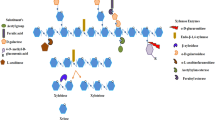
Abstract.
Despite an increased knowledge of microbial xylanolytic systems in the past few years, further studies are required to achieve a complete understanding of the mechanism of xylan degradation by microorganisms and their enzymes. The enzyme system used by microbes for the metabolism of xylan is the most important tool for investigating the use of the second most abundant polysaccharide (xylan) in nature. Recent studies on microbial xylanolytic systems have generally focussed on induction of enzyme production under different conditions, purification, characterization, molecular cloning and expression, and use of enzyme predominantly for pulp bleaching. Rationale approaches to achieve these goals require a detailed knowledge of the regulatory mechanism governing enzyme production. This review will focus on complex xylan structure and the microbial enzyme complex involved in its complete breakdown, studies on xylanase regulation and production and their potential industrial applications, with special reference to biobleaching.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received revision: 25 April 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beg, .Q., Kapoor, .M., Mahajan, .L. et al. Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56, 326–338 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100704
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100704