Abstract
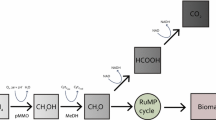
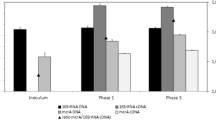
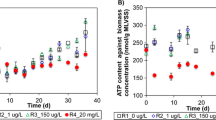
Over the last decades, anaerobic bioreactor technology proved to be a competitive technology for purifying wastewater while producing biogas. Methanogens perform the crucial final step in methane production, and monitoring their activity is of paramount importance for system understanding and management. Cofactor F430 is an essential prosthetic group of the methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) enzyme catalysing this final step. This research investigates whether the quantification of cofactor F430 in bioreactor systems is a viable intermediate-complexity monitoring tool in comparison to the conventional biogas and volatile fatty acid (VFA) concentration follow-up and molecular genetic techniques targeting the mcrA gene encoding the MCR protein or its transcripts. Cofactor F430 was quantified in a lab-scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) using liquid chromatography. The system was subjected to two organic loading rate shocks, and the F430 content of the sludge was followed up alongside mcrA gene copy and transcript numbers and classical performance monitoring tools. The research showed for the first time the combined mcrA gene transcript and F430 content dynamics in an anaerobic bioreactor system and reveals their significant positive correlation with in situ methane production rate. The main difference between the two monitoring methods relates to the cofactor’s slower degradation kinetics. The work introduces the use of cofactor F430 as a biomarker for methanogenic activity and, hence, as a monitoring tool that can be quantified within half a working day, yielding information directly related to in situ methanogenic activity in methanogenic reactors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen KD, Wegener G, White RH (2014) Discovery of multiple modified F430 coenzymes in methanogens and anaerobic methanotrophic archaea suggests possible new roles for F430 in nature. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(20):6403–6412. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02202-14
Alvarado A, Montández-Hernañdez LE, Palacio-Molina SL, Oropeza-Navarro R, Luévanos-Escareño MP, Balagurusamy N (2014) Microbial trophic interactions and mcrA gene expression in monitoring of anaerobic digesters. Front Microbiol 5(597):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00597
Amha YM, Zohaib Anwar M, Brower A, Jacobsen CS, Stadler LB, Webster TM, Smith AL (2017) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion processes: applications of molecular tools. Bioresour Technol (in press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.210
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (1995), 21st edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC
Castellano M, Ruiz-Filippi G, González W, Roca E, Lema JM (2007) Selection of variables using factorial discriminant analysis for the state identification of an anaerobic UASB-UAF hybrid pilot plant, fed with winery effluents. Water Sci Technol 56(2):139–145. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2007.482
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162(1):156–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90021-2
De Bok FAM, Plugge CM, Stams AJM (2004) Interspecies electron transfer in methanogenic propionate degrading consortia. Water Res 38(6):1368–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.11.028
De Vrieze J, Verstraete W, Boon N (2013) Repeated pulse feeding induces functional stability in anaerobic digestion. Microb Biotechnol 6(4):414–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12025
Dereli RK, Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Ozturk I, Jeison D, van der Zee F, van Lier JB (2012) Potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors to overcome treatment limitations induced by industrial wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 122:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.139
Diekert G, Konheiser U, Piechulla K, Thauer RK (1981) Nickel requirement and factor nickel requirement and factor F430 content of methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol 148(2):459–464
Diekert G, Weber B, Thauer RK (1980) Nickel dependence of factor F430 content in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol 127(3):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427204
Dimarco AA, Bobik TA, Wolfe RS (1990) Unusual coenzymes of methanogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem 59(1):355–394. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002035
Duin EC (2009) Role of coenzyme F430 in methanogenesis. In: Warren M, Smith A (eds) Tetrapyrroles: birth, life and death. Landes Bioscience and Springer Science and Business Media, New York, pp 352–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-78518-9_23
Ellefson WL, Whitman WB, Wolfe RS (1982) Nickel-containing factor F430: chromophore of the methylreductase of Methanobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79(12):3707–3710. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.79.12.3707
Fang HHP (2000) Microbial distribution in UASB granules and its resulting effects. Water Sci Technol 42:201–208
Freitag TE, Toet S, Ineson P, Prosser JI (2010) Links between methane flux and transcriptional activities of methanogens and methane oxidizers in a blanket peat bog. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00871.x
Gorris LGM, van der Drift C, Vogels GD (1988) Separation and quantification of cofactors from methanogenic bacteria by high-performance liquid chromatography: optimum and routine analyses. J Microbiol Methods 8(3):175–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(88)90018-8
Jensen PD, Yap SD, Boyle-Gotla A, Janoschka J, Carney C, Pidou M, Batstone DJ (2015) Anaerobic membrane bioreactors enable high rate treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. Biochem Eng J 97:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.02.009
Jiang B (2006) The effect of trace elements on the metabolism of methanogenic consortia. Dissertation, Wageningen University
Kampmann K, Ratering S, Baumann R, Schmidt M, Zerr W, Schnell S (2012) Hydrogenotrophic methanogens dominate in biogas reactors fed with defined substrates. Syst Appl Microbiol 35(6):404–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2012.07.002
Kaneko M, Takano Y, Ohkouchi N, Sakata S (2017) Does intact coenzyme F430 accumulate?: implication for its use as proxies for methane production and consumption. In: 28 th International Meeting on Organic Geochemistryh International Meeting on Organic Geochemistry
Kaneko M, Takano Y, Chikaraishi Y, Ogawa NO, Asakawa S, Watanabe T, Shima S, Kruger M, Matsushita M, Kimura H, Ohkouchi N (2014) Quantitative analysis of coenzyme F430 in environmental samples: a new diagnostic tool for methanogenesis and anaerobic methane oxidation. Anal Chem 86(7):3633–3638. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500305j
Kaneko M, Takano Y, Ogawa NO, Sato Y, Yoshida N, Ohkouchi N (2016) Estimation of methanogenesis by quantification of coenzyme F430 in marine sediments. Geochem J 50(6):1–8. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.2.0410
Kangle KM, Kore SV, Kore VS, Kulkarni GS (2012) Recent trends in anaerobic codigestion: a review. Univers J Environ Res Technol 2:210–219
Kida K, Shigematsu T, Kijima J, Numaguchi M, Mochinaga Y, Abe N, Morimura S (2001) Influence of Ni2+ and Co2+ on methanogenic activity and the amounts of coenzymes involved in methanogenesis. J Biosci Bioeng 91(6):590–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80179-1
Larson DR, Singer RH, Zenklusen D (2009) A single molecule view of gene expression. Trends Cell Biol 19(11):630–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2009.08.008
Luton PE, Wayne JM, Sharp RJ, Riley PW (2002) The mcrA gene as an alternative to 16S rRNA in the phylogenetic analysis of methanogen populations in landfill. Microbiology 148(11):3521–3530. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-148-11-3521
Ma K, Conrad R, Lu Y (2012) Responses of methanogen mcrA genes and their transcripts to an alternate dry/wet cycle of paddy field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(2):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06934-11
Mayr S, Latkoczy C, Krüger M, Günther D, Shima S, Thauer RK, Widdel F, Jaun B (2008) Structure of an F430 variant from archaea associated with anaerobic oxidation of methane. J Am Chem Soc 130(32):10758–10767. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja802929z
Morris RL, Schauer-Gimenez A, Bhattad U, Kearney C, Struble CA, Zitomer D, Maki JS (2013) Methyl coenzyme M reductase (mcrA) gene abundance correlates with activity measurements of methanogenic H2/CO2-enriched anaerobic biomass. Microb Biotechnol 7(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12094
Morris RL, Tale VP, Mathai PP, Zitomer DH, Maki JS (2015) mcrA gene abundance correlates with hydrogenotrophic methane production rates in full-scale anaerobic waste treatment systems. Lett Appl Microbiol 62(2):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12515
Moura I, Moura JJG, Santos H, Xavier AV, Burch G, Peck HD, LeGall J (1983) Proteins containing the factor F430 from Methanosarcina barkeri and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Isolation and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)/Protein Struct Mol 742(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4838(83)90362-X
Munk B, Bauer C, Gronauer A, Lebuhn M (2012) A metabolic quotient for methanogenic archaea. Water Sci Technol 66(11):2311–2317. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.436
Nielsen HB, Uellendahl H, Ahring BK (2007) Regulation and optimization of the biogas process: propionate as a key parameter. Biomass Bioenergy 31(11-12):820–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.04.004
Ramos C, García A, Diez V (2014) Performance of an AnMBR pilot plant treating high-strength lipid wastewater: biological and filtration processes. Water Res 67:203–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.021
Schauer-Gimenez AE, Zitomer DH, Maki JS, Struble CA (2010) Bioaugmentation for improved recovery of anaerobic digesters after toxicant exposure. Water Res 44(12):3555–3564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.03.037
Shigematsu T, Era S, Mizuno Y, Ninomiya K, Kamegawa Y, Morimura S, Kida K (2006) Microbial community of a mesophilic propionate-degrading methanogenic consortium in chemostat cultivation analyzed based on 16S rRNA and acetate kinase genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(2):401–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0275-4
Switzenbaum MS, Giraldo-Gomez E, Hickey RF (1990) Monitoring of the anaerobic methane fermentation process. Enzym Microb Technol 12(10):722–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(90)90142-D
Wang L, Shammas N, Hung Y-T (2009) Advanced biological treatment processes. Humana Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-170-7
Watanabe T, Kimura M, Asakawa S (2009) Distinct members of a stable methanogenic archaeal community transcribe mcrA genes under flooded and drained conditions in Japanese paddy field soil. Soil Biol Biochem 41(2):276–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.10.025
Weiland P (2010) Biogas production: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(4):849–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2246-7
Wijekoon KC, Visvanathan C, Abeynayaka A (2011) Effect of organic loading rate on VFA production, organic matter removal and microbial activity of a two-stage thermophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 102(9):5353–5360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.081
Zhang TC, Noike T (1994) Influence of retention time on reactor performance and bacterial trophic populations in anaerobic digestion processes. Water Res 28(1):27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90116-3
Zhou J, Bruns MANN, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Acknowledgements
P.V.G. is supported as doctoral candidate (aspirant) by the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO). The scientific responsibility is assumed by its authors. We thank Pentair (The Netherlands) for kindly providing the membrane.
Funding
This study was funded by the KU Leuven Industrial Research Fund (IOF AnMBR Knowledge Platform project—KP/13/004) and by the BELSPO IAP-project μ-manager no. P7/25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 785 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passaris, I., Van Gaelen, P., Cornelissen, R. et al. Cofactor F430 as a biomarker for methanogenic activity: application to an anaerobic bioreactor system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 1191–1201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8681-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8681-y