Abstract
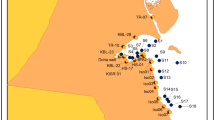
Evolution of the shallow groundwater quality under saline intrusion in porous aquifer system has been studied with environmental isotopes and geochemistry in the Laizhou Bay area, China. Two campaigns of water sampling from various sources were carried out in spring and winter for environmental isotopic and chemical analyses. The origin of groundwater salinity from intrusion of both modern seawater and deep brine water was identified by analysing the correlations between 18O, D, T, Cl−, SO 2−4 and electrical conductivity. The results indicate that the brine is originated from evaporating and concentrating of intruded seawater and its δD and δ18O are different from modern seawater but similar to those of mixture of seawater with fresh groundwater. It is hard to distinguish the salinity origin in this area by the δD–δ18O relationship alone. The relations between δ18O and conductivity, Cl− and SO 2−4 have been used to identify the salinity origin due to the distinct difference in salinity between the brine and seawater, conjunctively with use of T. A threshold of T = 12 TU was adopted to identify the origin of saline groundwater.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bath A, Richards H, Metcalfe R, McCartney R, Degnan P, Littleboy A (2006) Geochemical indicators of deep groundwater movements at Sellafield, UK. J Geochem Explor 90:24–44
Bendavid OK, Sass E, Katz A (2004) The evolution of marine evaporitic brines in inland basins: The Jordan–Dead Sea Rift valley. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(8):1763–1775
Bennetts DA, Webb JA, Stone DJM, Hill DM (2006) Understanding the salinisation process for groundwater in an area of south-eastern Australia, using hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. J Hydrol 323:178–192
Carreon-Diazconti C, Nelson ST, Mayo AL, Tingey DG, Smith M (2003) A mixed groundwater system at Midway, UT: discriminating superimposed local and regional discharge. J Hydrol 273:119–138
Chen M, Ma F (2002) Groundwater and environment of China (in Chinese). Seismological Press, Beijing, 481p
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC-Press LLC, Florida, p 328
Conti A, Sacchi E, Chiarle M, Martinelli G, Zuppi GM (2000) Geochemistry of the formation waters in the Po plain (Northern Italy): an overview. Appl Geochem 15:51–65
Cruz JV, Silva MO (2000) Groundwater salinization in Pico Island (Azores, Portugal): origin and mechanisms. Environ Geol 39(10):1181–1189
Dutkiewicz A, Herczeg AL, Dighton JC (2000) Past changes to isotopic and solute balances in a continental playa: clues from stable isotopes of lacustrine carbonates. Chem Geol 165:309–329
Farber E, Vengosh A, Gavrieli I, Marie A, Bullen TD, Mayer B, Holtzman R, Segal M, Shavit U (2004) The origin and mechanisms of salinization of the Lower Jordan River. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1989–2006
Fritz P, Fontes JCH (1980) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, 1. The terrestrial environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 75–140
González PE, Carrillo AC, Levresse G, Tello EH, Venegas SS, Ramirez GS, Pal-Verma M, Tritlla J, Camprubi A (2005) Hydro-geochemical and isotopic fluid evolution of the Los Azufres geothermal field. Central Mexico Appl Geochem 20(1):23–39
Grobe M, Machel HG, Heuser H (2000) Origin and evolution of saline groundwater in the Munsterland Cretaceous Basin, Germany: oxygen, hydrogen, and strontium isotope evidence. J Geochem Explor 69–70:5–9
Huddart PA, Longstaffe FJ, Crowe AS (1999) δD and δ18O evidence for inputs to groundwater at a wetland coastal boundary in the southern Great Lakes region of Canada. J Hydrol 214:18–31
Jørgensen NO (2002) Origin of shallow saline groundwater on the Island of Denmark. Chem Geol 184:359–370
Kendall C, McDonnell JJ (eds) (1998) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 839p
Kim Y, Lee K-S, Koh D-C, Lee D, Lee S, Park W, Koh G, Woo N (2003) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: a case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea. J Hydrol 270:282–294
Lee J, Kim R, Chang H (2003) Interaction between groundwater quality and hydraulic head in an area around an underground LPG storage cavern, Korea. Environ Geol 43:901–912
Louvat D, Michelot JL, Aranyossy JF (1999) Origin and residence time of salinity in the Äspö groundwater system. Appl Geochem 14:917–925
Ma F, Yang Y, Cai Z, Chen M, Yuan R (2005) Dynamic process analyses of saline intrusion with over-exploitation by coupled flow and dispersive modeling. Environ Geol 48(6):818–828
Ortega GA (2003) Origin and geochemical evolution of groundwater in a closed-basin clayey aquitard, Northern Mexico. J Hydrol 284:26–44
Sivan O, Yechieli Y, Herut B, Lazar B (2005) Geochemical evolution and timescale of seawater intrusion into the coastal aquifer of Israel. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(3):579–592
Starkel L, Soja R, Michczynska DJ (2006) Past hydrological events reflected in Holocene history of Polish rivers. Catena 66:24–33
Turner JV, Macpherson DK (1990) Mechanisms affecting streamflow and streamwater quality: an approach via stable isotope, hydrogeochemical and time series analysis. Water Resour Res 26:3005–3019
Wilcox WM, Solo-Gabriele HM, Sternberg LO (2004) Use of stable isotopes to quantify flows between the Everglades and urban areas in Miami-Dade County Florida. J Hydrol 293:1–19
Yang YS, Cronin A, Elliot T, Kalin RM (2004) Characterizing heterogeneous systems through inverse groundwater flow and geochemical modelling. J Hydraul Res 42:147–155
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the “973” Special Funds for Major State Research Projects under grant No. 2002CB412702 and the KC Wong Education Funds, the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The authors wish also to thank the effort from the anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, F., Yang, Y.S., Yuan, R. et al. Study of shallow groundwater quality evolution under saline intrusion with environmental isotopes and geochemistry. Environ Geol 51, 1009–1017 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0370-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0370-6