Abstract
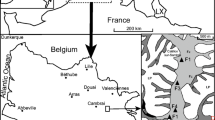
Since 1975, Europe sets up its policy to limit the degradation and the pollution of the aquatic environments through 30 directives and regulations. In the north of France, the nitrate concentrations measured in the groundwater exceed the water drinking limit fixed at 50 mg/L by the European framework directive in the field of water (2000/60/EC). This high concentration is due to intensive agriculture, industrialization and demographic growth. Several programs were launched in order to resolve this situation: “Ferti-better” or the use of fertilizer in moderation and installation and amelioration of wastewater collect and treatment systems. In order to estimate the influence of the anthropic activities on the quality of groundwater in the “Artois-Picardy” basin, a preliminary validation on parcel and district scale were necessary. The impact of these programs in the “Cambrai district” was evaluated using an integrated approach, which is based on the use of four numerical models: AgriFlux, VS2DT, Modflow and MT3D. The results illustrate an improvement due to the “Ferti-Better” program initiated in 1990 and punctual degradation under urbanized areas. Predictions (2015) show a spatial evolution of nitrates concentration varying with the thickness of unsaturated layer. The integrated model constitutes an efficient tool for predicting the evolution of the groundwater quality. This approach is important to control the application of the new European laws in the water field.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
AEAP (2004) Water Agency of Artois Picardy, état des lieux établi au titre de la Directive Cadre sur l’Eau, basé sur les statistiques 2000.
Banton O, Larocque M, Surateau F, Villeneuve JP (1993) AgriFlux Logicield’évaluation des pertes en composés azotés vers les eaux souterraines et superficielles. INRS-Eau (Rapport de recherche No. R-380). Quebec, Canada
Barroin G, Dorioz JM, Durand P, Merot P (1996) Entraînement de l’azote dans les eaux de surface et conséquence sur les écosystèmes aquatique. Maîtrise de l’azote dans les agrosystèmes, Reims, France, pp 39–53
Bear J (1988) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Dover publications, Inc., New York
Boiffin J, Fleury A (1974) Quelques conséquences agronomiques de retournements de prairies permanentes. Ann Agron 25(4):555–575
Carlier E, El Khattabi J (2005) Proposal for a probabilistic model of dispersion: a first validation. Math Comput Model 42:1137–1144
Carlier E, El Khattabi J, Potdevin JL (2006) Solute transport in sand and chalk: a probabilistic approach, Hydrological processes, 20th edn. Wiley, pp 1047–1055
Dupuy A (1997) Simulation de la contamination diffuse des eaux souterraines par les nitrates à l’échelle du bassin versant. Thesis, University of Poitiers, France
Ford M, Tellam JH (1994) Source, type and extend of inorganic contamination within Birmingham urbain aquifere system. J Hydrol 156:101–135
Gaury F (1992) Systèmes de culture et teneurs en nitrates des eaux souterraines. Dynamique passée et actuelle, en région de polyculture—élevage, sur le périmètre d’un gîte hydrominéral. Thesis, ENSA Rennes, INRA–SAD, France
Healey RW (1990) Simulation of solute transport in variably saturated porous media with supplemental information on modifications to the US Geological Survey computer program VS2D. Water resource investigations report 90 (4025). Denver, Colorado
IFEN SCEES (2001) Enquête: Eau potable, réalisée par l’institut français de l’environnement (Ifen), le service central des enquêtes et des études statistiques du Ministère de l’agriculture et de la pêche (Scees)
Johnsson H, Bergström L, Jansson PE, Paustian K (1987) Simulated nitrogen dynamics and losses in a layered agricultural soil. Agric Ecosys Environ 18:333–356
Lacherez-Bastin S (2005) Contribution à l’étude des vitesses de migration des nitrates dans le sol et la zone non saturée de la nappe de la craie—Modélisation en intégrée des nitrates dans le bassin versant de l’Escrebieux. Thesis, University of Lille 1, France
Lafrance P, Banton O (1995) Implication of spatial variability of organic carbon on predicting pesticide mobility in soil. Geoderma 65:331–338
Lappala EG (1981) Modeling of water and solute transport under variably saturated conditions. In state of the art: modeling and low-level waste management, an interagency workshop. Proceedings, 1980, Denver, Colorado, pp 81–116
Lefèvre E (2005) Etude de la minéralisation de la nappe de la craie sous pressions naturelles et anthropiques : application à la présence de l’azote, du soufre et du nickel dans les eaux souterraines. Thesis, University of Lille1, France, 162 p
Lerner DN, Yang Y, Barrett MH, Tellam JH (1999) Loadings of non-agricultural nitrogen in urban groundwater. In: Ellis JB (ed) Impacts of urban growth on surface and ground waters, Proceedings of IAHS symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999. IAHS publication no. 259, pp 117–123
Maison P (2000) Un modèle hydrologique de suivi de la pollution diffuse en bassin versant (Approche mécaniste simplifiée de la zone non saturée). Thesis, Institut National de Polytechnique de Toulouse, France
Mariotti A (1986) La dénitrification dans les eaux souterraines. Principes et méthodes de son identification. A revue. J Hydrol 88(1–2):1–23
Mariotti A, Landreau A, Simon B (1988) 15N isotope biogeochemistry and natural denitrification process in groundwater: application to the chalk aquifer of northern France. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:1869–1878
McDonald MG, Harbaugh AW (1988) MODFLOW, a modular three-dimesional finite-difference grouund-watrer flow model. Technique of Water resources Investigations of the U.S. Geological Surver. Book 6
Préaux C (1986) Constat de l’état actuel de la distribution publique et prospective d’aménagement. Rapport inédit BRGM, 86 SGN 435 NPC
Rawls WJ, Brakensiek DL (1989) Estimation of soil water retention and hydraulic properties. In: Morel S (ed) Unsaturated flow in hydrologic modeling. Theory and practice, pp 275–300
Ritchie JT (1991) Wheat phasic development. In: Hanks J, Ritchie JT (eds) Modeling plant and soil systems. Madison, 545 pp
Schroder H, Harrenmöes P, Simonsen JF (1985) Water pollution caused by nitrogen from urban wastewater and from agriculture. International congress, Nitrates dans les eaux, vol. 1. Paris, France
Serhal H (2006) Influence des pressions anthropiques sur l’évolution des concentrations en nitrates dans la nappe de la craie du Nord de la France. (Applications au Cambrésis et nord Audomarois). Thesis, University of Lille 1, France
Simon B (1986) Apports de la biogéochimie isotopique à la connaissance de la dénitrification dans les eaux souterraines. Thesis, Univeristy of Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris VI
Van Genuchten MTH (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. J Soil Sci 44:892–898
Zheng CC (1990) MT3D, a modular three-dimensional transport model. S·S. Report to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Papadopulos and Associates, Inc., Rockville, p 170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serhal, H., Bernard, D., Khattabi, J.E. et al. Impact of fertilizer application and urban wastes on the quality of groundwater in the Cambrai Chalk aquifer, Northern France. Environ Geol 57, 1579–1592 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1433-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1433-7