Abstract
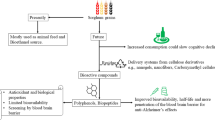
Alzheimer's disease is seen mainly in individuals over the age of 65, and the morbidity rate increases with age. Regarding the health function of Monascus-fermented red mold rice (RMR), besides hypolipidemic and hypotensive effects, other health functions of RMR such as anti-oxidation, cancer prevention, anti-fatigue, and anti-obesity have also been reported. Many published studies have shown the efficacy of RMR in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease. The current article discusses and provides evidence to support the beneficial potential of RMR in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease by discussing the pathogenic factors of Alzheimer's disease and the secondary metabolites of Monascus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akihisa T, Mafune S, Ukiya M, Kimura Y, Yasukawa K, Suzuki T, Tokuda H, Tanabe N, Fukuoka T (2004) (+)- and (−)-syn-2-isobutyl-4-methylazetidine −2,4-dicarboxylic acids from the extract of Monascus pilosus-fermented rice (red-mold rice). J Nat Prod 67:479–480
Akihisa T, Tokuda H, Yasukawa K, Ukiya M, Kiyota A, Sakamoto N, Suzuki T, Tanabe N, Nishino H (2005) Azaphilones, furanoisophthalides, and amino acids from the extracts of Monascus pilosus-fermented rice (red-mold rice) and their chemopreventive effects. J Agric Food Chem 53:562–565
Andrews-Zwilling Y, Bien-Ly N, Xu Q, Li G, Bernardo A, Yoon SY, Zwilling D, Yan TX, Chen L, Huang Y (2010) Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and tau-dependent impairment of GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice. J Neurosci 30:13707–13717
Aniya Y, Ohtani II, Higa T, Miyagi C, Gibo H, Shimabukuro M, Nakanishi H, Taira J (2000) Dimerumic acid as an antioxidant of the mold, Monascus anka. Free Radic Biol Med 28:999–1004
Araki W, Kitaguchi N, Tokushima Y, Ishii Y, Aratake K, Shimohama H, Nakamura S, Kimura J (1991) Trophic effect of beta-amyloid precursor protein on cerebral cortical neurons in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:265–271
Buxbaum JD, Thinakaran G, Koliatsos V, O'Callahan J, Slunt HH, Price DL, Sisodia SS (1998) Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor in the rat hippocampus: transport and processing through the perforant path. J Neurosci 18:9629–9637
Checler F (1995) Processing of the beta-amyloid precursor protein and its regulation in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 65:1431–1444
Combs CK, Johnson DE, Karlo JC, Cannady SB, Landreth GE (2000) Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease: inhibition of beta-amyloid-stimulated proinflammatory responses and neurotoxicity by PPARgamma agonists. J Neurosci 20:558–567
Cordle A, Koenigsknecht-Talboo J, Wilkinson B, Limpert A, Landreth G (2005) Mechanisms of statin-mediated inhibition of small G-protein function. J Biol Chem 280:34202–34209
Cordle A, Landreth G (2005) 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors attenuate beta-amyloid-induced microglial inflammatory responses. J Neurosci 25:299–307
Crisby M, Carlson LA, Winblad B (2002) Statins in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 16:131–136
Endo A (1979) Monacolin K, a new hypocholesterolemic agent produced by a Monascus species. The Journal of Antibiot (Tokyo) 32:852–854
Esposito G, De Filippis D, Maiuri MC, De Stefano D, Carnuccio R, Iuvone T (2006) Cannabidiol inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase protein expression and nitric oxide production in beta-amyloid stimulated PC12 neurons through p38 MAP kinase and NF-kappaB involvement. Neurosci Lett 399:91–95
Fassbender K, Stroick M, Bertsch T, Ragoschke A, Kuehl S, Walter S, Walter J, Brechtel K, Muehlhauser F, Von Bergmann K, Lutjohann D (2002) Effects of statins on human cerebral cholesterol metabolism and secretion of Alzheimer amyloid peptide. Neurology 59:1257–1258
Frears ER, Stephens DJ, Walters CE, Davies H, Austen BM (1999) The role of cholesterol in the biosynthesis of beta-amyloid. Neuroreport 10:1699–1705
Freund-Levi Y, Eriksdotter-Jonhagen M, Cederholm T, Basun H, Faxen-Irving G, Garlind A, Vedin I, Vessby B, Wahlund LO, Palmblad J (2006) Omega-3 fatty acid treatment in 174 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: OmegAD study: a randomized double-blind trial. Arch Neurol 63:1402–1408
Ghribi O, Larsen B, Schrag M, Herman MM (2006) High cholesterol content in neurons increases BACE, beta-amyloid, and phosphorylated tau levels in rabbit hippocampus. Exp Neurol 200:460–467
Giacobini E, Mori F, Lai CC (1996) The effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on the secretion of APPS from rat brain cortex. Ann N Y Acad Sci 777:393–398
Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Agdul H, Shido O (2005) Docosahexaenoic acid-induced amelioration on impairment of memory learning in amyloid beta-infused rats relates to the decreases of amyloid beta and cholesterol levels in detergent-insoluble membrane fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1738:91–98
Hauss-Wegrzyniak B, Dobrzanski P, Stoehr JD, Wenk GL (1998) Chronic neuroinflammation in rats reproduces components of the neurobiology of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 780:294–303
Jick H, Zornberg GL, Jick SS, Seshadri S, Drachman DA (2000) Statins and the risk of dementia. Lancet 356:1627–1631
Juzlova PM, Martinkova L, Kren V (1996) Secondary metabolites of the fungus Monascus: a review. J Ind Microbiol 16:163–170
Kirsch C, Eckert GP, Mueller WE (2003) Statin effects on cholesterol micro-domains in brain plasma membranes. Biochem Pharmacol 65:843–856
Kuo YM, Emmerling MR, Bisgaier CL, Essenburg AD, Lampert HC, Drumm D, Roher AE (1998) Elevated low-density lipoprotein in Alzheimer's disease correlates with brain abeta 1–42 levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:711–715
Lee CL, Kuo TF, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2007) Red mold rice ameliorates impairment of memory and learning ability in intracerebroventricular amyloid beta-infused rat by repressing amyloid beta accumulation. J Neurosci Res 85:3171–3182
Lee CL, Kuo TF, Wu CL, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2010) Red mold rice promotes neuroprotective sAPPalpha secretion instead of Alzheimer's risk factors and amyloid beta expression in hyperlipidemic Abeta40-infused rats. J Agric Food Chem 58:2230–2238
Lee CL, Tsai TY, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2006a) In vivo hypolipidemic effects and safety of low dosage Monascus powder in a hamster model of hyperlipidemia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:533–540
Lee CL, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2008) Red mold rice extract represses amyloid beta peptide-induced neurotoxicity via potent synergism of anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effect. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:829–841
Lee CL, Wang JJ, Kuo SL, Pan TM (2006b) Monascus fermentation of dioscorea for increasing the production of cholesterol-lowering agent-monacolin K and antiinflammation agent-monascin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:1254–1262
Li L, Cao D, Kim H, Lester R, Fukuchi K (2006) Simvastatin enhances learning and memory independent of amyloid load in mice. Ann Neurol 60:729–739
Liao JK (2002) Isoprenoids as mediators of the biological effects of statins. J Clin Invest 110:285–288
Liao JK, Laufs U (2005) Pleiotropic effects of statins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:89–118
Ma J, Li Y, Ye Q, Li J, Hua Y, Ju D, Zhang D, Cooper R, Chang M (2000) Constituents of red yeast rice, a traditional Chinese food and medicine. J Agric Food Chem 48:5220–5225
Mackenzie IR, Munoz DG (1998) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and Alzheimer-type pathology in aging. Neurology 50:986–990
Morimoto T, Ohsawa I, Takamura C, Ishiguro M, Kohsaka S (1998) Involvement of amyloid precursor protein in functional synapse formation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res 51:185–195
Naidu A, Xu Q, Catalano R, Cordell B (2002) Secretion of apolipoprotein E by brain glia requires protein prenylation and is suppressed by statins. Brain Res 958:100–111
Perez‐Severiano F, Rodriguez‐Perez M, Pedraza‐Chaverri J, Maldonado PD, Medina‐Campos ON, Ortiz‐Plata A, Sanchez‐Garcia A, Villeda‐Hernandez J, Galvan‐Arzate S, Aguilera P, Santamaria A (2004) S‐Allylcysteine, a garlic‐derived antioxidant, ameliorates quinolinic acid‐induced neurotoxicity and oxidative damage in rats. Neurochem Int 45:1175–1183
Poirier J (2003) Apolipoprotein E and cholesterol metabolism in the pathogenesis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Mol Med 9:94–101
Pollen DA, Baker S, Hinerfeld D, Swearer J, Evans BA, Evans JE, Caselli R, Rogaeva E, St George-Hyslop P, Moonis M (2010) Prevention of Alzheimer's disease in high risk groups: statin therapy in subjects with PSEN1 mutations or heterozygosity for apolipoprotein E epsilon 4. Alzheimers Res Ther 2:31
Rockwood K, Kirkland S, Hogan DB, MacKnight C, Merry H, Verreault R, Wolfson C, McDowell I (2002) Use of lipid-lowering agents, indication bias, and the risk of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people. Arch Neurol 59:223–227
Roher AE, Kuo YM (1999) Isolation of amyloid deposits from brain. Methods Enzymol 309:58–67
Sastre M, Klockgether T, Heneka MT (2006) Contribution of inflammatory processes to Alzheimer's disease: molecular mechanisms. Int J Dev Neurosci 24:167–176
Schubert D, Behl C (1993) The expression of amyloid beta protein precursor protects nerve cells from beta-amyloid and glutamate toxicity and alters their interaction with the extracellular matrix. Brain Res 629:275–282
Schubert D, Behl C, Lesley R, Brack A, Dargusch R, Sagara Y, Kimura H (1995) Amyloid peptides are toxic via a common oxidative mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:1989–1993
Small DH, Nurcombe V, Reed G, Clarris H, Moir R, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (1994) A heparin-binding domain in the amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease is involved in the regulation of neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 14:2117–2127
Stewart R (1998) Cardiovascular factors in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65:143–147
Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS, Roses AD (1993) Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1977–1981
Su YC, Wang JJ, Lin TT, Pan TM (2003) Production of the secondary metabolites gamma-amino butyric acid and monacolin K by Monascus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:41–46
Tang F, Nag S, Shiu SY, Pang SF (2002) The effects of melatonin and Ginkgo biloba extract on memory loss and choline acetyltransferase activities in the brain of rats infused intracerebroventricularly with beta-amyloid 1–40. Life Sci 71:2625–2631
Townsend KP, Pratico D (2005) Novel therapeutic opportunities for Alzheimer's disease: focus on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. FASEB J 19:1592–1601
Wang R, Zhang HY, Tang XC (2001) Huperzine A attenuates cognitive dysfunction and neuronal degeneration caused by beta-amyloid protein-(1–40) in rat. Eur J Pharmacol 421:149–156
Wolozin B, Kellman W, Ruosseau P, Celesia GG, Siegel G (2000) Decreased prevalence of Alzheimer disease associated with 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Arch Neurol 57:1439–1443
Wong HC, Bau YS (1977) Pigmentation and antibacterial activity of fast neutron- and x-ray-induced strains of Monascus purpureus Went. Plant Physiol 60:578–581
Yamada K, Ren X, Nabeshima T (1999) Perspectives of pharmacotherapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Jpn J Pharmacol 80:9–14
Yamaguchi Y, Miyashita H, Tsunekawa H, Mouri A, Kim HC, Saito K, Matsuno T, Kawashima S, Nabeshima T (2006) Effects of a novel cognitive enhancer, spiro[imidazo‐[1,2‐a]pyridine‐3,2‐indan]‐2(3H)‐one (ZSET1446), on learning impairments induced by amyloid‐beta1‐40 in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:1079–1087
Zhao B (2005) Natural antioxidants for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 31:283–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CL., Pan, TM. Red mold fermented products and Alzheimer's disease: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91, 461–469 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3413-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3413-1