Abstract
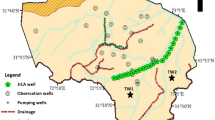
An innovative approach to solve the problem of lowering water table was carried out in a quarry lake south of the city of Milan (northern Italy): the project, based upon pumping out water at a rate of 1,000 L/s can be considered a strategic medium to long-term solution to hinder the rise of groundwater level interfering with underground structures (foundation, construction, subway) in urban areas. The basic idea is to pump a high groundwater rate as close as possible to the stagnation point of the piezometric depression located in the city. After a pilot-test was carried out in November 1998, experimental activities started in July 2001 and lasted one year; water withdrawal was discharged into artificial channels used in agricultural practice. Maximum drawdowns measured in the quarry lake by the monitoring network resulted in more than 5 m, and a significant drawdown was registered up to 1.5 km of distance from the quarry in the important historical site of Chiaravalle Abbey, threatened by groundwater rise. The results of this pumping activity confirm the importance of the project, its lower cost compared with traditional solutions (such as drainage by wells) and remarkable effects on the improvement of surface water quality. A groundwater model was implemented to evaluate further scenarios of discharge rate and pumping location, too.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avanzini M, Beretta GP, Pagotto A, Peterlongo G (1998) Sollevamento della falda a Milano ed hinterland. Ambiente, n. 5, IPSOA, Milano
Beretta GP, Avanzini M (1998) La gestione sostenibile del sollevamento della falda a Milano ed hinterland. L’ACQUA, Rivista bimestrale dell’Associazione Idrotecnica Italiana, n. 1–2, Roma
Beretta GP, Pagotto A, Vandini R, Zanni S (1992) Aquifer overexploitation in the Po Plain: hydrogeological, geotechnical and hydrochemical aspects. In: Selected papers on aquifer overexploitation, 23rd International Congress of the I.A.H., Puerto de la Cruz, Tenerife (Spain), April 15–19, vol 3, Heise, Hannover, pp 115–130
Maione U (1989) Vulnerabilità e controllo delle falde acquifere. Gruppo Nazionale per la Difesa dalle Catastrofi Idrogeologiche. L.R.4, rapporto 1986–1989, Presidenza del Consiglio dei Ministri, Dipartimento della Protezione Civile, Roma
Mazzarella S, De Felice G (1980) Criteri idrogeologici nella lotta all’inquinamento dell’acquifero milanese. Ingegneria Ambientale, vol 9, n. 6, Milano
McDonald MG, Harbaugh AW (1988) A modular three-dimensional finite difference groundwater flow model. USGS TWI 6-A1
Provincia di Milano (1998) Indagine idrogeologica per un progetto pilota di drenaggio della falda mediante il ricorso ad un bacino di cava posto nel settore Sud Milano – Atti provinciali n.59364/571/97, Provincia di Milano
Regione Lombardia (2001) Acque sotterranee in Lombardia: gestione sostenibile di una risorsa strategica. Assessorato alle Risorse idriche e Servizi di pubblica utilità, Milano
Regione Lombardia, ENI Agip (2002) Geologia degli Acquiferi Padani della Regione Lombardia, S.E.L.C.A., Firenze
Riemann U (1997) Engineering investigation and technological solutions for the groundwater lowering in the city of Dessau (Germany). In: Chilton et al. (eds) Groundwater in the urban environment: problems, process and management. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 255–260
Simpson B, Blower T, Craig RN, Wilkinson WB (1989) The engineering implication of rising groundwater levels in the deep aquifer beneath London. Construction Industry Research & Information Association-Spec Publ no 69, CIRIA, London
Vasquez-Suñé E, Sanchez-Vila X, Carrera J, Marizza M, Arandes R, Gutierrez LA (1997) Rising groundwater levels in Barcelona: evolution and effects on urban structures. In: Chilton et al. (eds) Groundwater in the urban environment: problems, process and management. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 267–271
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Environmental Department of the Milan Province Government for support to the implementation of the project and the authorization to the publishing of its results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beretta, G.P., Avanzini, M. & Pagotto, A. Managing groundwater rise: Experimental results and modelling of water pumping from a quarry lake in Milan urban area (Italy). Env Geol 45, 600–608 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0918-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0918-7