Abstract
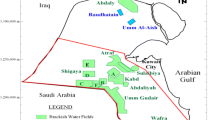
Aquifers consisting of unconsolidated sediments in the coastal area near Zhanjiang in southern China are grouped into the shallow, middle-deep and deep aquifer systems. Groundwater exploitation began in the 1950s in this district and has increased from year to year since 1980. Measurements of groundwater levels and monitoring data of groundwater chemistry at some 60 wells since 1981 are examined to analyze the evolution of hydrodynamics and hydrochemistry in the coastal aquifers. The results indicate that groundwater levels in the middle-deep and deep aquifer systems have fallen continuously and the extents of the depression cones in water levels have increased in the past two decades, even though the water levels recovered to some degree during the period of 1997–2001. In 2004, the lowest water levels in the middle-deep and deep aquifer systems were 23.58 and 21.84 m below sea level, respectively. The groundwater has TDS ranging from 40 to 550 mg/L, and is of low pH, commonly varies between 4 and 7. Concentrations of total iron and manganese exceed the concentration limits of the drinking water standards. The hardness is in the range of 10–250 mg/L. Chloride contents of the groundwater range from 10 to 60 mg/L. The chloride and TDS do not show systematically increasing trends. Although the water levels in the exploitation center near the coast are significantly lower than the sea level and the depression cones of water levels in the middle-deep and deep aquifer systems have expanded to the sea, sea water intrusion has not been observed until recently. This phenomenon is quite unique in the coastal area near Zhanjiang.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulla FA, Al-khatib MA, Al-Ghazzawi ZD (2000) Development of groundwater modeling for the Azraq Basin, Jordan. Environ Geol l40(1/2):11–18
Cao X (1997) Formation and development of the depression cone of the confined aquifer in the Sushui Basin (in Chinese). Groundwater 19(3):94–97
Edet AE, Okereke CS (2001) A regional study of saltwater intrusion in southeastern Nigeria based on the analysis of geoelectrical and hydrochemical data. Environ Geol 40(10):1278–1289
Edmunds WM, Carrillo-Rivera JJ, Cardona A (2002) Geochemical evolution of groundwater beneath Mexico City. J Hydrol 258(1–4):1–24
Herbert AW, Lloyd JW (2000) Modelling saline intrusion in the assessment of small limestone island resources. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 33:77–86
Guangdong Bureau of Geology (1981) Report of regional hydrogeologic investigation of China: Leizhou Peninsula (1/200000) (in Chinese)
Guvarasen V, Wade SC, Barcelo MD (2000) Simulation of regional ground water flow and salt water intrusion in Herrado County, Florida. Ground Water 38(5):772–783
Lawrence AK, Gooddy AK, Kanatharana P, Meesilp W, Ramnarong V (2000) Groundwater evolution beneath Hat Yai, a rapidly developing city in Thailand. Hydrogeol J 8:564–575
Sadeg SA, Karahanoglu N (2001) Numerical assessment of seawater intrusion in the Tripoli region, Libya. Environ Geol 40(9):1151–1168
Shao J (1998) An analysis of the depression cone of the deep-seated confined aquifer in Langfang (in Chinese). Eng Inv 5:44–45
Song X, Kayane L, Tanaka T, Shimada J (1999) Conceptual model of the evolution of groundwater quality at the wet zone in Sri Lanka. Environ Geol 39(2):149–164
Su Z (1997) Strategies of development of groundwater regarding prevention of sea water intrusion in Zhanjinag (in Chinese). Eng Inv 2:29–33
Wang G (1999) A model of the depression cone of groundwater to the west of Liaocheng (in Chinese). Groundwater 21(1):27–29
Zhang Z, Shen Z, Xie Y et al (2000) Evolution in the groundwater environment in the North China Plain (in Chinese). Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Zhou X, Chen M, Wan L, Wang J, Ning X (2000a) Optimal groundwater development in coastal aquifers near Beihai, China. J China Univ Geosci 11(3):334–340
Zhou X, Chen M, Ju X, Ning X, Wang J (2000b) Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion near Beihai, China. Environ Geol 40(1/2):223–233
Zhou X, Chen M, Liang C (2003) Optimal schemes of groundwater exploitation for prevention of sea water intrusion in the Leizhou Peninsula, southern China. Environ Geol 43(8):978–985
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Project of the Ministry of Education of China (No. 105032). The authors would like to thank Mr. Liang Chisheng from the Guangdong Bureau of Geology and Exploration, and Mr. Kang Xinghong, from the First Party of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology of Guangdong, for their help in the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xun, Z., Xia, Y., Juan, L. et al. Evolution of the groundwater environment under a long-term exploitation in the coastal area near Zhanjiang, China. Environ Geol 51, 847–856 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0364-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0364-4