Abstract
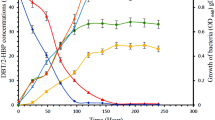
Biodesulfurization is regarded as a promising alternative technology for desulfurization from diesel oil due to its mild operating conditions and its ability to remove sulfur from alky dibenzothiophenes (Cx-DBTs). The diesel oil contains complex mixtures of Cx-DBTs in which individual microbial biodesulfurization may be altered. In this work, interactions among three typical Cx-DBTs such as dibenzothiophenes (DBT), 4-methyldibenzothiophene (4-MDBT), and 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene (4,6-DMDBT) were investigated using Mycobacterium sp. ZD-19 in an airlift reactor. The experimental results indicated that the desulfurization rates would decrease in the multiple Cx-DBTs system compared to the single Cx-DBT system. The extent of inhibition depended upon the substrate numbers, concentrations, and affinities of the co-existing substrates. For example, compared to individual desulfurization rate (100 %), DBT desulfurization rate decreased to 75.2 % (DBT + 4,6-DMDBT), 64.8 % (DBT + 4-MDBT), and 54.7 % (DBT + 4,6-DMDBT + 4-MDBT), respectively. This phenomenon was caused by an apparent competitive inhibition of substrates, which was well predicted by a Michaelis–Menten competitive inhibition model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boltes K, del Aguila RA, Garcia-Calvo E (2007) Biodesulfurization of alkylated forms of dibenzothiophene by Pseudomonas putida CECT5279. J Biotechnol 131:S143–S144
Boltes K, Caro A, Leton P, Rodriguez A, Garcia-Calvo E (2008) Gas–liquid mass transfer in oil–water emulsions with an airlift bio-reactor. Chem Eng Process 47:2408–2412
Chen H, Zhang WJ, Chen JM, Cai YB, Li W (2008a) Desulfurization of various organic sulfur compounds and the mixture of DBT + 4,6-DMDBT by Mycobacterium sp. ZD-19. Bioresour Technol 99:3630–3634
Chen H, Zhang WJ, Cai YB, Zhang Y, Li W (2008b) Elucidation of 2-hydroxybiphenyl effect on dibenzothiophene desulfurization by Microbacterium sp. strain ZD-M2. Bioresour Technol 99:6928–6933
Chen H, Cai YB, Zhang WJ, Li W (2009) Methoxylation pathway in biodesulfurization of model organosulfur compounds with Mycobacterium sp. Bioresour Technol 100:2085–2087
Feng JH, Zeng YY, Ma CQ, Cai XF, Zhang Q, Tong MY, Yu B, Xu P (2006) The surfactant tween-80 enhances biodesulfurization. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7390–7393
Gunam IBW, Yaku Y, Hirano M, Yamamura K, Tomita F, Sone T, Asano K (2006) Biodesulfurization of alkylated forms of dibenzothiophene and benzothiophene by Sphingomonas subarctica T7b. J Biosci Bioeng 101:322–327
Izumi Y, Ohshiro T, Ogino H, Hine Y, Shimao M (1994) Selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:223–226
Kirimura K, Furuya T, Nishii Y, Ishii Y, Kino K, Usami S (2001) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and its derivatives through the selective cleavage of carbon–sulfur bonds by a moderately thermophilic bacterium Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B. J Biosci Bioeng 91:262–266
Kirkwood KM, Andersson JT, Fedorak PM, Foght JM, Gray MR (2007) Sulfur from benzothiophene and alkylbenzothiophenes supports growth of Rhodococcus sp. strain JVH1. Biodegradation 18(5):541–549
Kobayashi M, Horiuchi K, Yoshikawa O, Hirasawa K, Ishii Y, Fujino K, Sugiyama H, Maruhashi K (2001) Kinetic analysis of microbial desulfurization of model and light gas oils containing multiple alkyl debenzothiophenes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65(2):298–304
Konishi J, Onaka T, Ishii Y, Suzuki M (2000) Demonstration of the carbon–sulfur bond targeted desulfurization of benzothiophene by thermophilic Paenibacillus sp. strain A11-2 capable of desulfurizing dibenzothiophene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 187:151–154
Li FL, Xu P, Ma CQ, Luo LL, Wang XS (2003) Deep desulfurization of hydrodesulfurization-treated diesel oil by a facultative thermophilic bacterium Mycobacterium sp. X7B. FEMS Microbiol Lett 223:301–307
Li FL, Xu P, Feng JH, Meng L, Zheng Y, Luo LL, Ma CQ (2005) Microbial desulfurization of gasoline in a Mycobacterium goodii X7B immobilized-cell system. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:276–281
Li W, Wang MD, Chen H, Chen JM, Shi Y (2006) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by growing cells of Gordonia sp. in batch cultures. Biotechnol Lett 28:1175–1179
Li YG, Ma J, Zhang QQ, Wang CS, Chen Q (2007) Sulfur selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and diesel oil by newly isolated Rhodococcus erythropolis NCC-1. Chin J Chem 25:400–405
Liang F, Lu MM, Birch ME, Keener MC, Liu ZF (2006) Determination of polycyclic aromatic sulfur heterocycles in diesel particular matter and diesel fuel by gas chromatography with atomic emission detection. J Chromatogr A 1114:145–153
Luo MF, Xing JM, Gou ZX, Li S, Liu HZ, Chen JY (2003) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by lyophilized cells of Pseudomonas delafieldii R-8 in the presence of dodecane. Biochem Eng J 13:1–6
Marcelis CLM, van Leeuwen M, Polderman HG, Janssen AJH, Lettinga G (2003) Model description of dibenzothiophene mass transfer in oil/water dispersions with respect to biodesulfurization. Biochem Eng J 16:253–264
Mehrnia MR, Towfighi J, Bonakdarpour B, Akbarnegad MM (2004) Influence of top-section design and draft-tube height on the performance of airlift bioreactors containing water-in-oil microemulsion. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:260–267
Naito M, Kawamoto T, Fujino K, Kobayashi M, Maruhashi K, Tanaka A (2001) Long-term repeated biodesulfurization by immobilized Rhodococcus erythropolis KA2-5-1 cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:374–378
Nekodzuka S, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nomura N, Lu J, Nakahara T (1997) Specific desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Mycobacterium sp. strain G3. Biocatal Biotransform 15(1):17–27
Nomura N, Takada M, Okada H, Shinohara Y, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nakahara T, Uchiyama H (2005) Identification and functional analysis of genes required for desulfurization of alkyl dibenzothiophenes of Mycobacterium sp. G3. J Biosci Bioeng 100:398–402
Okada H, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Maruhashi K (2002) Analyses of dibenzothiophene metabolic pathway in Mycobacterium sp. G3. J Biosci Bioeng 93:491–497
Piddington CS, Kovacevich BR, Rambosed J (1995) Sequence and molecular characterization of a DNA region encoding the dibenzothiophene desulfurization operon of Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:468–475
Segel IH (1975) Enzyme kinetics. Wiley, New York
Shafi R, Hutchings GJ (2000) Hydrodesulfurization of hindered dibenzothiophenes: an overview. Catal Today 59:423–442
Shavandi M, Sadeghizadeh M, Khajeh K, Mohebali G, Zomorodipour A (2010) Genomic structure and promoter analysis of the dsz operon for dibenzothiophene biodesulfurization from Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(4):1455–1461
Tanaka Y, Matsui T, Konishi J, Maruhashi K, Kurane R (2002) Biodesulfurization of benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene by a newly isolated Rhodococcus strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:325–328
Wang SJ (2006) Sulfur species in diesels and their desulfurization reactivates. Master dissertation (in Chinese)
Wang MD, Li W, Shi Y, Wang DH, Feng H (2006) Effects of surfactant on biodesulfurization by Corynebacterium sp. ZD-1 in the presence of organic phase. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 7:371–375
Xu P, Yu B, Li FL, Cai XF, Ma CQ (2006) Microbial degradation of sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles. Trends Microbiol 14:398–405
Xu P, Feng J, Yu B, Li F, Ma C (2009) Recent developments in biodesulfurization of fossil fuels. Adv Biochem Eng/Biotechnol 113:255–274
Yin CL, Zhao HJ, Xu YQ, Xin JX, Zhao RY, Liu CG (2007) Study on transformation of sulfides in the process of deep hydrodesulfurization of diesel. J China Univ Petrol 31:134–138 (in Chinese)
Yu B, Xu P, Zhu SS, Cai XF, Wang Y, Li L, Li FL, Liu XY, Ma CQ (2006) Selective biodegradation of S and N heterocycles by a recombinant Rhodococcus erythropolis strain containing carbazole dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2235–2238
Zhang Q, Tong MY, Li YS, Gao HJ, Fang XC (2007) Extensive desulfurization of diesel by Rhodococcus erythropolis. Biotechnol Lett 29:123–127
Acknowledgments
This research work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20276068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, SH., Chen, H. & Li, W. Kinetic analysis of biodesulfurization of model oil containing multiple alkyl dibenzothiophenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 2193–2200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4048-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4048-6