novel FAD-, FMN-, and ATP-containing L-proline dehydrogenase complex from Pyrococcus horikoshii. J Biol Chem 280:31045–31049
Zheng H, Hirose Y, Kimura T, Hori T, Suye S, Katayama H, Arai H, Kawakami R, Ohshima T (2006) L-Proline sensor based on layer-by-layer immobilization of thermostable dye-linked L-proline dehydrogenase and polymerized mediator. Sci Technol Adv Mater 7:243–248
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (no. 18380060) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Japan Foundation of Applied Enzymology and by a grant from the Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Satomura and X.-D. Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satomura, T., Zhang, XD., Hara, Y. et al. Characterization of a novel dye-linked l-proline dehydrogenase from an aerobic hyperthermophilic archaeon, Pyrobaculum calidifontis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 1075–1082 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2914-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2914-7