Abstract
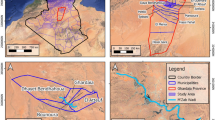
The qanat water supply technology, which gravity drains mountain aquifers into valleys, is considered as a culturally appropriate and ecological sustainable design to meet northern Cyprus’ drinking water development needs. This research estimates the boundary and water budget for the proposed qanat recharge area of 370 km2, which is in the upper elevations of the limestone dominated Five Finger Mountain Range. The mountain drainage was analyzed using global elevation data from the Shuttle Ranging Topography Mission (SRTM). Efforts to use Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) annual precipitation for water budget inputs failed due to extreme error when tested against 10–30 years of meteorological station data; TRMM under-estimated depths on the narrow mountain peaks. Gage records, while few in number, were area averaged to set average annual precipitation inputs at 530 mm year−1. Evaporation was estimated using a complementary relationship areal evapotranspiration (CRAE) model, setting average atmospheric outputs at 221 mm year−1. Recharge to the qanat aquifer was set by subtracting evaporation from precipitation, and then allocating 50% of the remaining water to environmental services. At 25% development, the qanat system supplies 14 mm3 year−1 of water, meeting the drinking water deficit of 13 mm3.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atapour H, Aftabi A (2002) Geomorphological, geochemical and geo-environmental aspects of karstification in the urban areas of Kerman city, southeastern, Iran. Environ Geol 42(7):783–792
Banks D, Soldal O (2002) Towards a policy for sustainable use of groundwater by non-governmental organisations in Afghanistan. Hydrogeol J 10(3):377–392
Bicak HA, Jenkins GP (1999) Costs and pricing policies related to transporting water by tanker from Turkey to North Cyprus Harvard Institute for International Development Discussion Papers 689 (March)
Bicak HA, Jenkins G (2000) Transporting water by tanker from Turkey to North Cyprus: costs and pricing policies, Chap 7. In: Brooks DB, Mehmet O (eds) Water balances in The Eastern Mediterranean. IDRC, Ottawa
Bicak HA, Jenkins GP et al (2000) Resource costs, resettlement costs, and political constraints in the choice of dam locations. Harvard Institute for International Development Discussion Papers 750 (February)
Biyikoglu G (1995) Rainfall analysis in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus. Proceedings of the Second Water Congress. Engineer and Architecture Chamber Association, Nicosia, North Cyprus, Cyprus, pp 23–24
Bonine ME (1996) Qanats and Rural Societies: sustainable agriculture and irrigation cultures in contemporary Iran. In: Mabry JB (ed) Canals and communities: small-scale irrigation systems. University of Arizona Press, Tucson, pp 183–209, 273
CIA (2005) The world fact book: Cyprus. Retrieved 2004 (04/11/2004), from http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/cy.html
Cox CW (1999) Water supply enhancement in Cyprus through evaporation reduction. Civil & Environmental Engineering. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Cressy GB (1958) Qanats, Farez, and Foggaras. Geograph Rev 48(1):27–44
Cyprus WDD (2002) Use and conservation of water in Cyprus. Nicosia, Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources & Environment Water Development Department: 19
ESRI (2005) ArcGIS 9.0 Documentation. Redlands, ESRI
FAO (1995) Cyprus: country report to the international conference and programme on plant genetic resource. F. a. A. O. o. t. U. Nations, United Nations, p 38
Foppen JWA (2002) Impact of high-strength wastewater infiltration on groundwater quality and drinking water supply: the case of Sana’a, Yemen. J Hydrol 263(1–4):198–216
Gardner-Outlaw T, Engelman R (1997) Sustaining water, easing scarcity: a second update on the report: sustaining water. Population and the future of renewable water supplies. Population Action International, Population and Environment Program, p 18
Goblot H (1979) Les Qanats: Une Technique d’Acquisition de l’Eau. Paris, Mouton
Gokcekus H, Cucel S et al (2005) The impacts of misuse of lands on the habitats and biodiversity: Northern Cyprus. In: Proceedings of the EUROPEAN ecological congress 2005, Aydin, Turkey
Hatem-Moussallem M, Gaffney B (1999) Cyprus drought water bank. Civil & Environmental Engineering. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Huffman GJ, Adler RF et al (2005) Global rainfall analyses at monthly and 3-hr time scales. In: Levizzani P, Bauer, Turk J (eds) Measuring precipitation from space: EURAINSTAT and the future, Chap 4. The Netherlands
Kazemi GA (2004) Temporal changes in the physical properties and chemical composition of the municipal water supply of Shahrood, northeastern Iran. Hydrogeol J 12(6):723–734
Lightfoot DR (1996) Syrian qanat Romani: history, ecology, abandonment. J Arid Environ 33(3):321–336
Lightfoot DR (2000) Ghayl and miyan in Arabia Felix: the ecology of diffusion and recesion of use. The Arab World Geogr 3(1):2–21
Mark B (1999) Economics of seawater desalination in Cyprus. Civil & Environmental Engineering. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
MOA (2005) Vegetation and flora of Cyprus. Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources and Environment, Forestry Department
MOANR (1971) Hydrological year-book of Cyprus: 1968–69. Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Department of Water Development, Nicosia, Cyprus, p 231
MOANR (1975) Hydrological year-book of Cyprus: 1971–72. Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Department of Water Development, Nicosia, Cyprus, p 217
Morton FI (1983) Operational Estimates of Areal Evapotranspiration and their Significance to the Science and Practice of Hydrology. Journal of Hydrology 66:1–76
Necdet M (2003) Enriched: overview of the karst occurrences in northern Cyprus. Acta Carsologica 32(2):269–276
Ozdemirag A (1998) Thesis: investment appraisal of a dam to be built in Yesilirmak. Department of Economics. MSc, Eastern Mediterranean University, Gazimagusa, North Cyprus
Price C, Michaclides S et al (1999) Long term changes in diurnal temperature range in Cyprus Atmos Res 51(2):85–98
Rabus B, Eineder M et al (2003) The shuttle ranging topography mission—a new class of digital elevation models acquired by spaceborne radar. ISPRS J Photogrammetry Remote Sensing 57:241–262
Reimann C, Banks D (2004) Setting action levels for drinking water: are we protecting our health or our economy (or our backs!)? Sci Total Environ 332(1–3):13–21
Robertson AHF, Woodcock NH (1996) The role of the Kyrenia Range Lineament, Cyprus, in the geological evolution of the eastern Mediterranean area. Philos Trans Roy Soc Lond Ser A 317(1539):141–177
Rubin R (1988) Water conservation methods in Israel’s Negev desert in late antiquity. J Hist Geogr 14(3):229–244
Vojdani F (2004) Efficiency in water planning and management (an implementation experience). Water Sci Technol Water Supply 4(3):67–80
Wessels J (2003) Qanats in Syria ease the water shortage. Waterlines 22(2):8–10
Wood EF, Lettenmaier DP et al (1998) The project for intercomparison of land-surface parameterization schemes (PILPS) Phase-2c Red-Arkansas River Basin Experiment: 1. Experiment description and summary intercomparisons. Global Planet Change 19(1–4):115–135
Xu C-Y, Singh VP (2005) Evaluation of three complementary relationship evapotranspiration models by water balance approach to estimate actual regional evapotranspiration in different climatic regions. J Hydrol 308:105–121
Acknowledgments
This research was made possible by generous support from the Cyprus Fulbright Commission through a grant to the primary author. The assistance of Dr. C.-Y Xu in use of the CRAE model is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Endreny, T.A., Gokcekus, H. Ancient eco-technology of qanats for engineering a sustainable water supply in the Mediterranean Island of Cyprus. Environ Geol 57, 249–257 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1274-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1274-4