Abstract
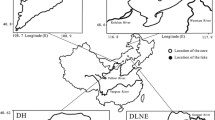
Organic matter in sediments, for instance, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, can be used to reconstruct the paleoecological and pollution history of lakes and their catchment basins. In this paper, the contents of allochthonous organic carbon (allochthonous OC) and autochthonous organic carbon (autochthonous OC) in sediment cores taken from Wuliangsuhai Lake and Daihai Lake in northern China are quantified by using a binary model, and phosphorus forms in the sediment cores from the two lakes are extracted by sequential extraction techniques. The results indicate that the palaeoenvironment and paleoclimate of Daihai Lake and its catchment basin in the recent 250 years can be well reconstructed based on the content of allochthonous OC. The climate was relatively humid and warm in the period of 1865–2005, while relatively dry and cold in the period of 1765–1865. The sedimentary information of allochthonous OC in the 22–42-cm portion of the sediment cores in Daihai Lake corresponds to the final cold fluctuation of the Little Ice Age that occurred since the Middle Holocene. The difference of phosphorus forms in the sediment cores between the two lakes indicates that phosphorus input to the lakes and the correlation between phosphorus forms and distribution and the changes of environment are influenced by the eutrophication mechanisms and environmental conditions of the two lakes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertini A (2006) The Northern Apennines palynological record as a contribute for the reconstruction of the Messinian palaeoenvironments. Sediment Geol 188:235–258
Bränvall ML, Bindler R, Emteryd O et al (2001) Four thousand years of atmospheric lead pollution in northern Europe: a summary from Swedish lake sediments. J Paleolimnol 25(4):421–435
Callender E (1982) Benthic phosphorus regeneration in the Potomac River Estuary. Hydrobiologia 91(1):431–446
Cao JT, Shen J, Wang SM et al (2001) Geochemical record for the characteristics of climate change during the Little Ice Age in Daihai Lake, Nei Mongol. Geochim (Chin) 30(3):231–235
Cao JT, Wang SM, Shen J (2000a) The primary study of paleoclimate changes during the past millennium in Daihai Lake, Inner Mongolia. Mar Geol Quaternary Geol (Chin) 20(2):15–20
Cao JT, Wang SM, Shen J et al (2000b) The paleoclimate changes during the past millennium lnferred from the lacustrine core in Daihai Lake, Inner Mongolia. Sci Geogr Sin (Chin) 20(5):391–396
Dai J, Sun MY (2007) Organic matter sources and their use by bacteria in the sediments of the Altamaha estuary during high and low discharge periods. Org Geochem 38(1):1–15
Duan XN, Wang XK, Mu YJ et al (2005) Seasonal and diurnal variations in methane emissions from Wuliangsu Lake in arid regions of China. Atmos Environ 39(25):4479–4487
Duan XN, Wang XK, Ouyang ZY et al (2004) The biomass of Phragmites Australis and its influencing factors in Wuliangsuhai. Acta Phytoecol Sin (Chin) 28(2):246–251
Editorial Committee of Analytical Methods of Water, Wastewater Monitoring (ECAMWWM) (2002) Analytical methods of water and wastewater monitoring (in Chinese), 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Filippelli GM, Delaney ML (1996) Phosphorus geochemistry of equatorial Pacific sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60(9):1479–1495
Fox LE (1991) Phosphorus chemistry in the tidal Hudson River. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55(6):1529–1538
Fox LE, Sager SL, Wofsy SC (1985) Factors controlling the concentrations of soluble phosphorus in the Mississippi estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 30(4):826–832
Fox LE, Sager SL, Wofsy SC (1986) The chemical control of soluble phosphorus in the Amazon estuary. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50(5):783–794
Froelich PN (1988) Kinetic control of dissolved phosphate in natural rivers and estuaries: a primer on the phosphate buffer mechanism. Limnol Oceanogr 33(4):649–668
Gao L, Yang H, Zhou JM (2005) Phosphorus release from sediments in Dianchi Lake under different environmental conditions. Soil (Chin) 37(2):216–219
Garcia-Rodriguez F, Del Puerto L, Castineira C et al (2001) Preliminary paleolimnological study of rocha lagoon, SE Uruguay. Limnol Ecol Manage Inland Waters 31(3):221–228
Hearn PP (1995) Controls on phosphorus mobility in Potomac river near the Blue Plains waste water treatment plant. US Geol Surv Water Supply Pap 2231:46
Herczeg AL, Smith AK, Dighton JC (2001) A 120 year record of changes in nitrogen and carbon cycling in Lake Alexandrina, South Australia: C:N, δ15N and δ13C in sediments. Appl Geochem 16(1):73–84
Jia GD, Peng PA (2003) Temporal and spatial variations in signatures of sedimented organic matter in Lingding Bay (Pearl estuary), southern China. Mar Chem 82(1):47–54
Jin Z, Wang S, Shen J et al (2001a) Chemical weathering since the Little Ice Age recorded in lake sediments: a high-resolution proxy of past climate. Earth Surf Process Landforms 26(7):775–782
Jin ZD, Wang SM, Shen J (2003) Carbonate versus silicate Sr isotope in lake sediments and its response to Little Ice Age. Chin Sci Bull 48(1):95–100
Jin ZD, Wang SM, Shen J et al (2004) Watershed chemical weathering and its response to climate events in Daihai area during holocene. Geochimica (Chin) 33(1):29–36
Jin ZD, Wang SM, Shen J et al (2001b) The lacustrine sediment record of the slightly chemical weathering in the little ice age. Sci China (Ser D) 31(3):221–225
Kendall C, Silva SR, Kelly VJ (2001) Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in four large river systems across the United States. Hydrol Process 15(7):1301–1346
Li CY, Liu TX, Gao RZ et al (2004a) Study and synthetic assessment for the season-year change of the eutrophication main-control factors in Wuliangsuhai Lake. Hydrol (Chin) 24(3):14–17
Li XQ, Zhou J, Shen J et al (2004b) Vegetation history and climatic variations during the last 14 ka BP inferred from a pollen record at Daihai Lake, north-central China. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 132(3–4):195–205
Li Y, Wu DN, Xue YX (1998) A development sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in the sediments and its environmental geochemical significance. Mar Environ Sci (Chin) 17(1):15–20
Lindström M, Jonsson A, Brolin AA et al (2001) Heavy metal sediment load from the city of Stockholm. Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 1(3):103–118
Liu PT, Wang HD, Pan BL et al (1965) The hydrochemistry geography of the Daihai basin. Acta Geogr Sin (Chin) 31(1):36–62
Lü CW, He J, Sun HM et al (2007) Phosphorus speciation and distribution character in sediment of Wuliangsuhai Lake. J Agro-Environ Sci (Chin) 26(3):878–885
Lüniger G, Schwark L (2002) Characterisation of sedimentary organic matter by bulk and molecular geochemical proxies: an example from Oligocene maar-type Lake Enspel, Germany. Sediment Geol 148(1–2):275–288
Luque JA, Julia R (2002) Lake sediment response to land-use and climate change during the last 1000 years in the oligotrophic Lake Sanabria (northwest of Iberian Peninsula). Sediment Geol 148(1–2):343–355
Meyers PA (1997) Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes. Org Geochem 27(5):213–250
Meyers PA (2003) Applications of organic geochemistry to paleolimnological reconstructions: a summary of examples from the Laurentian Great Lakes. Org Geochem 34(2):261–289
Meyers PA, Ishiwatari R (1993) Lacustrine organic geochemistry—an overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org Geochem 20(7):867–900
Östlund P, Sternbeck J (2001) Total lead and stable lead isotopes in Stockholm sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 1(3):229–239
Peng YJ, Xiao JL, Nakamura T et al (2005) Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 233(3–4):467–479
Perdue EM, Koprivnjak J-F (2007) Using the C/N ratio to estimate terrigenous inputs of organic matter to aquatic environments. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73(1–2):65–72
Preda M, Cox ME (2002) Trace metal occurrence and distribution in sediments and mangroves, Pumicestone region, southeast Queensland, Australia. Environ Int 28(5):433–449
Qian JL, Wang SM, Xue B et al (1997) A method of quantitatively calculating amount of allochthonous organic carbon in lake sediments. Chin Sci Bull (Chin) 42(21):1821–1823
Renberg I, Brannvall ML, Bindler R et al (2002) Stable lead isotopes and lake sediments–a useful combination for the study of atmospheric lead pollution history. Sci Total Environ 292(1–2):45–54
Routh J, Meyers PA, Gustafsson O et al (2004) Sedimentary geochemical record of human-induced environmental changes in the Lake Brunnsviken watershed, Sweden. Limnol Oceanogr 49(5):1560–1569
Ruttenberg KC (1992) Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 37(7):1460–1482
Ruttenberg KC, Berner RA (1993) Authigenic apatite formation and burial in sediments from non-upwelling, continental margin environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57(5):991–1007
Shen J, Matsumoto R, Wang SM (2002) Quantitative reconstruction of the lake water paleotemperature of Daihai Lake, Inner Mongolia, China and its significance in paleoclimate. Sci China Ser D 45(9):792–800
Sternbeck J, Östlund P (2001) Metals in sediments from the Stockholm region: geographical pollution patterns and time trends. Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 1(3) 151–165
Sun HM, He J, Gao XD et al (2006a) Distribution of total phosphorus in sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake. Acta Sedimentol Sin (Chin) 24(4):579–584
Sun HM, He J, Lü CW et al (2006b) Nitrogen pollution and spatial distribution pattern of Wuliangsuhai Lake. Geogr Res (Chin) 25(6):1003–1012
Sun HM, He J, Lü CW et al (2006c) Distribution characteristics of organic matter and total nitrogen in sediments of Lake Wuliangsuhai. Chin J Appl Ecol (Chin) 17(4):620–624
Sun QL, Zhou J, Peng ZC et al (2001a) High-precision TIMS age from the sediment of carbonate in Daihai Lake. Sci Bull (Chin) 46(2):150–153
Sun QL, Zhou J, Shen J et al (2006d) Environmental characteristics of Mid-Holocene recorded by lacustrine sediments from Lake Daihai, north environment sensitive zone, China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences 49(9):968–981
Sun QL, Zhou J, Xiao JL (2001b) Grain-size characteristics of Lake Daihai sediments and its paleaoenvironment significance. Mar Geol Quaternary Geol (Chin) 21(1):93–95
Sundby B, Gobeil C, Silverberg N et al (1992) The phosphorus cycle in coastal marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 37(6):1129–1145
Wan GJ, Bai ZG, Wang HR et al (2000) The geochemical records of C–N–S–P in recent sediments of Lake Erhai, China. Geochim (Chin) 29(2):189–197
Wang SM and Feng M (1991) The relationship between the environmental changes and the variation of southeast monsoon in the Daihai Lake, Inner Mongolia. Science in China (Series B) (in Chinese), pp 759–768
Wang SM, Yu YS, Wu RJ (1990) The Daihai Lake—lake environment and climate change. University of Science and Technology of China Press, Hefei
Wu JL, Huang CM, Zeng H et al (2007) Sedimentary evidence for recent eutrophication in the northern basin of Lake Taihu, China: human impacts on a large shallow lake. J Paleolimnol 38(1):13–23
Xiao JL, Nakamura T, Lu HY et al (2002) Holocene climate changes over the desert/loess transition of north-central China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 197(1–2):11–18
Xiao JL, Xu QH, Nakamura T et al (2004) Holocene vegetation variation in the Daihai Lake region of north-central China: a direct indication of the Asian monsoon climatic history. Quaternary Sci Rev 23(14–15):1669–1679
Xu QH, Li YC, Yang XL et al (2005) Source and distribution of pollen in the surface sediment of Daihai Lake, inner Mongolia. Quaternary Int 136(1):33–45
Yu RH, Li CY, Liu TX et al (2004) Change of wetland environment in Wuliangsuhai. Acta Geogr Sin (Chin) 59(6):948–955
Zhu GW, Qin BQ and Zhang L (2006a) Phosphorus forms and bioavailability of lake sediments in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49(Supp.):28–37
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Zhang L et al (2006b) Geochemical forms of phosphorus in sediments of three large, shallow lakes of China. Pedosphere 16(6):726–734
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiangdong Jiang for his helpful comments and revisions in the English presentation of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lü, C., He, J., Sun, H. et al. Application of allochthonous organic carbon and phosphorus forms in the interpretation of past environmental conditions. Environ Geol 55, 1279–1289 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1076-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1076-0