Abstract
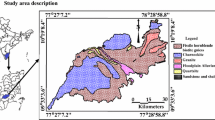
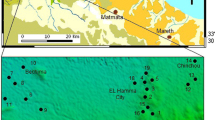
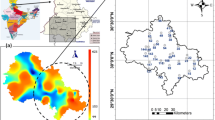
Radon concentration was measured in 133 water samples from tubewells, handpumps, dug wells and springs of the Doon Valley, Outer Himalaya, India. The observed radon values were found to vary from 10 to 154 Bq/l whereas radium in selected water samples varied from 0.11 to 0.75 Bq/l. Three different clusters of high radon values were observed in the north-western, central and south-eastern parts of the Doon Valley. These clusters were found to be associated with tectonics (thrust/fault) and associated uranium mineralization in the area. In general, radon concentration in groundwater was found to be positively correlated with the depth of the wells, whereas no significant correlation was observed between radon concentration in groundwater and the water temperature, pH value, conductivity and altitude of the water samples. An attempt has also been made to determine the nature and extent of aquifers in the Doon Valley on radon concentration in groundwater. The variation in radon concentration within the groundwater of the study area was found to be controlled by the neotectonic activity and geohydrological processes that occur in the area. The impact of these activities on radon concentration in groundwater are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 September 1999 · Accepted: 11 April 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choubey, V., Bartarya, S., Saini, N. et al. Impact of geohydrology and neotectonic activity on radon concentration in groundwater of intermontane Doon Valley, Outer Himalaya, India. Environmental Geology 40, 257–266 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540000177
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540000177