Abstract
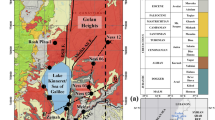
Seawater intrusion into the shallow aquifer in the Syrian coast, north of Latakia (Damsarkho, Ras Ibn Hani) and south of Tartous (Al Hamidieh, Ein Zarka) was studied using hydrochemical and isotopic techniques. The electrical conductivity (EC) distribution map north of Latakia revealed that mixing in this area is the consequence of a frontal intrusion of seawater within the fresh groundwater aquifer which, in turn, results from intensive pumping since the 1960s which has lowered the water table inland below sea level. In Ein Zarka, south of Tartous, in contrast, the EC distribution revealed that seawater intrusion is due to local up-coning as a result of intensive pumping. The deuterium and oxygen-18 relationship is that of a mixing line with a slope of 5.55, indicating an intrusion between freshwater and seawater. In addition, the relationship between oxygen-18 and chloride reveals that the mixing has a dominant role compared to evaporation process. The mixing ratios are estimated to be between 6 and 10% north of Latakia, while they do not exceed 3% south of Tartous. A tritium model was applied to compute the “mean transit time”, which is estimated to be around 10 years, on average, to reach the equilibrium that existed originally between the fresh groundwater and seawater, provided that severe pumping is completely halted and the aquifer is naturally recharged by rainfall and deep percolation of irrigation water, thereby allowing the restoration of the hydraulic gradient.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed Rabo R (2000) Study of seawater intrusion into fresh groundwater in the coastal area. Ms thesis, civil engineering, Damascus University, Damascus, Syria
Abou Zakhem B, Hafez R (2003) Environmental isotopes study of the aquifer system in the coastal area (Syria). AECS-G/FRSR report no. 285, Syria
Ahn JS, Kim SJ, Kim JW (1992) Environmental isotope studies on seawater intrusion into the southeastern coastal aquifer on Cheju Island. IAEA-SM-319/60P (1991). IAEA, Vienna
Al-Charideh A (2004) Coastal submarine springs in Lebanon and Syria: geological, geochemical and radio-isotope study. Atomic Energy Commission of Syria (AECS), final report, AECS-G/FRSR no. 315
Ayoub G, Khoury R, Ghannam J, Acra A, Hamdar B (2002) Exploitation of submarine springs in Lebanon: assessment of potential. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA/51.1/2002:46–64
Custodio E, Bruggeman GA (1987) Groundwater problems in coastal areas. Studies and Reports in Hydrology No 45. UNESCO, Paris
Custodio E, Pascal JM, Bayo A, Bosch X (1989) Processes in the mixing zone in carbonate formations: Central and South Catalonia. Natuurweten Tijdschr Gent 70:263–277
Custodio E, Baron A, Rodriguez-Morillo H, Poncela R, Bayo A (1993) Saline water in S’Albufera Natural Park aquifer system, Mallorca island (Spain): a preliminary study, and modeling of saltwater intrusion into aquifers. CIMNE-CIHS, Barcelona
Dancer T, Payne B R (1971) An environmental isotope study of the south-western karst region of Turkey. J Hydrol 14:233–258
IAEA (1992) Statistical treatment of data on environmental isotopes in precipitation, Technical Report No. 331. IAEA, Vienna
FAO (1997) Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers. Guidelines for study, monitoring and control. FAO, Rome
Gat JR, Gonfiantini R (1981) Stable isotope hydrology: deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle. Technical Report Series No. 210. IAEA, Vienna
GCWS (1987) Study of Al-Sin spring basin project. Coastal area, vol. I. General hydrogeology report, Syria
Gonfiantini R, Araguas L (1988) Los isotopes ambientales en el estudio de la intrusion marina. Tecnologia de la intrusion en acuiferos. (Environmental isotope study of seawater intrusion. Intrusion mechanism in the aquifer). Inst Geol Minero Espana, Madrid, I, pp 135–190
Gonfiantini R, Simonot M (1987) Isotopic investigation of groundwater in the Cul-De-Sac plain, Haiti. IAEA-SM-299/132, IAEA, Vienna
Ho HD, Aranyossy JF, Louvat D, Hua MQ, Nguyen TV (1992) Environmental isotope study related to the origin, salinization and movement of groundwater in the Mekong Delta (Viet Nam). IAEA-SM-319/38 (1991), IAEA, Vienna
Khouri J, Droubi A (1981) Groundwater movement in the fissured karstic rocks (Eastern of Mediterranean Sea), ACSAD/dm/no. 10, Damascus, 58 p
Kurttas T, Bayari CS, Günay G (1996) Long-term observations on the seawater contribution rate in the Gökova Plain Karstic Spring (SW Turkey) as revealed from oxygen-18, chloride and 87Sr/86Sr data. International Research & Application Center for Karst Water Resources, Hacettepe University, Beytepe, Ankara-06532, Turkey
Malakani M (1979) A viscous fluid model study of various saline groundwater problems. PhD thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
Malakani M (1997) Seawater intrusion in Syria: Damsarkho and Akkar areas. In: FAO, water reports 11, 1997. FAO, Rome
Payne BR (1983) Groundwater salinization: guidebook on nuclear techniques in hydrology. Technical Report Series No. 91, IAEA, Vienna
Ponikarov (1966) Explanatory notes of the geological map of Syria, scale ½00000, sheets 1–37 XIX, 1–36 XXIV
Selkhozpromexport (1979) Hydrogeological and hydrological surveys and investigation in four areas of Syrian Arab Republic, vol. 1 and 2, Hydrology
Yurtsever Y (1979) Environmental isotopes as a tool in hydrogeological investigation of southern karst region of Turkey. In: Proc Int Seminar Karst Hydrogeol. Oymapinar-Antalya, Turkey
Yurtsever Y (1983) Model for tracer data analysis: guidebook on nuclear techniques in hydrology. Technical Report Series no. 91, IAEA, Vienna
Yurtsever Y, Payne BR (1978) Application of environmental isotopes to groundwater investigations in Qatar. IAEA-SM-228/24, IAEA, Vienna
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. I. Othman, General Director of the Atomic Energy Commission of Syria, for his encouragement and support. Many thanks are extended to Dr. Y. Yurtsever, the technical officer of the project in IAEA, and to the Isotope Hydrology laboratory team for their help in performing the isotopic analyses.
Thanks are due to the head of the chemical department and the head of protection and its staff for performing the chemical analyses. Finally, we thank all our colleagues in the Geology Department, especially Mrs. R. Saadeh and Mr. B. Kattaa for their great effort in drawing the maps, Mr. J. Naameh for his help in the field work and Mr. I. Abou Madi for performing the isotopic and chemical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Y. Yurtsever.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou Zakhem, B., Hafez, R. Environmental isotope study of seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer (Syria). Environ Geol 51, 1329–1339 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0431-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0431-x