Abstract
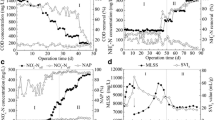
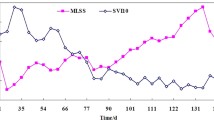
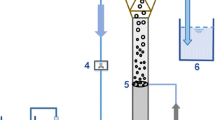
Aerobic granules offer enhanced biological nutrient removal and are compact and dense structures resulting in efficient settling properties. Granule instability, however, is still a challenge as understanding of the drivers of instability is poorly understood. In this study, transient instability of aerobic granules, associated with filamentous outgrowth, was observed in laboratory-scale sequencing batch reactors (SBRs). The transient phase was followed by the formation of stable granules. Loosely bound, dispersed, and pinpoint seed flocs gradually turned into granular flocs within 60 days of SBR operation. In stage 1, the granular flocs were compact in structure and typically 0.2 mm in diameter, with excellent settling properties. Filaments appeared and dominated by stage 2, resulting in poor settleability. By stage 3, the SBRs were selected for larger granules and better settling structures, which included filaments that became enmeshed within the granule, eventually forming structures 2–5 mm in diameter. Corresponding changes in sludge volume index were observed that reflected changes in settleability. The protein-to-polysaccharide ratio in the extracted extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) from stage 1 and stage 3 granules was higher (2.8 and 5.7, respectively), as compared to stage 2 filamentous bulking (1.5). Confocal laser scanning microscopic (CLSM) imaging of the biomass samples, coupled with molecule-specific fluorescent staining, confirmed that protein was predominant in stage 1 and stage 3 granules. During stage 2 bulking, there was a decrease in live cells; dead cells predominated. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) fingerprint results indicated a shift in bacterial community composition during granulation, which was confirmed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. In particular, Janthinobacterium (known denitrifier and producer of antimicrobial pigment) and Auxenochlorella protothecoides (mixotrophic green algae) were predominant during stage 2 bulking. The chitinolytic activity of Chitinophaga is likely antagonistic towards Auxenochlorella and may have contributed to stage 3 stable granule formation. Rhodanobacter, known to support complete denitrification, were predominant in stage 1 and stage 3 granules. The relative abundance of Rhodanobacter coincided with high protein concentrations in EPS, suggesting a role in microbial aggregation and granule formation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Show KY, Tay JH (2008a) Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 26:411–423
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2008b) Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res 42:1644–1650
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2009) Functional consortium from aerobic granules under high organic loading rates. Bioresour Technol 100:3465–3470
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2010) Potential cause of aerobic granular sludge breakdown at high organic loading rates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1601–1610
Anuar AN, Ujang Z, Loosdrecht MV, Kreuk MD (2007) Settling behaviour of aerobic granular sludge. Water Sci Technol 56:55–64
Bartram AK, Lynch MD, Stearns JC, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Neufeld JD (2011) Generation of multimillion-sequence 16S rRNA gene libraries from complex microbial communities by assembling paired-end Illumina reads. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3846–3852
Basuvaraj M, Fein J, Liss SN (2015) Protein and polysaccharide content of tightly and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances and the development of a granular activated sludge floc. Water Res 82:104–114
Beun JJ, Hendriks A, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Morgenroth E, Wilderer PA, Heijnen JJ (1999) Aerobic granulation in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 33:2283–2290
Bura R, Cheung M, Liao B, Finlayson J, Lee B, Droppo I, Leppard G, Liss S (1998) Composition of extracellular polymeric substances in the activated sludge floc matrix. Water Sci Technol 37:325–333
Cao J, Yuan H, Li B, Yang J (2014) Significance evaluation of the effects of environmental factors on the lipid accumulation of Chlorella minutissima UTEX 2341 under low-nutrition heterotrophic condition. Bioresour Technol 152:177–184
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chang IS, Lee CH (1998) Membrane filtration characteristics in membrane-coupled activated sludge system e the effect of physiological states of activated sludge on membrane fouling. Desalination 120:221–233
Chen MY, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2007) Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1463–1469
De Bruin L, de Kreuk M, van der Roest H, Uijterlinde C, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Aerobic granular sludge technology: an alternative to activated sludge? Water Sci Technol 49:11–12
De Kreuk MK, Heijnen JJ, Van Loosdrecht MCM (2005) Simultaneous COD, nitrogen, and phosphate removal by aerobic granular sludge. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:761–769
Del Rio TG, Abt B, Spring S, Lapidus A, Nolan M, Tice H, Lucas S (2010) Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034T). Stand Genomic Sci 2:87
Denkhaus E, Meisen S, Telgheder U, Wingender J (2007) Chemical and physical methods for characterisation of biofilms. Microchim Acta 158:1–27
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Rice EW, Greenberg AE (eds) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Faith DP (1992) Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol Conserv 61:1–10
Flemming H, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633
Flemming HC, Neu TR, Wozniak DJ (2007) The EPS matrix: the house of biofilm cells. J Bacteriol 189:7945–7947
Green SJ, Leigh MB, Neufeld JD (2010) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) for microbial community analysis. Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 4137–4158
Green SJ, Prakash O, Jasrotia P, Overholt WA, Cardenas E, Hubbard D, Kostka JE (2012) Denitrifying bacteria from the genus Rhodanobacter dominate bacterial communities in the highly contaminated subsurface of a nuclear legacy waste site. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1039–1047
Hashidoko Y, Takakai F, Toma Y, Darung U, Melling L, Tahara S, Hatano R (2008) Emergence and behaviors of acid-tolerant Janthinobacterium sp. that evolves N2O from deforested tropical peatland. Soil Biol Biochem 40:116–125
Henderson RK, Baker A, Parsons SA, Jefferson B (2008) Characterisation of algogenic organic matter extracted from Cyanobacteria, green algae and diatoms. Water Res 42:3435–3445
Hu B, Min M, Zhou W, Li Y, Mohr M, Cheng Y, Ruan R (2012) Influence of exogenous CO2 on biomass and lipid accumulation of microalgae Auxenochlorella protothecoides cultivated in concentrated municipal wastewater. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:1661–1673
Kim IS, Kim SM, Jang A (2008) Characterization of aerobic granules by microbial density at different COD loading rates. Bioresour Technol 99:18–25
Kragelund C, Levantesi C, Borger A, Thelen K, Eikelboom D, Tandoi V, Nielsen PH (2008) Identity, abundance and ecophysiology of filamentous bacteria belonging to the Bacteroidetes present in activated sludge plants. Microbiology 154:886–894
Lee CS, Kim KK, Aslam Z, Lee ST (2007) Rhodanobacter thiooxydans sp. nov., isolated from a biofilm on sulfur particles used in an autotrophic denitrification process. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1775–1779
Lee DJ, Chen YY, Show KY, Whiteley CG, Tay JH (2010) Advances in aerobic granule formation and granule stability in the course of storage and reactor operation. Biotechnol Adv 28:919–934
Li AJ, Zhang T, Li XY (2010) Fate of aerobic bacterial granules with fungal contamination under different organic loading conditions. Chemosphere 78:500–509
Liao B, Allen D, Droppo G, Leppard G, Liss SN (2001) Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res 35:339–350
Liss SN, Liao BQ, Droppo IG, Allen DG, Leppard GG (2002) Effect of solids retention time on floc structure. Water Sci Technol 46:431–438
Liu Y, Liu QS (2006) Causes and control of filamentous growth in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol Adv 24:115–127
Liu Y, Tay JH (2004) State of the art of biogranulation technology for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 22:533–563
Liu J, Liu C, Edwards E, Liss SN (2006) Effect of phosphorus limitation on microbial floc structure and gene expression in activated sludge. Water Sci Technol 54:247–255
Lu HF, Zheng P, Ji QX, Zhang HT, Ji JY, Wang L, Chen JW (2012) The structure, density and settlability of anammox granular sludge in high-rate reactors. Bioresour Technol 123:312–317
Lynch MD, Masella AP, Hall MW, Bartram AK, Neufeld JD (2013) AXIOME: automated exploration of microbial diversity. GigaScience 2:3
Mahapatra DM, Chanakya HN, Ramachandra TV (2014) Bioremediation and lipid synthesis through mixotrophic algal consortia in municipal wastewater. Bioresour Technol 168:142–150
Mahendran B, Lishman L, Liss SN (2012) Structural, physicochemical and microbial properties of flocs and biofilms in integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFFAS) systems. Water Res 46:5085–5101
Masella AP, Bartram AK, Truszkowski JM, Brown DG, Neufeld JD (2012) PANDAseq: paired-end assembler for Illumina sequences. BMC Bioinforma 13:31
McSwain B, Irvine R, Wilderer P (2004) The effect of intermittent feeding on aerobic granule structure. Water Sci Technol 49:19–25
McSwain BS, Irvine RL, Hausner M, Wilderer PA (2005) Composition and distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic flocs and granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1051–1057
Muyzer G, Brinkhoff T, Nübel U, Santegoeds C, Schäfer H, Wawer C (1998) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) in microbial ecology. In: Akkermans ADL, van Elsas JD, de Bruijn FJ (eds) Molecular microbial ecology manual. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 1–27
Pantanella F, Berlutti F, Passariello C, Sarli S, Morea C, Schippa S (2007) Violacein and biofilm production in Janthinobacterium lividum. J Appl Microbiol 102:992–999
Prakash O, Green SJ, Jasrotia P, Overholt WA, Canion A, Watson DB, Kostka JE (2012) Rhodanobacter denitrificans sp. nov., isolated from nitrate-rich zones of a contaminated aquifer. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2457–2462
Raszka A, Chorvatova M, Wanner J (2006) The role and significance of extracellular polymers in activated sludge. Part I: literature review. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 34:411–425
Sangkhobol V, Skerman VBD (1981) Chitinophaga, a new genus of chitinolytic myxobacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 31:285–293
Schwarzenbeck N, Borges JM, Wilderer PA (2005) Treatment of dairy effluents in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:711–718
Sheng G, Yu H, Li X (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28:882–894
Shirata A, Tsukamoto T, Yasui H, Hata T, Hayasaka S, Kojima A, Kato H (2000) Isolation of bacteria producing bluish-purple pigment and use for dyeing. Jpn Agr Res Q 34:131–140
Show KY, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2012) Aerobic granulation: advances and challenges. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167:1622–1640
Stewart JR, Brown RM (1969) Cytophaga that kills or lyses algae. Science 164:1523–1524
Tay JH, Liu QS, Liu Y (2001) The role of cellular polysaccharides in the formation and stability of aerobic granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:222–226
Wang ZW, Liu Y, Tay JH (2005) Distribution of EPS and cell surface hydrophobicity in aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:469–473
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang J, Yang H, Wang F (2014) Mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae for biodiesel production: status and prospects. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:3307–3329
Weissbrodt DG, Neu TR, Kuhlicke U, Rappaz Y, Holliger C (2013) Assessment of bacterial and structural dynamics in aerobic granular biofilms. Front Microbiol 4:175
Williams J, de los Reyes F (2006) Microbial community structure of activated sludge during aerobic granulation in an annular gap bioreactor. Water Sci Technol 54:139–146
Zheng YM, Yu HQ, Liu SJ, Liu XZ (2006) Formation and instability of aerobic granules under high organic loading conditions. Chemosphere 63:1791–1800
Zhou W, Li Y, Min M, Hu B, Zhang H, Ma X, Ruan R (2012) Growing wastewater-born microalga Auxenochlorella protothecoides UMN280 on concentrated municipal wastewater for simultaneous nutrient removal and energy feedstock production. Appl Energy 98:433–440
Acknowledgments
We thank Katja Engel for assistance with sequencing. SNL and JDN acknowledge funding from Discovery Grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). SNL and HA acknowledge funding from Queen’s University and NSERC Collaborative Research and Training Experience (CREATE).
The authors declare that the research is in compliance with ethical standards, and they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aqeel, H., Basuvaraj, M., Hall, M. et al. Microbial dynamics and properties of aerobic granules developed in a laboratory-scale sequencing batch reactor with an intermediate filamentous bulking stage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 447–460 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6981-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6981-7