Abstract
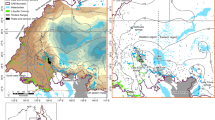
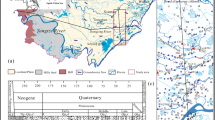
Surface- vs. ground-water chemistry in the Heihe River basin, assessed through field sampling of precipitation, surface water and groundwater, allowed geographical zones and chemical types to be differentiated. The geographical zones included: alpine ice-snow (>3,900 m), alpine meadow (3,400–3,900 m), mountain forest and shrub (2,600–3,400 m), mountain grassland (1,900–2,600 m) and desert grassland (1,500–1,900 m). Groundwater chemical types included: (1) mountain fissure and piedmont gravel, bicarbonate, (2) piedmont diluvial, alluvial and lacustrine plain, sulphate, and (3) desert salt-accumulating depression, chloride. Since the 1960s, large volumes of river water diverted for irrigation have been found to re-emerge as spring water at the edge of alluvial fans and then reintegrate the Heihe River. After a number of reuses and re-emergences in the middle reaches, the river’s level of mineralization has doubled. Hydrological changes have resulted in the marked degradation of aquatic habitats, and caused substantial, and expanding, land salinization and desertification. Solving these largely anthropogenic problems requires concerted, massive and long-term efforts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bu-Awwad AM (1999) Effects of sand column, furrow and supplemental irrigation on agricultural production in an arid environment. Irrig Sci 18(4):191–197
Chen JQ, Xia J (1999) Facing the challenge: barriers to sustainable water resources development in China. Hydrol Sci J 44(4):507–510
Cheng LH, Li FX, Di XM, Zhang JX (1998) Aeolian sandy soils in China (in Chinese). Sciences Press, Beijing
Feng Q (1999) Sustainable utilization of water resources in Gansu Province. Chin J Arid Land Res 11:293–299
Feng Q, Cheng GD (1998) Current situation, problem and rational utilization of water resources in arid north-western China. J Arid Environ 40:373–382
Feng Q, Cheng GD, Endo KH (2001) Towards sustainable development of the environmentally degraded river Heihe basin, China. Hydrol Sci J 46(5):651–660
Feng Q, Cheng GD, Masao MK (2000) Trends of water resource development and utilization in arid north-west China. Environ Geol 39(8):831–832
Feng Q, Cheng GD, Mikami M (1999) Water resources in China: problems and countermeasures. Ambio 28:202–203
Feng Q, Endo KH, Cheng GD (2002a) Dust storms in China: a case study of dust storm variation and dust characteristics. Bull Eng Geol Environ 61(5): 253–261
Feng Q, Endo KH, Cheng GD (2002b) Soil water and chemical characteristics of sandy soils and their significance to land reclamation. J Arid Environ 51:35–54
Goldsmith JR, Graf DL (1958) Relationship between lattice constants and composition of the Ca-Mg carbonates. Am Mineral 42:84–101
Greiner R (1997) Optimal farm management responses to emerging soil salinisation in a dry land catchment in eastern Australia. Land Degrad Dev 8(4):281–303
Kang SZ, Shi P, Pan Y, Liang HZ, Hu SXT, Zhang J (2000) Soil water distribution, uniformity and water-use efficiency under alternate furrow irrigation in arid areas. Irrig Sci 19(4):181–190
Kang Y, Yuan BZ, Nishiyama SC (1999) Design of micro-irrigation laterals at minimum cost. Irrig Sci 18(3):125–133
Kundzewicz ZW (1997) Water resources for sustainable development. Hydrol Sci J 42(4):467–480
Latif SA, Oura Y, Ebihara M, Kallemeyn GW, Nakahara H, Yonezawa C, Matusue T, Sawahata H (1999) Prompt gamma ray analysis (PGA) of meteorite samples, with emphasis on the determination of Si. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 239: 577–580
Liu YC (1988) A preliminary study on the ecological environment evolution in Min in Oasis-Hexi Corridor. Chin J Arid Land Res 1(3):55–57
Liu YC (1991) An approach to the ecological structure of irrigation oasis agriculture in the Heihe valley-Hexi Corridor. Chin J Arid Land Res 4(2):15–20
Liu YS, Gao J (2002) Trend analysis of land degradation in the zone along the Great Wall in Northern Shaanxi. Acta Geographica Sinica 57(4):443–450
Munsell C (1975) Munsell color chart. In: Munsell color. Baltimore, pp 18–19
Rhoades JD (1978) Monitoring soil salinity: a review of methods. In: Everett LG, Schmidt KD (eds) Establishment of water quality monitoring programs. American Water Research Association, St Paul MN, pp 150–165
Second Geology Investigation Team of Northwest China (1995) Groundwater Resources in Northwest China (in Chinese). Geology Press, Beijing
Smil V (1987) Land degradation in China: an ancient problem getting worse. In: Blaikie P, Brookfield H (eds) Land degradation and society. Methuen, London
Smil V (1993) China’s environmental crisis: an inquiry into the limits of national development. ME Sharpe, New York
Sueki K, Kobayashi K, Sato W, Nakahara H, Tomizawa T (1996) Nondestructive determination of major elements in a large sample by prompt γ-ray neutron activation analysis. Anal Chem 68:2203–2209
Xia J, Takeuchi K (1999) Introduction to special issue on barriers to sustainable management of water quantity and quality. Hydro Sci J 44 (4):503–506
Yonezawa C, Wood AKH, Hoshi M, Ito Y, Tachikawa E (1993) The characteristics of the prompt gamma-ray analyzing system at the neutron beam guides of JRR-3 M. Nucl Instr Meth A329:207–216
Zhang H, Wang X, You M, Liu C (1999) Water-yield relations and water-use efficiency of winter wheat in the north China plain. Irrig Sci 19(1):37–45
Zhang HP (2002) Relationship between Ejina Oasis and water resources in the lower river basin of Heihe. Adv Water Sci 13(2):223–228
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the Hundred Talent Scholar Foundation (2003401), Key Project (KZCX1-09-03) and (KZCX1-10-06) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and National Nature Sciences Foundation of China (40171007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Liu, W., Su, Y. et al. Distribution and evolution of water chemistry in Heihe River basin. Env Geol 45, 947–956 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0950-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0950-7