Abstract
The process of protein crosslinking comprises the chemical, enzymatic, or chemoenzymatic formation of new covalent bonds between polypeptides. This allows (1) the site-directed coupling of proteins with distinct properties and (2) the de novo assembly of polymeric protein networks. Transferases, hydrolases, and oxidoreductases can be employed as catalysts for the synthesis of crosslinked proteins, thereby complementing chemical crosslinking strategies. Here, we review enzymatic approaches that are used for protein crosslinking at the industrial level or have shown promising potential in investigations on the lab-scale. We illustrate the underlying mechanisms of crosslink formation and point out the roles of the enzymes in their natural environments. Additionally, we discuss advantages and drawbacks of the enzyme-based crosslinking strategies and their potential for different applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The process of joining protein molecules through intermolecular covalent bonds is commonly referred to as protein crosslinking. It gives rise to the creation of new macromolecular assemblies that frequently reveal physicochemical properties and functionalities different from those of the sole parent compounds. As illustrated by Wong and Jameson (2012), the terms “protein crosslinking” and “protein conjugation” are sometimes used to discriminate between the covalent linkage of proteins that have a natural affinity in vivo and the covalent coupling of two unrelated protein species. To avoid confusion in the terminology, we shall use the term “protein crosslinking” in a general sense throughout this review article to specify the formation of one or more covalent bonds between proteins. Consequently, we will cover approaches that result either in the targeted fusion of distinct protein molecules by a single covalent bond or in the formation of protein networks by multiple covalent bonding.
Modifying the properties of proteins by site-directed fusion or network formation is of great significance for applications in many fields such as food processing, leather and textile fabrication, tissue engineering as well as biochemical and biomedical research. The generation of covalent bonds between proteins can be induced physicochemically by application of heat, alkaline conditions, mechanical agitation, or photooxidative treatment (Gerrard 2002; Singh 1991) by addition of chemical crosslinkers or by enzyme catalysis. Chemical crosslinking methodologies take advantage of the enormous diversity of available crosslinking reagents that differ in chemical functionality, reactivity, and size (Wong and Jameson 2012). Homobifunctional and heterobifunctional chemical crosslinkers carry two reactive groups to target proteins at the same or at different functional groups, respectively. Among these, glutaraldehyde probably represents the most commonly used crosslinking reagent (Migneault et al. 2004). Additionally, there are a few examples of multifunctional crosslinkers that can be used to target proteins at more than two functional groups simultaneously. Protein crosslinking with bi- and multifunctional crosslinkers leads to the incorporation of molecular spacer groups of defined length and composition between the reaction partners. By contrast, monofunctional crosslinkers (e.g., formaldehyde) react such that with the exception of the reactive moiety no additional linker is introduced into the final product. Furthermore, activating agents such as carbodiimides are widely used to directly connect proteins without incorporating a spacer (Wong and Jameson 2012).
In addition to the prevalent chemical crosslinking reagents, enzymes are increasingly employed as catalysts to promote the introduction of covalent bonds between protein molecules. In this article, we review the diversity of enzymatic approaches that can be used for protein crosslinking in vitro. By addressing the physiological backgrounds of the enzymes and their underlying coupling mechanisms, we illustrate how these biomimetic approaches have emerged to complement the toolbox of protein crosslinking strategies. Eventually, we discuss advantages and limitations of choosing and utilizing enzyme-based crosslinking strategies for different practical scenarios.
Enzymatic protein crosslinking in vivo
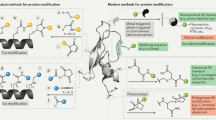
The posttranslational covalent modification of proteins is essential to pro- and eukaryotic cells in order to increase the structural and functional diversity of the proteome (Walsh 2006; Walsh et al. 2005). Most of these modifications are catalyzed by specific enzymes that have evolved for their respective tasks. Enzymatically introduced modifications of proteins occur at the functional groups of amino acid side chains, which are, in some cases, embedded in the context of sequence-specific recognition motifs. They comprise (1) the addition of organic molecules including cofactors (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/CoFactor), oligosaccharides, nucleotides, lipids, and small moieties such as methyl, acetyl, and phosphoryl groups; (2) intramolecular transformations such as disulfide bond formation and proteolytic processing; and (3) intermolecular crosslinking by covalent bond formation between individual protein molecules (Fig. 1).
Schematic illustration of enzyme-catalyzed covalent modifications of proteins in vivo; for a more comprehensive overview we refer to Walsh (2006) and Walsh et al. (2005). The cartoon depicted in the center was created with the program PyMOL and shows the structure of ubiquitin (PDB ID: 1ubq) (Schrodinger 2010)
One of the most extensively studied cellular protein crosslinking events is the enzyme-catalyzed covalent tethering of ubiquitin to target proteins. Ubiquitin represents a small protein of 76 amino acid residues with a size of ~8 kDa. The process of ubiquitin attachment, designated as “ubiquitylation” or “ubiquitination,” is traditionally associated with protein trafficking to the eukaryotic 26S proteasome for specific degradation (Hershko and Ciechanover 1998; Hershko et al. 1982). Proteins directed to the proteasome carry a minimum of four covalently linked ubiquitin molecules that are connected through highly proteolysis-resistant isopeptide bonds between the ε-amine of Lys48 and the C-terminus of the successive subunit. The activation and transfer of ubiquitin to target proteins is catalyzed by a cascade of three enzymes (E1, E2, and E3) in an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-dependent manner (Fig. 2). Nowadays, it is evident that modifications of proteins with ubiquitin and other ubiquitinlike proteins influences a great variety of cellular signaling and regulatory processes depending on the type and length of the attached ubiquitin chain (mono- or polyubiquitination) and on the lysine residues involved in the connection between the individual ubiquitin subunits (Hochstrasser 2009; Spasser and Brik 2012; Weissman et al. 2011). Only recently, even a prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein (Pup) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been described (Darwin 2009), which is coupled to target proteins by the action of the ligase PafA (Guth et al. 2011).
Simplified schematic illustration of the enzymatic cascade leading to ubiquitination of target proteins in eukaryotic cells (Spasser and Brik 2012)
Many physiologically important protein crosslinking reactions in higher eukaryotes are accomplished by transglutaminases. Eukaryotic transglutaminases are calcium-dependent enzymes that catalyze the formation of protein networks by introducing glutamyl-lysyl isopeptide bonds between target proteins (Fig. 3). The most prominent member of the mammalian tissue transglutaminases is the fibrin-stabilizing factor XIII, which participates in blood coagulation by crosslinking antiparallel fibrin chains to mechanically stable clots. For additional information on the functional diversity of eukaryotic transglutaminases, we refer to a review article by Lorand and Graham (2003). In the late 1980s, the first calcium-independent transglutaminase from the microbial strain Streptomyces mobaraensis (formerly classified as Streptoverticillium mobaraense) was described in the patent and peer-reviewed literature (Ando et al. 1989; Motoki et al. 1993). Diverse physiological functions including mycelium growth and differentiation in S. mobaraensis (Pasternack et al. 1998) as well as spore coat formation in Bacillus subtilis (Zilhão et al. 2005) are associated with microbial transglutaminases.
Another naturally occurring crosslinking reaction between proteins is catalyzed by sortases that constitute a group of calcium-dependent enzymes embedded in the membrane of Gram-positive bacteria (http://nihserver.mbi.ucla.edu/Sortase/). Based on their primary amino acid sequence, sortases are currently assigned to six different classes (A–F) that exert highly site-specific transpeptidation reactions (Fig. 3) at the bacterial cell surface (Spirig et al. 2011). These include the anchoring of diverse functional proteins to the growing cell wall by sortase A (Marraffini et al. 2006; Mazmanian et al. 1999) and the assembly of pili from individual pilin subunits by sortase C (Hendrickx et al. 2011).
In contrast to the transamidation reactions catalyzed by transglutaminases and sortases, lysyl oxidases induce the oxidative crosslinking of collagen and elastin chains in the extracellular matrix of eukaryotic cells (Lucero and Kagan 2006). The enzymatic step catalyzed by lysyl oxidases comprises the deamination of lysyl side chains in collagen and elastin with the concomitant formation of hydrogen peroxide (Fig. 4). The resulting aldehydes can react spontaneously either with a second aldehyde to yield the corresponding aldol condensation product or add to the primary amine of a neighboring lysine residue to generate a Schiff base. The so-formed crosslinked chains of collagen and elastin constitute fibrous network structures that largely contribute to the stabilization of eukaryotic tissues.
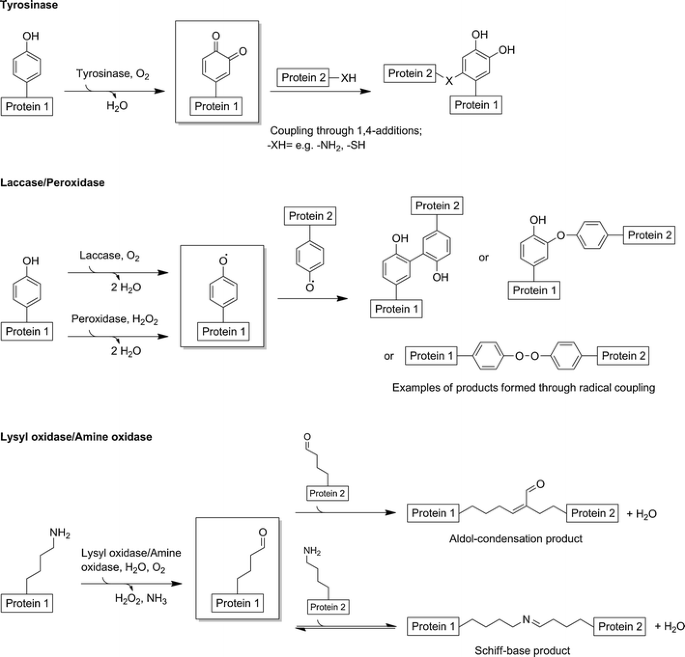
Crosslinking of proteins mediated through oxidation by oxidoreductases. The reactive species generated by the enzymes are framed. The illustration of the laccase- and peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation reactions is simplified and does not show the stoichiometry of substrates and products (laccase oxidizes four substrate molecules per molecule of oxygen, whereas peroxidase oxidizes only two substrate molecules per molecule of hydrogen peroxide)
Enzymes used for protein crosslinking in vitro
The capability of enzymes to crosslink proteins in vivo immediately suggests their use for diverse applications in vitro. Of the aforementioned enzymes, mainly transglutaminases have been successfully applied for the introduction of crosslinks into various protein matrices (Kuraishi et al. 2001; Zhu and Tramper 2008), and also, the crosslinking reactions catalyzed by sortase A and lysyl oxidase have recently gained increasing attention. By contrast, the enzymatic cascade responsible for protein ubiquitination has not been investigated for crosslinking applications in vitro, and indeed, its practical usefulness seems very limited due to the ATP dependence of the reaction and the complex interplay of the enzymes E1, E2, and E3 (Fig. 2). Interestingly, further oxidoreductases that catalyze reactions with nonproteinogenic substrates in vivo have been investigated for the synthesis of new covalent bonds between proteins in vitro. Regarding the enzymatic mechanisms, two types of crosslinking reactions can be distinguished, i.e., (1) direct covalent bonding catalyzed by transferases (EC 2) and hydrolases (EC 3) via proteinyl–enzyme–thioester intermediates and (2) enzyme-mediated covalent bonding via reactive species that are enzymatically generated by oxidoreductases (EC 1) and spontaneously react further with proteins to form protein networks. In this section, we outline the physiological functions and biochemical properties of enzymes relevant to protein crosslinking applications in vitro. For summaries of the enzymes discussed herein and the proposed underlying crosslinking reactions, we refer to Table 1 and to Figs. 3 and 4, respectively.
Transferases and hydrolases
The common crosslinking reaction catalyzed by transferases and hydrolases entirely occurs at the active site of the enzymes and proceeds via formation of a covalent proteinyl–enzyme–thioester intermediate. Nucleophilic attack by an incoming amine nucleophile at the carbonyl group of the thioester intermediate releases the bound protein moiety from the enzyme, leading to formation of a new peptide bond between the target molecules (Fig. 3).
Transglutaminases (EC 2.3.2.13)
As outlined previously, transglutaminases catalyze a transamidation reaction between glutamyl and lysyl side chains of target proteins. The catalytic reaction proceeds via glutamine deamination and formation of a protein–glutamyl–thioester at the active site of the enzyme. Nucleophilic attack by a lysyl ε-amino group of a second protein at the carbonyl moiety of the thioester intermediate generates isopeptide-crosslinked proteins that are largely resistant to proteolysis by common peptidases (Mariniello et al. 2007). In contrast to eukaryotic transglutaminases, transglutaminases from microbial origin are calcium-independent, which represents a major advantage for their practical use (Griffin et al. 2002; Yokoyama et al. 2004).
Peptidases (EC 3.4.x)
An exceptional enzyme, which crosslinks proteins in a highly site-specific manner, is the sortase SrtA (EC 3.4.22.70) from Staphylococcus aureus (Mazmanian et al. 1999). Although SrtA is formally assigned to the class of peptidases, the enzyme in vivo catalyzes a transpeptidation reaction to tether surface proteins to the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. SrtA recognizes target proteins containing a conserved LPXTG amino acid motif, where X represents any proteinogenic amino acid (Kruger et al. 2004). The catalytic reaction proceeds via nucleophilic attack by the enzyme's catalytic cysteinyl thiol group at the threonine–glycine amide bond within the sorting motif of the target protein. Subsequently, a proteinyl–enzyme–thioester intermediate is formed with concomitant release of the C-terminal target protein moiety. An amine nucleophile, the terminal amino group of an oligoglycine polypeptide in vivo, eventually releases the covalently bound protein moiety from the enzyme under formation of a peptide bond crosslink.
Although common peptidases are associated with peptide bond hydrolysis, examples of enzymes are described that can, under certain conditions, catalyze peptide bond formation between polypeptide fragments (Bordusa 2002). In the so-called kinetically controlled approach, a synthetic polypeptide ester serves as the substrate for enzymatic coupling by peptidases. The crosslinking reaction is initiated by formation of a covalent reaction intermediate between the catalytic nucleophile of the peptidase and the carboxy terminus of the substrate. Eventually, nucleophilic attack by the terminal amino group of an acceptor polypeptide leads to release of the bound acyl moiety from the enzyme and crosslink formation between the polypeptide fragments through a newly established peptide bond.
Oxidoreductases
With the exception of lysyl oxidase, most oxidoreductases are not explicitly destined by nature to promote the formation of covalent bonds between proteins. Nevertheless, members of the oxidoreductases have been widely investigated for their potential to crosslink proteins in vitro because they lack pronounced substrate specificity. Many oxidoreductases react with a broad range of small molecules such as low molecular weight phenols and/or macromolecular substrates including functional amino acid side chains of proteins. Covalent bond formation between proteins initiated by the action of oxidoreductases involves at least two sequential chemical steps (Fig. 4). Of these, only the initial redox reaction with the primary substrate is directly catalyzed by the enzyme. The resulting reactive species, i.e., quinones, radicals, or aldehydes may subsequently undergo nonenzymatic conversions to form various types of covalent bonds. In this article, we focus on oxidoreductases that have been experimentally shown to catalyze redox reactions directly at functional amino acid side chains of target proteins. Hence, we do not include glucose oxidases (Wong et al. 2008) and sulfhydryl oxidases (Faccio et al. 2011) that are proposed to induce intermolecular crosslinking of food proteins mainly by producing reactive hydrogen peroxide from small-molecule sugars and thiols, respectively.
Tyrosinases (EC 1.14.18.1)
Tyrosinases are dicopper enzymes that are widespread in pro- and eukaryotic organisms (Claus and Decker 2006; Faccio et al. 2012; Halaouli et al. 2006). They initiate the biosynthetic production of melanins by converting l-tyrosine to dopaquinone, which subsequently undergoes spontaneous reactions to yield melanin. Furthermore, they are attributed to other distinct functions including phenol detoxification in bacteria and cuticle sclerotization in invertebrates. Activated tyrosinases have both monophenolase and diphenolase activity as they are able to catalyze the hydroxylation of monophenolic compounds to o-diphenols as well as the subsequent oxidation of these o-diphenols to the respective o-quinones with concomitant reduction of molecular oxygen to water (Espín et al. 2000). In addition to many low molecular weight mono- and diphenolic molecules, surface-exposed tyrosyl side chains of proteins may also serve as substrates for tyrosinases that convert them to the respective o-quinones (Ito et al. 1984; Matheis and Whitaker 1984a). These are proposed to react spontaneously mainly via 1,4-additions with the side chains of lysine, tyrosine, histidine, and cysteine residues, depending on their abundance and accessibility on the target protein, to form covalent protein–protein crosslinks (Bittner 2006). Proteins with weakly defined three-dimensional structure and unfolded proteins are the preferred targets for crosslinking by tyrosinases, whereas globular proteins are poorly, if at all, converted by the enzyme (Hellman et al. 2011; Selinheimo et al. 2007b). However, it has been shown that crosslink formation between proteins that are not accessible to tyrosinases can be induced by the addition of small-molecule phenolic compounds (Fairhead and Thöny-Meyer 2010; Jus et al. 2012; Thalmann and Lötzbeyer 2002). These molecules likely function as crosslinking mediators to overcome the absence of surface-exposed tyrosine residues on the target proteins.
Laccases (EC 1.10.3.2)
Laccases are “blue” multicopper oxidases that have been discovered in fungi, plants, and bacteria (http://www.lcced.uni-stuttgart.de/). Most of the characterized laccases originating from fungi contribute to the degradation of lignins, whereas laccases derived from plants are mainly related to lignin and cell wall biosynthesis (Mayer and Staples 2002; Singh Arora and Kumar Sharma 2010). Prokaryotic laccases have been proposed to be involved in many intra- and extracellular processes, but their exact physiological functions remain mostly elusive (Santhanam et al. 2011). The active sites of laccases harbor a total of four copper atoms organized at three distinct sites (T1, T2, and T3) that can be distinguished by their spectral properties (Quintanar et al. 2007). They catalyze single-electron abstractions from a wide range of phenols and anilines among other substrates (Reiss et al. 2011; Witayakran and Ragauskas 2009). The oxidation of four substrate molecules by laccases goes along with the concomitant reduction of one equivalent of molecular oxygen to water that is the sole by-product of the reaction. The formed radicals may undergo subsequent coupling reactions of various types leading to the formation of different covalently linked products. In proteins, mainly exposed tyrosyl side chains serve as substrates for oxidation by laccases, and the resulting phenoxy radicals may spontaneously initiate subsequent protein crosslinking reactions (Mattinen et al. 2006). As for tyrosinases, the addition of phenolic compounds as crosslinking mediators can be necessary to promote protein crosslinking by laccases (Steffensen et al. 2008).
Peroxidases (EC 1.11.1.x)
The group of peroxidases encompasses miscellaneous enzymes that universally occur in microorganisms, plants, and animals. Presently, members of the peroxidases are assigned to 20 classes with different EC numbers. Due to the great complexity and diversity of peroxidases, the database PeroxiBase has been created to summarize information on properties, functions, and regulation of these enzymes (https://peroxibase.toulouse.inra.fr/) (Koua et al. 2009). Most peroxidases contain a prosthetic heme group that is required for the electron transfer reaction, and also, peroxidases with other cofactors including flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) are described. Peroxidases abstract single electrons from a broad range of substrates of mostly aromatic nature (Gumiero et al. 2010), including surface-accessible tyrosine residues of proteins (Matheis and Whitaker 1984b). The oxidation of two substrate molecules is accompanied by the concomitant reduction of hydrogen peroxide to water. The phenoxy radicals resulting from tyrosine oxidation by peroxidases may undergo various spontaneous reactions including radical couplings, which mainly leads to the formation of different dityrosyl-type crosslinks between proteins (Heijnis et al. 2011; Matheis and Whitaker 1984a).
Lysyl oxidases (EC 1.4.3.13)
As described above, lysyl oxidases initiate the crosslinking of collagen and elastin chains in the extracellular matrix of higher eukaryotes (Lucero and Kagan 2006). Hence, they are among the few enzymes that promote the formation of protein crosslinks in their physiological environments and likewise have been used for practical crosslinking applications in vitro (Bakota et al. 2011). Lysyl oxidases require two cofactors for catalysis, namely, a covalently bound lysine tyrosinyl quinone (LTQ) cofactor and a copper ion. They oxidize the primary amine groups of accessible lysyl side chains on target proteins to the corresponding aldehydes, which may undergo subsequent reactions to form the covalently crosslinked aldol condensation or Schiff base product.
Formation of protein networks
The covalent assembly of proteins into macromolecular networks by enzyme catalysis has been extensively investigated in various areas of applications where biological protein matrices with material-like structural and mechanical properties are required. The ability of enzymes to form crosslinked protein networks has, for instance, been exploited to modify the texture and appearance of food products, to develop new biomimetic tissue scaffolds, or to strengthen protein-based fibers for textile fabrication. In this section, we give an overview of enzymatic approaches that are used in different fields to create products composed of covalent protein networks.
Food processing
The modification of food proteins by enzymatic crosslinking can affect the long-term stability required for storage or the organoleptic properties such as structure, texture, appearance, and flavor of food products. There is extensive literature available on the enzymatic crosslinking of proteins in foods, and many aspects of this field have been covered in a comprehensive book and review articles (Whitehurst and van Oort 2010; Buchert et al. 2010; Gerrard 2002; Singh 1991). For this reason, we restrict our discussion to the general aspects of enzyme-catalyzed crosslinking approaches that are used to modify the properties of proteins in food products, and we explicitly highlight selected studies from this rapidly progressing field of research.
Enzyme preparations suitable for applications in the food industry must be tested for toxicity and immunogenicity and certified with the status Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) defined by the US Food and Drug Association (FDA). For instance, a GRAS status has been assigned to transglutaminase preparations from S. mobaraensis for protein crosslinking in seafood, meat, dairy, and cereal products (FDA/CFSAN agency response letters: GRAS notice numbers 000004 (1998), 000029 (1999), 000055 (2001), and 000095 (2002)). Nowadays, microbial transglutaminase is produced on large scale and distributed under the trade name ACTIVA® by Ajinomoto US, Inc. (http://www.transglutaminase.com). Transglutaminase is commonly referred to as “meat glue” due to its ability to assemble pieces of meat by crosslink formation, thereby restoring the structure of meat from low-quality fresh meat cuts (Kuraishi et al. 1997) or improving the textural properties of processed meat gels (Sun and Arntfield 2011). The transglutaminase-catalyzed crosslinking reaction in meat and fish products is predominantly directed towards the myofibrillar protein myosin (Chanarat et al. 2012; Huang et al. 1992; Lantto et al. 2005), which represents the primary constituent of thick muscle filaments. In addition to muscle proteins, microbial transglutaminase shows high crosslinking activity with caseins from milk (Sharma et al. 2001) and glutenins from wheat grains (Autio et al. 2005; Basman et al. 2002). This makes the use of the enzyme attractive for applications in other areas of the food industry such as the dairy and the baking sectors (Jaros et al. 2006; Joye et al. 2009). For example, transglutaminase has been used to induce protein crosslinking during yoghurt making with the aim of superseding the addition of dry matter stabilizers that are commonly added to enhance the strength of acidified caseinate gels (Bönisch et al. 2007; Jaros et al. 2006). In noodle and bread making, transglutaminase-catalyzed crosslinking has been shown to change the rheological properties and the microstructure of dough preparations as compared to untreated doughs (Kim et al. 2008; Steffolani et al. 2010; Wu and Corke 2005). For more detailed summaries on the applications of transglutaminase in the food sector, we refer to review articles by Motoki and Kumazawa (2000) and Kuraishi et al. (2001).
The generation of protein crosslinks by oxidative enzymes including tyrosinases, laccases, and peroxidases has also been investigated in several areas of the food industry (reviewed in Buchert et al. (2010); Whitehurst and van Oort (2010)). However, in comparison to transglutaminase, relatively little is known on how exactly these enzymes affect the chemical compositions of protein matrices in foods. It should be noted here that the reaction of quinones generated by tyrosinases with free amino acids may influence the color and aroma of the food product, which may limit the use of tyrosinases in certain applications of the food industry (Bittner 2006). Nevertheless, tyrosinase from the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei has been shown to induce the gelation of acidified milk gels. In contrast to transglutaminase, the studied tyrosinase did not require preheating of the milk to allow the enzymatic crosslinking reaction, which could be advantageous for the production of certain milk products (Ercili Cura et al. 2010). It has been proposed that the allergenic properties of the milk protein casein might be mitigated by enzymatic crosslinking (Stanic et al. 2010). Selinheimo et al. (2007a) evaluated the application of tyrosinase from T. reesei and laccase from Trametes hirsuta on dough preparations from wheat flour for bread making. Although protein crosslinking of gliadins and glutenins induced by these enzymes made the doughs harder and less extensible, the resulting breads were more voluminous and had softer crumbs than ordinary breads.
Food packaging
The development of polysaccharide- and protein-based polymeric films has recently received attention due to the need for biocompatible and biodegradable materials that possess mechanical, swelling, and barrier properties suitable for food packaging. Edible thin films from various different proteins have been prepared by enzyme-catalyzed crosslinking with microbial transglutaminase (Di Pierro et al. 2006; Mariniello et al. 2010), and recently, also with tyrosinase and laccase (Juvonen et al. 2011). For example, films containing transglutaminase-crosslinked whey proteins embedded in a chitosan matrix showed (1) low solubility in water (2) reduced permeability for oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor, and (3) enhanced elongation to break but lower deformability than noncrosslinked films (Di Pierro et al. 2006). Similar changes regarding the barrier properties were observed in thin film preparations of grapefruit albedo homogenates combined with the bean protein phaseolin after transglutaminase-catalyzed crosslinking. However, in contrast to the whey protein films studied by Di Pierro et al. (2006), the transglutaminase-treated albedo homogenate–phaseolin films not only revealed higher tensile strength but also an approximately twofold increase in their elasticity (Mariniello et al. 2010).
Biomimetic materials
Protein- and polysaccharide-based hydrogels (i.e., highly water-absorbent polymeric networks) have emerged as biological scaffolds to support three-dimensional tissue formation because their mesh structures represent good mimics of the natural extracellular matrix and offer the possibility to entrap bioactive molecules such as growth factors. Extensive research has been directed towards the development of enzymatic approaches for hydrogel network formation (Moreira Teixeira et al. 2012). The use of enzymes has gained increasing attention particularly for the synthesis of injectable in situ-forming hydrogels because enzymes usually react under physiological conditions and, in contrast to many chemicals, are mostly regarded as biocompatible. Protein hydrogels have been created by enzyme-catalyzed crosslinking from various protein sources, mostly from collagen or its denatured form gelatin. For example, Yung et al. (2007) used microbial transglutaminase to generate crosslinked gelatin hydrogels that are thermally stable in saline solution at body temperature, allow proliferation of encapsulated HEK293 cells, and facilitate the transport of secreted therapeutic proteins such as interleukin-2 (Yung et al. 2010). Moreover, synthetic glutamine- and lysine-rich oligopeptides have been crosslinked with two eukaryotic transglutaminases to yield modular cytocompatible protein hydrogels (Davis et al. 2010). Besides hydrogels, a microfluidic device composed of a transglutaminase-crosslinked gelatin mold has been designed to analyze attached cell cultures in an in vivo-like environment mimicking the extracellular matrix (Paguirigan and Beebe 2006).
In addition to transglutaminases, horseradish peroxidase has been exploited to induce the gelation of mainly polysaccharide-based building blocks including chitosan or dextran derivatives for applications in tissue engineering (Jin et al. 2009; Jin et al. 2010). Furthermore, Sofia et al. (2002) demonstrated the peroxidase-catalyzed crosslinking of protein hydrogels from differently substituted polyaspartic acid derivatives. Fetal bovine serum, which contains lysyl oxidase as a natural enzymatic component, and commercially available plasma amine oxidase have been employed as catalysts for the production of hydrogels by oxidative crosslinking of lysine-rich synthetic peptide nanofibers (Bakota et al. 2011). Gradually advancing gelation with time was observed, going along with a steady increase of robustness of the formed peptide hydrogels as determined by rheology. Lau et al. (2006) reported the development of a gene delivery system that allowed gene uptake and local expression of lysyl oxidase by fibroblasts embedded in a collagen layer mimicking the extracellular matrix. After 3 weeks of culturing, collagen gels with lysyl oxidase-transfected cells showed threefold increased mechanical strength over gels harboring control transgenic cells. This effect could be attributed to additional crosslinking of the collagen fibers induced by expression of lysyl oxidase in the matrix-embedded cells.
Textile and leather manufacturing
The treatment of wool proteins, i.e., mainly keratins, with proteolytic enzymes is a field of active research in textile-processing applications. Limited enzymatic hydrolysis of keratin fibers has been shown to improve the shrink resistance and antifelting behavior of woolen fabrics (Wang et al. 2011). However, the breakdown of keratin has to be tightly controlled because excessive proteolysis causes drastic fiber damage and reduces tensile strength. The introduction of additional crosslinks into the keratin network by the use of enzymes represents an approach to compensate for the loss of tensile strength caused by peptidase-catalyzed hydrolysis. Several studies indicated that keratin fibers crosslinked by microbial transglutaminase maintain higher fabric strength after (1) proteinase treatment (Cortez et al. 2004; Du et al. 2007), (2) repeated washing cycles with proteinase-containing detergents (Cortez et al. 2005), or (3) bleaching with hydrogen peroxide (Montazer et al. 2011) as compared to the corresponding fibers without enzyme treatment. Furthermore, transglutaminase has been employed to graft casein (Cui et al. 2011), gelatin (Cui et al. 2009), and silk proteins (Cortez et al. 2007) onto wool yarns, generating products with improved physicomechanical properties such as increased tensile strength and higher smoothness. In a similar approach, wool fibers have been functionalized with ε-linked polylysine, an FDA-approved biomolecule with antibacterial properties (Wang et al. 2010). Recent studies demonstrated that tyrosinase can be employed to oxidize tyrosyl side chains of keratin, allowing crosslinking of proteins such as collagen and elastin to wool fibers (Jus et al. 2009; Lantto et al. 2012). In the leather industry, transglutaminase-crosslinked preparations of gelatin and casein have been examined as low-cost filling materials to stuff voids in animal hides. The crosslinked fillers were shown to be homogeneously distributed in the hides, to resist the washing steps during leather processing and to improve properties of the leather such as grain smoothness and fullness (Liu et al. 2011; Taylor et al. 2009; Taylor et al. 2007).
Stabilization of technical enzymes
Approaches using chemical crosslinking reagents such as glutaraldehyde are extensively used for the preparation of crosslinked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) from synthetically relevant enzymes. CLEAs generally exhibit properties desirable for process development such as good operational stability, high productivity, and recyclability (Sheldon 2011). To the best of our knowledge, only one enzyme-based approach to yield CLEAs has been reported in the scientific literature. Using the tyrosinase from Verrucomicrobium spinosum in the presence of phenol, Fairhead and Thöny-Meyer (2010) reported the formation of catalytically active CLEAs from Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB). A further evaluation of enzymatically formed CLEAs is needed in order to assess their usefulness for biocatalytic transformations as compared to CLEAs produced by traditional chemical crosslinking strategies. Especially factors including catalyst activity and stability, production costs, sustainability, and possibility of enzymatically introduced cross-contaminations should be addressed.
Site-directed protein fusion
In accordance with the definition given in the “Introduction”, protein crosslinking not only covers the formation of covalently linked protein networks with material-like properties but also includes the specific linkage of two proteins on the molecular level. Traditionally, this is achieved by genetic assembly of the respective encoding DNA regions and subsequent heterologous expression of the fusion protein. This allows combination of the properties of distinct protein species, for example, the binding specificity of an antibody with the immunoregulatory function of a cytokine to create antibody–cytokine fusion proteins for anticancer therapy (Kontermann 2012). However, if expression or correct folding of the fusion protein fails, alternative methods are required to link two separately expressed proteins in a site-specific manner. Native chemical ligation (NCL) represents the most robust and widely applied strategy for the chemoselective ligation of two synthetically produced, unprotected polypeptide chains (Dawson and Kent 2000). In NCL, a native peptide bond is formed between one polypeptide bearing a chemically introduced C-terminal thioester and a second polypeptide containing an N-terminal cysteine residue. NCL has been complemented by intein-based methods, namely, expressed protein ligation (EPL) and protein trans-splicing (PTS); for a review on EPL and PTS, we refer to Muralidharan and Muir (2006). Besides these synthetic and semisynthetic techniques, hydrolytic enzymes have been used for the formation of native peptide bonds between polypeptide fragments. The best known example is the blockwise assembly of fully active ribonuclease A from six esterified peptide segments in aqueous solution using a genetically optimized double mutant of subtilisin BPN′ (named “subtiligase”) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Jackson et al. 1994).
Due to its site specificity for the LPXTG sorting motif, the sortase SrtA from S. aureus has recently emerged as an enzymatic tool for the site-directed assembly of proteins by transpeptidation (Tsukiji and Nagamune 2009). Examples for the SrtA-catalyzed fusion of proteins include the site-specific coupling of various globular proteins to an IgG antibody (Levary et al. 2011) and to a single-chain antibody (Ta et al. 2011). Under optimized reaction conditions, product yields of 40–85 % were reached and it was shown that the antibody specificity was retained in the fusion proteins. It is worth mentioning that SrtA can also be employed for the oriented immobilization of proteins on glycine-modified solid supports (Parthasarathy et al. 2007), for the site-specific introduction of various molecular probes (Popp et al. 2009), and for protein circularization (Antos et al. 2009). In addition to SrtA, microbial transglutaminase (Takazawa et al. 2004; Tanaka et al. 2004) as well as horseradish peroxidase (Minamihata et al. 2011) have been investigated as catalysts to promote the site-specific coupling of proteins carrying engineered peptide tags.
Advantages, challenges, and limitations of enzymatic crosslinking strategies
The ability of enzymes to promote the formation of covalent crosslinks between amino acid residues of proteins offers versatile possibilities for protein modifications, thereby complementing the toolbox of chemical crosslinking methodologies. As shown in the previous sections, only a very limited number of enzymes are frequently used for protein crosslinking purposes. Because these enzymes differ fundamentally with regard to their biochemical properties, reaction mechanisms, and substrate specificities (Table 1 and Figs. 3 and 4), they can be exploited to access miscellaneous crosslinked protein products ranging from fusion proteins connected through a single covalent bond to protein networks linked through a multitude of intermolecular covalent bonds.
Polymeric networks composed of proteins feature material-like structural and mechanical properties that are desirable in many fields of applications, as outlined above. Unlike many chemicals, enzymes are most active under mild aqueous reaction conditions and their crosslinking reactions can often be controlled by modifying temperature, pH, or ionic strength (as shown, for example, in Heijnis et al. 2010). For the purpose of generating or extending covalent protein networks, enzymes with a low degree of specificity towards the amino acid sequence of their target proteins are preferred. In this respect, microbial transglutaminase from S. mobaraensis is by far the most extensively studied and applied enzyme because (1) it is commercially available in large quantities, (2) it is rated as nontoxic and nonimmunogenic by the FDA, (3) it does not require cofactors, and (4) it is active over a wide pH range and resists temperatures up to 50 °C (Motoki and Kumazawa 2000). Transglutaminase shows residue, but not sequence specificity, and forms defined isopeptide crosslinks between glutamine and lysine residues of proteins. Similarly, phenol oxidation by tyrosinases, laccases, and peroxidases can be regarded as a residue-specific reaction in the context of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids because tyrosine represents the only proteinogenic amino acid that contains a phenolic moiety. Nevertheless, crosslink formation mediated by oxidoreductases is difficult to control because only the initial activation of the tyrosyl side chains is enzyme-catalyzed, and the resulting reactive species may undergo spontaneous follow-up reactions to form a wide array of diverse covalent crosslinks involving C–C, C–O, C–N, and C–S bonds (Fig. 4). Transglutaminases as well as oxidoreductases accept diverse proteins as substrates for crosslinking, provided they carry the respective amino acid residue required for the enzymatic reaction at a surface-exposed position. On the one hand, this implies that any protein lacking accessible target amino acids will not be enzymatically crosslinked. On the other hand, the enzyme itself may potentially serve as substrate for the crosslinking reaction, which could consequently cause its incorporation into the crosslinked protein network. It should be noted here that oxidoreductases may also abstract electrons from a wide range of phenols of low molecular weight such as ferulic or caffeic acid. These molecules, once activated to the corresponding quinone or radical species, may act as mediators to crosslink target proteins that are not directly converted by the enzyme due to a lack of enzyme-accessible tyrosyl side chains.
While the generation of protein-based polymer networks relies on the formation of multiple covalent bonds among individual polypeptide chains, the oriented intermolecular fusion of two distinct proteins requires the precise formation of a single covalent bond at a defined position between the reaction partners. Therefore, the coupling process has to be tightly controlled and demands a reaction that ensures site rather than residue specificity. Unlike densely crosslinked protein matrices, which are commonly intended for industrial bulk applications, site specifically linked fusion proteins are usually produced on a comparably small scale. Their applications are highly specialized and mostly restricted to the areas of biochemical and biomedical research. In addition to the prevalent synthetic and semisynthetic ligation strategies (NCL, EPL, and PTS) (Dawson and Kent 2000; Muralidharan and Muir 2006), proteolytic enzymes may be employed to catalyze the site-specific formation of peptide bonds. Although, in most cases, protease-catalyzed approaches have been exploited to produce peptides of only short-chain length (Bordusa 2002), the potential of commercially available proteases to assemble intact proteins from synthetic polypeptide esters has also been demonstrated (Jackson et al. 1994; Machova et al. 2003). The sortase SrtA from S. aureus catalyzes transpeptidation reactions of proteins in vivo and probably represents the most straightforward enzymatic approach in vitro to generate site specifically linked fusion proteins. While the aforementioned chemical- and protease-based approaches to fusion protein synthesis ensure site specificity by the presence of synthetically introduced C-terminal ester or thioester groups, site specificity of the SrtA-catalyzed coupling reaction is provided by the presence of a short LPXTG amino acid motif, which can be introduced genetically near the C-terminus of the recombinant target polypeptide (Fig. 3). Advantages associated with the use of SrtA for the generation of fusion proteins include (1) facile and efficient production of the enzyme in E. coli, (2) minimal requirements for target protein modification due to small recognition motifs, (3) mild aqueous reaction conditions that sustain the native conformation of most target proteins, and (4) high yields of transpeptidation products. However, it is important to mention that despite the site specificity of SrtA for the LPXTG-sorting motif, unproductive side reactions may occur due to the presence of different nucleophiles competing for the release of the enzyme-bound protein substrate. While nucleophilic attack by the N-terminal oligoglycine amino moiety of the fusion partner leads to formation of the directionally linked protein product (Fig. 3), hydrolysis of the recognition motif and formation of isopeptidyl-crosslinked fusion products may also occur as side reactions (Möhlmann et al. 2011). Thus, thorough reaction optimization and a final purification step may be necessary for obtaining the desired fusion protein in a sufficiently pure form. Furthermore, the need for engineered protein substrates may limit the application of the SrtA-catalyzed reaction to the production of high-value protein products that are difficult to access by chemical fusion strategies.
Besides the enzymes described in this review, chemical crosslinking reagents with a broad variety of chemical features are available to target the functional groups present in the amino acid side chains of proteins (Wong and Jameson 2012). While some chemical crosslinkers possess residue specificity in the context of the naturally occurring amino acids, others may selectively target different functional groups in amino acids showing similar chemical reactivity. Crosslinking strategies based on chemical crosslinkers are widely used for diverse applications, ranging from fundamental studies of protein–protein interactions at the molecular level to the large-scale production of crosslinked aggregates of technical enzymes. Furthermore, crosslinking reagents may be employed to provide target proteins with new noncanonical functionalities for subsequent chemical modifications, to attach molecular probes such as fluorophores, or to covalently immobilize proteins on solid carriers. In contrast to enzymes that serve a catalytic function and thus are restored after each cycle of crosslink formation, chemical reagents are consumed during the reaction and hence are usually supplied in at least stoichiometric amounts in order to allow the crosslinking reaction to proceed to completion.
Despite their broad commercial availability, reaction efficiency, and versatility, the use of chemical crosslinking reagents can be unfavorable particularly when applied in the areas of food processing and tissue engineering, because many of these compounds are rated as toxic or may form harmful by-products leaching from the crosslinked protein matrix. To overcome these limitations, the study of enzymes that catalyze the formation of protein crosslinks in vitro has gained broad attention. However, except the established approaches based on microbial transglutaminase, the field of enzymatic protein crosslinking is still in its infancy. There is a need not only to explore and further improve the protein crosslinking technology using the currently known enzymes but also to direct future investigations towards the discovery of enzymes with new crosslinking activities in order to broaden the range of target amino acids and protein substrates accessible to enzymatic crosslinking.
References
Ando H, Adachi M, Umeda K, Matsuura A, Nonaka M, Uchio R, Tanaka H, Motoki M (1989) Purification and characteristics of a novel transglutaminase derived from microorganisms. Agr Biol Chem Tokyo 53:2613–2617
Antos JM, Popp MWL, Ernst R, Chew GL, Spooner E, Ploegh HL (2009) A straight path to circular proteins. J Biol Chem 284:16028–16036. doi:10.1074/jbc.M901752200
Autio K, Kruus K, Knaapila A, Gerber N, Flander L, Buchert J (2005) Kinetics of transglutaminase-induced cross-linking of wheat proteins in dough. J Agric Food Chem 53:1039–1045. doi:10.1021/Jf0485032
Bakota EL, Aulisa L, Galler KM, Hartgerink JD (2011) Enzymatic cross-linking of a nanofibrous peptide hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 12:82–87. doi:10.1021/Bm1010195
Basman A, Köksel H, Ng PKW (2002) Effects of transglutaminase on SDS-PAGE patterns of wheat, soy, and barley proteins and their blends. J Food Sci 67:2654–2658. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb08794.x
Bittner S (2006) When quinones meet amino acids: chemical, physical and biological consequences. Amino Acids 30:205–224. doi:10.1007/s00726-005-0298-2
Bönisch MP, Huss M, Weitl K, Kulozik U (2007) Transglutaminase cross-linking of milk proteins and impact on yoghurt gel properties. Int Dairy J 17:1360–1371. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.01.019
Bordusa F (2002) Proteases in organic synthesis. Chem Rev 102:4817–4867. doi:10.1021/Cr010164d
Buchert J, Ercili Cura D, Ma H, Gasparetti C, Monogioudi E, Faccio G, Mattinen M, Boer H, Partanen R, Selinheimo E, Lantto R, Kruus K (2010) Crosslinking food proteins for improved functionality. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:113–138. doi:10.1146/annurev.food.080708.100841
Chanarat S, Benjakul S, H-Kittikun A (2012) Comparative study on protein cross-linking and gel enhancing effect of microbial transglutaminase on surimi from different fish. J Sci Food Agric 92:844–852. doi:10.1002/Jsfa.4656
Claus H, Decker H (2006) Bacterial tyrosinases. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:3–14. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2005.07.012
Cortez J, Bonner PLR, Griffin M (2004) Application of transglutaminases in the modification of wool textiles. Enzyme Microb Technol 34:64–72. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2003.08.004
Cortez J, Bonner PLR, Griffin M (2005) Transglutaminase treatment of wool fabrics leads to resistance to detergent damage. J Biotechnol 116:379–386. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.12.007
Cortez J, Anghieri A, Bonner PLR, Griffin M, Freddi G (2007) Transglutaminase mediated grafting of silk proteins onto wool fabrics leading to improved physical and mechanical properties. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1698–1704. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.10.013
Cui L, Wang Q, Wang P, Huan Q, Fan X (2009) Transglutaminase-mediated crosslinking of gelatin onto wool surfaces to improve the fabric properties. J Appl Polym Sci 113:2598–2604. doi:10.1002/App.30300
Cui L, Fan X, Wang P, Wang Q, Fu G (2011) Casein and transglutaminase-mediated modification of wool surface. Eng Life Sci 11:201–206. doi:10.1002/elsc.201000110
Darwin KH (2009) Prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein (Pup), proteasomes and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:485–491. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro2148
Davis NE, Ding S, Forster RE, Pinkas DM, Barron AE (2010) Modular enzymatically crosslinked protein polymer hydrogels for in situ gelation. Biomaterials 31:7288–7297. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.06.003
Dawson PE, Kent SBH (2000) Synthesis of native proteins by chemical ligation. Annual Rev Biochem 69:923–960. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.923
Di Pierro P, Chico B, Villalonga R, Mariniello L, Damiao AE, Masi P, Porta R (2006) Chitosan–whey protein edible films produced in the absence or presence of transglutaminase: analysis of their mechanical and barrier properties. Biomacromolecules 7:744–749. doi:10.1021/Bm050661u
Du G, Cui L, Zhu Y, Chen J (2007) Improvement of shrink-resistance and tensile strength of wool fabric treated with a novel microbial transglutaminase from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1753–1757. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.12.001
Ercili Cura D, Lille M, Partanen R, Kruus K, Buchert J, Lantto R (2010) Effect of Trichoderma reesei tyrosinase on rheology and microstructure of acidified milk gels. Int Dairy J 20:830–837. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2010.06.008
Espín JC, Varón R, Fenoll LG, Gilabert MA, García-Ruíz PA, Tudela J, García-Cánovas F (2000) Kinetic characterization of the substrate specificity and mechanism of mushroom tyrosinase. Eur J Biochem 267:1270–1279. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01013.x
Faccio G, Nivala O, Kruus K, Buchert J, Saloheimo M (2011) Sulfhydryl oxidases: sources, properties, production and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:957–966. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3440-y
Faccio G, Kruus K, Saloheimo M, Thöny-Meyer L (2012) Bacterial tyrosinases and their applications. Process Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2012.08.018
Fairhead M, Thöny-Meyer L (2010) Cross-linking and immobilisation of different proteins with recombinant Verrucomicrobium spinosum tyrosinase. J Biotechnol 150:546–551. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.10.068
Fairhead M, Thöny-Meyer L (2012) Bacterial tyrosinases: old enzymes with new relevance to biotechnology. New Biotechnol 29:183–191. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2011.05.007
Gerrard JA (2002) Protein–protein crosslinking in food: methods, consequences, applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 13:391–399. doi:10.1016/S0924-2244(02)00257-1
Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002) Transglutaminases: nature's biological glues. Biochem J 368:377–396. doi:10.1042/BJ20021234
Gumiero A, Murphy EJ, Metcalfe CL, Moody PCE, Raven EL (2010) An analysis of substrate binding interactions in the heme peroxidase enzymes: a structural perspective. Arch Biochem Biophys 500:13–20. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2010.02.015
Gupta R, Beg QK, Lorenz P (2002) Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:15–32. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-0975-y
Guth E, Thommen M, Weber-Ban E (2011) Mycobacterial ubiquitin-like protein ligase PafA follows a two-step reaction pathway with a phosphorylated Pup intermediate. J Biol Chem 286:4412–4419. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.189282
Halaouli S, Asther M, Sigoillot JC, Hamdi M, Lomascolo A (2006) Fungal tyrosinases: new prospects in molecular characteristics, bioengineering and biotechnological applications. J Appl Microbiol 100:219–232. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02866.x
Heijnis WH, Wierenga PA, Berkel WJH, Gruppen H (2010) Directing the oligomer size distribution of peroxidase-mediated cross-linked bovine α-lactalbumin. J Agr Food Chem 58:5692–5697. doi:10.1021/Jf100168x
Heijnis WH, Dekker HL, de Koning LJ, Wierenga PA, Westphal AH, de Koster CG, Gruppen H, van Berkel WJH (2011) Identification of the peroxidase-generated intermolecular dityrosine cross-link in bovine α-lactalbumin. J Agr Food Chem 59:444–449. doi:10.1021/Jf104298y
Hellman M, Mattinen ML, Fu B, Buchert J, Permi P (2011) Effect of protein structural integrity on cross-linking by tyrosinase evidenced by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biotechnol 151:143–150. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.11.006
Hendrickx APA, Budzik JM, Oh SY, Schneewind O (2011) Architects at the bacterial surface—sortases and the assembly of pili with isopeptide bonds. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:166–176. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro2520
Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:425–479. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.425
Hershko A, Eytan E, Ciechanover A, Haas AL (1982) Immunochemical analysis of the turnover of ubiquitin-protein conjugates in intact cells—relationship to the breakdown of abnormal proteins. J Biol Chem 257:13964–13970
Hochstrasser M (2009) Origin and function of ubiquitin-like proteins. Nature 458:422–429. doi:10.1038/nature07958
Huang YP, Seguro K, Motoki M, Tawada K (1992) Cross-linking of contractile proteins from skeletal muscle by treatment with microbial transglutaminase. J Biochem Tokyo 112:229–234
Ito S, Kato T, Shinpo K, Fujita K (1984) Oxidation of tyrosine residues in proteins by tyrosinase—formation of protein-bonded 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and 5-S-cysteinyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine. Biochem J 222:407–411
Jackson DY, Burnier J, Quan C, Stanley M, Tom J, Wells JA (1994) A designed peptide ligase for total synthesis of ribonuclease A with unnatural catalytic residues. Science 266:243–247. doi:10.1126/science.7939659
Jaros D, Partschefeld C, Henle T, Rohm H (2006) Transglutaminase in dairy products: chemistry, physics, applications. J Texture Stud 37:113–155. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4603.2006.00042.x
Jin R, Moreira Teixeira LS, Dijkstra PJ, Karperien M, van Blitterswijk CA, Zhong ZY, Feijen J (2009) Injectable chitosan-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:2544–2551. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.01.020
Jin R, Moreira Teixeira LS, Dijkstra PJ, van Blitterswijk CA, Karperien M, Feijen J (2010) Enzymatically-crosslinked injectable hydrogels based on biomimetic dextran-hyaluronic acid conjugates for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 31:3103–3113. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.013
Joye IJ, Lagrain B, Delcour JA (2009) Use of chemical redox agents and exogenous enzymes to modify the protein network during breadmaking—a review. J Cereal Sci 50:11–21. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2009.04.001
Jus S, Kokol V, Guebitz GM (2009) Tyrosinase-catalysed coating of wool fibres with different protein-based biomaterials. J Biomater Sci 20:253–269. doi:10.1163/156856209X404523
Jus S, Stachel I, Fairhead M, Meyer M, Thöny-Meyer L, Guebitz GM (2012) Enzymatic cross-linking of gelatine with laccase and tyrosinase. Biocatal Biotransfor 30:86–95. doi:10.3109/10242422.2012.646036
Juvonen H, Smolander M, Boer H, Pere J, Buchert J, Peltonen J (2011) Film formation and surface properties of enzymatically crosslinked casein films. J Appl Polym Sci 119:2205–2213. doi:10.1002/App.32943
Kim YS, Huang W, Du G, Pan Z, Chung O (2008) Effects of trehalose, transglutaminase, and gum on rheological, fermentation, and baking properties of frozen dough. Food Res Int 41:903–908. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2008.07.013
Kontermann RE (2012) Antibody–cytokine fusion proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 526:194–205. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2012.03.001
Koua D, Cerutti L, Falquet L, Sigrist CJA, Theiler G, Hulo N, Dunand C (2009) PeroxiBase: a database with new tools for peroxidase family classification. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D261–D266. doi:10.1093/Nar/Gkn680
Kruger RG, Otvos B, Frankel BA, Bentley M, Dostal P, McCafferty DG (2004) Analysis of the substrate specificity of the Staphylococcus aureus sortase transpeptidase SrtA. Biochemistry 43:1541–1551. doi:10.1021/bi035920j
Kuraishi C, Sakamoto J, Yamazaki K, Susa Y, Kuhara C, Soeda T (1997) Production of restructured meat using microbial transglutaminase without salt or cooking. J Food Sci 62:488–490. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1997.tb04412.x
Kuraishi C, Yamazaki K, Susa Y (2001) Transglutaminase: its utilization in the food industry. Food Rev Int 17:221–246. doi:10.1081/FRI-100001258
Lantto R, Puolanne E, Kalkkinen N, Buchert J, Autio K (2005) Enzyme-aided modification of chicken-breast myofibril proteins: effect of laccase and transglutaminase on gelation and thermal stability. J Agr Food Chem 53:9231–9237. doi:10.1021/Jf051602a
Lantto R, Ellis J, Fatarella E, Cortez J (2012) Influence of different pretreatments on the accessibility of transglutaminase and tyrosinase to wool fibre proteins. J Text Inst 103:55–63. doi:10.1080/00405000.2010.544103
Lau YKI, Gobin AM, West JL (2006) Overexpression of lysyl oxidase to increase matrix crosslinking and improve tissue strength in dermal wound healing. Ann Biomed Eng 34:1239–1246. doi:10.1007/s10439-006-9130-8
Levary DA, Parthasarathy R, Boder ET, Ackerman ME (2011) Protein–protein fusion catalyzed by sortase A. PLoS One 6:e18342. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018342.g002
Liu Q, Liu L, Li J, Zhang D, Sun J, Du G, Chen J (2011) Influence of microbial transglutaminase modified gelatin-sodium caseinate, as a filler, on the subjective mechanical and structural properties of leather. J Am Leather Chem As 106:200–207
Lorand L, Graham RM (2003) Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 4:140–156. doi:10.1038/Nrm1014
Lucero HA, Kagan HM (2006) Lysyl oxidase: an oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:2304–2316. doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6149-9
Machova Z, von Eggelkraut-Gottanka R, Wehofsky N, Bordusa F, Beck-Sickinger AG (2003) Expressed enzymatic ligation for the semisynthesis of chemically modified proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed 42:4916–4918. doi:10.1002/anie.200351774
Mariniello L, Giosafatto CVL, Di Pierro P, Sorrentino A, Porta R (2007) Synthesis and resistance to in vitro proteolysis of transglutaminase cross-linked phaseolin, the major storage protein from Phaseolus vulgaris. J Agr Food Chem 55:4717–4721. doi:10.1021/Jf0637269
Mariniello L, Giosafatto CVL, Di Pierro P, Sorrentino A, Porta R (2010) Swelling, mechanical, and barrier properties of albedo-based films prepared in the presence of phaseolin cross-linked or not by transglutaminase. Biomacromolecules 11:2394–2398. doi:10.1021/Bm100566j
Marraffini LA, DeDent AC, Schneewind O (2006) Sortases and the art of anchoring proteins to the envelopes of gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:192–221. doi:10.1128/Mmbr.70.1.192-221.2006
Matheis G, Whitaker JR (1984a) Modification of proteins by polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase and their products. J Food Biochem 8:137–162. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4514.1984.tb00322.x
Matheis G, Whitaker JR (1984b) Peroxidase-catalyzed cross linking of proteins. J Protein Chem 3:35–48. doi:10.1007/BF01024835
Mattinen ML, Hellman M, Permi P, Autio K, Kalkkinen N, Buchert J (2006) Effect of protein structure on laccase-catalyzed protein oligomerization. J Agr Food Chem 54:8883–8890. doi:10.1021/Jf062397h
Mayer AM, Staples RC (2002) Laccase: new functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry 60:551–565. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00171-1
Mazmanian SK, Liu G, Ton-That H, Schneewind O (1999) Staphylococcus aureus sortase, an enzyme that anchors surface proteins to the cell wall. Science 285:760–763. doi:10.1126/science.285.5428.760
Migneault I, Dartiguenave C, Bertrand MJ, Waldron KC (2004) Glutaraldehyde: behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 37:790–802
Minamihata K, Goto M, Kamiya N (2011) Protein heteroconjugation by the peroxidase-catalyzed tyrosine coupling reaction. Bioconjugate Chem 22:2332–2338. doi:10.1021/bc200420v
Möhlmann S, Mahlert C, Greven S, Scholz P, Harrenga A (2011) In vitro sortagging of an antibody Fab fragment: overcoming unproductive reactions of sortase with water and lysine side chains. Chembiochem 12:1774–1780. doi:10.1002/cbic.201100002
Montazer M, Lessan F, Pajootan E, Dadashian F (2011) Treatment of bleached wool with trans-glutaminases to enhance tensile strength, whiteness, and alkali resistance. Appl Biochem Biotech 165:748–759. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9293-0
Moreira Teixeira LS, Feijen J, van Blitterswijk CA, Dijkstra PJ, Karperien M (2012) Enzyme-catalyzed crosslinkable hydrogels: emerging strategies for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 33:1281–1290. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.067
Motoki M, Kumazawa Y (2000) Recent trends in transglutaminase technology for food processing. Food Sci Technol Res 6:151–160. doi:10.3136/fstr.6.151
Motoki M, Okiyama A, Nonaka M, Tanaka H, Uchio R, Matsuura A, Ando H, Umeda K (1993) Production of novel transglutaminase derived from Streptoverticillium. Japan Patent JP5023744
Muralidharan V, Muir TW (2006) Protein ligation: an enabling technology for the biophysical analysis of proteins. Nat Methods 3:429–438. doi:10.1038/Nmeth886
Paguirigan A, Beebe DJ (2006) Gelatin based microfluidic devices for cell culture. Lab Chip 6:407–413. doi:10.1039/b517524k
Parthasarathy R, Subramanian S, Boder ET (2007) Sortase A as a novel molecular “stapler” for sequence-specific protein conjugation. Bioconjugate Chem 18:469–476. doi:10.1021/Bc060339w
Pasternack R, Dorsch S, Otterbach JT, Robenek IR, Wolf S, Fuchsbauer HL (1998) Bacterial pro-transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium mobaraense—purification, characterisation and sequence of the zymogen. Eur J Biochem 257:570–576. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2570570.x
Popp MWL, Ploegh HL (2011) Making and breaking peptide bonds: protein engineering using sortase. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5024–5032. doi:10.1002/anie.201008267
Popp MWL, Antos JM, Ploegh HL (2009) Site-specific protein labeling via sortase-mediated transpeptidation. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 15:3.1–15.3.9. doi:10.1002/0471140864.ps1503s56
Quintanar L, Stoj C, Taylor AB, Hart PJ, Kosman DJ, Solomon EI (2007) Shall we dance? How a multicopper oxidase chooses its electron transfer partner. Acc Chem Res 40:445–452. doi:10.1021/Ar600051a
Reiss R, Ihssen J, Thöny-Meyer L (2011) Bacillus pumilus laccase: a heat stable enzyme with a wide substrate spectrum. BMC Biotechnol 11:9. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-11-9
Santhanam N, Vivanco JM, Decker SR, Reardon KF (2011) Expression of industrially relevant laccases: prokaryotic style. Trends Biotechnol 29:480–489. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.04.005
Schrodinger, LLC (2010) The PyMOL molecular graphics system, version 1.4.1.
Selinheimo E, Autio K, Krijus K, Buchert J (2007a) Elucidating the mechanism of laccase and tyrosinase in wheat bread making. J Agr Food Chem 55:6357–6365. doi:10.1021/Jf0703349
Selinheimo E, NiEidhin D, Steffensen C, Nielsen J, Lomascolo A, Halaouli S, Record E, O'Beirne D, Buchert J, Kruus K (2007b) Comparison of the characteristics of fungal and plant tyrosinases. J Biotechnol 130:471–480. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotech.2007.05.018
Serafini-Fracassini D, Del Duca S (2008) Transglutaminases: widespread cross-linking enzymes in plants. Ann Bot London 102:145–152. doi:10.1093/Aob/Mcn075
Sharma R, Lorenzen PC, Qvist KB (2001) Influence of transglutaminase treatment of skim milk on the formation of ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine and the susceptibility of individual proteins towards crosslinking. Int Dairy J 11:785–793. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00096-6
Sheldon RA (2011) Characteristic features and biotechnological applications of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:467–477. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3554-2
Singh H (1991) Modification of food proteins by covalent crosslinking. Trends Food Sci Technol 2:196–200. doi:10.1016/0924-2244(91)90683-A
Singh Arora D, Kumar Sharma R (2010) Ligninolytic fungal laccases and their biotechnological applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:1760–1788. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8676-y
Sofia SJ, Singh A, Kaplan DL (2002) Peroxidase-catalyzed crosslinking of functionalized polyaspartic acid polymers. J Macromol Sci Part A: Pure Appl Chem 39:1151–1181. doi:10.1081/Ma-120014843
Spasser L, Brik A (2012) Chemistry and biology of the ubiquitin signal. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2–25. doi:10.1002/anie.201200020
Spirig T, Weiner EM, Clubb RT (2011) Sortase enzymes in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol Microbiol 82:1044–1059. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07887.x
Stanic D, Monogioudi E, Dilek E, Radosavljevic J, Atanaskovic-Markovic M, Vuckovic O, Raija L, Mattinen M, Buchert J, Cirkovic Velickovic T (2010) Digestibility and allergenicity assessment of enzymatically crosslinked β-casein. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:1273–1284. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200900184
Steffensen CL, Andersen ML, Degn PE, Nielsen JH (2008) Cross-linking proteins by laccase-catalyzed oxidation: importance relative to other modifications. J Agric Food Chem 56:12002–12010. doi:10.1021/jf801234v
Steffolani ME, Ribotta PD, Pérez GT, León AE (2010) Effect of glucose oxidase, transglutaminase, and pentosanase on wheat proteins: relationship with dough properties and bread-making quality. J Cereal Sci 51:366–373. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2010.01.010
Sun XD, Arntfield SD (2011) Gelation properties of chicken myofibrillar protein induced by transglutaminase crosslinking. J Food Eng 107:226–233. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.06.019
Ta HT, Prabhu S, Leitner E, Jia F, von Elverfeldt D, Jackson KE, Heidt T, Nair AKN, Pearce H, von zur Muhlen C, Wang X, Peter K, Hagemeyer CE (2011) Enzymatic single-chain antibody tagging—a universal approach to targeted molecular imaging and cell homing in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 109:365–373. doi:10.1161/Circresaha.111.249375
Takazawa T, Kamiya N, Ueda H, Nagamune T (2004) Enzymatic labeling of a single chain variable fragment of an antibody with alkaline phosphatase by mircobial transglutaminase. Biotechnol Bioeng 86:399–404. doi:10.1002/Bit.20019
Tanaka T, Kamiya N, Nagamune T (2004) Peptidyl linkers for protein heterodimerization catalyzed by microbial transglutaminase. Bioconjugate Chem 15:491–497. doi:10.1021/Bc034209o
Taylor MM, Marmer WN, Brown EM (2007) Evaluation of polymers prepared from gelatin and casein or whey as potential fillers. J Am Leather Chem As 102:111–120
Taylor MM, Lee J, Bumanlag LP, Cooke PH, Brown EM, Hernandez Balada E (2009) Treatment of low-quality hides with fillers produced from sustainable resources: effect on properties of leather. J Am Leather Chem As 104:324–334
Thalmann CR, Lötzbeyer T (2002) Enzymatic cross-linking of proteins with tyrosinase. Eur Food Res Technol 214:276–281. doi:10.1007/s00217-001-0455-0
Tsukiji S, Nagamune T (2009) Sortase-mediated ligation: a gift from Gram-positive bacteria to protein engineering. Chembiochem 10:787–798. doi:10.1002/cbic.200800724
Veitch NC (2004) Horseradish peroxidase: a modern view of a classic enzyme. Phytochemistry 65:249–259. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2003.10.022
Walsh CT (2006) Posttranslational modification of proteins: expanding nature's inventory. Roberts, Greenwood Village
Walsh CT, Garneau-Tsodikova S, Gatto GJ (2005) Protein posttranslational modifications: the chemistry of proteome diversifications. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:7342–7372. doi:10.1002/anie.200501023
Wang Q, Jin G, Fan X, Zhao X, Cui L, Wang P (2010) Antibacterial functionalization of wool via mTGase-catalyzed grafting of ε-poly-l-lysine. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:2486–2497. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8708-7
Wang P, Wang Q, Cui L, Gao M, Fan X (2011) The combined use of cutinase, keratinase and protease treatments for wool bio-antifelting. Fiber Polym 12:760–764. doi:10.1007/s12221-011-0760-6
Weissman AM, Shabek N, Ciechanover A (2011) The predator becomes the prey: regulating the ubiquitin system by ubiquitylation and degradation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 12:605–620. doi:10.1038/Nrm3191
Whitehurst RJ, van Oort M (2010) Enzymes in food technology. Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester
Witayakran S, Ragauskas AJ (2009) Synthetic applications of laccase in green chemistry. Adv Synth Catal 351:1187–1209. doi:10.1002/adsc.200800775
Wong SS, Jameson DM (2012) Chemistry of protein and nucleic acid cross-linking and conjugation, 2nd edn. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Wong CM, Wong KH, Chen XD (2008) Glucose oxidase: natural occurrence, function, properties and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:927–938. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1407-4
Wu J, Corke H (2005) Quality of dried white salted noodles affected by microbial transglutaminase. J Sci Food Agric 85:2587–2594. doi:10.1002/Jsfa.2311
Yokoyama K, Nio N, Kikuchi Y (2004) Properties and applications of microbial transglutaminase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:447–454. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1539-5
Yung CW, Wu LQ, Tullman JA, Payne GF, Bentley WE, Barbari TA (2007) Transglutaminase crosslinked gelatin as a tissue engineering scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A 83A:1039–1046. doi:10.1002/Jbm.A.31431
Yung CW, Bentley WE, Barbari TA (2010) Diffusion of interleukin-2 from cells overlaid with cytocompatible enzyme-crosslinked gelatin hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res A 95A:25–32. doi:10.1002/Jbm.A.32740
Zhu Y, Tramper J (2008) Novel applications for microbial transglutaminase beyond food processing. Trends Biotechnol 26:559–565. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.06.006
Zilhão R, Isticato R, Martins LO, Steil L, Völker U, Ricca E, Moran CP, Henriques AO (2005) Assembly and function of a spore coat-associated transglutaminase of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 187:7753–7764. doi:10.1128/Jb.187.22.7753-7764.2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Heck, T., Faccio, G., Richter, M. et al. Enzyme-catalyzed protein crosslinking. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 461–475 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4569-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4569-z