Abstract.
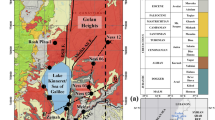
The chemical content of the Souss unconfined groundwater displays spatial variations in conductivity (between 400 and 6,000 µS cm–1). The chemical tracers (Cl–, SO4 2–, Sr2+, Br–), which characterize the different components of the groundwater, allowed the determination of the origin of water salinity. Cl– and SO4 2–, reaching respectively 2,000 and 1,650 mg L–1, display localized salinity anomalies. Br–/Cl– ratio distinguishes marine-influenced impoverished zones versus the oceanic domain. Thus, salinity anomalies can be attributed: (1) downstream, to a currently existing salt-encroachment (with added waste water) and sedimentary palaeosalinity, (2) in the middle-Souss, to High Atlas evaporites and to irrigation water recycling. Sr2+/Ca2+ ratio (evaporites if >1‰), confirms the evaporitic origin of the anomalies along the right bank of oued Souss. Furthermore, it facilitates the distinction between the different aquifer contributions (Cretaceous, Jurassic and Triassic), and it highlights leakage from deep Turonian limestones in the groundwater recharge system. To the south, recharge is from the Anti Atlas (evaporite-free) waters. Oxygen-18 measurements confirm the groundwater recharge from the High and Anti Atlas as piezometric maps and chemical tracers suggested, plus from leakage from the Turonian and the marine aquifers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsissou, .Y., Bouchaou, .L., Mudry, .J. et al. Use of chemical tracing to study acquisition modalities of the mineralization and behaviour of unconfined groundwaters under a semi-arid climate: the case of the Souss plain (Morocco). Env Geol 42, 672–680 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0576-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0576-1