Abstract
Background
To determine the accuracy of contrast-enhanced multislice computed tomography (CT) in the assessment of treatment success immediately after CT-guided radiofrequency (RF) ablation.
Methods
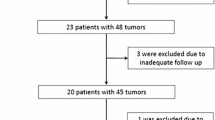
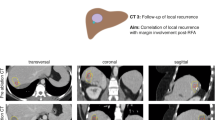
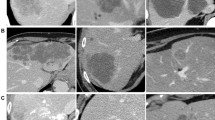
26 patients with 38 Colorectal liver metastasis (CRM) were treated by CT-guided RF ablation. Pre-contrast and portal phase CT features before and immediately after ablation were retrospectively evaluated quantitatively and qualitatively: Influence of attenuation characteristics, safety margin, congruency between tumor and coagulation, and morphological criteria (shape, margin distinction, margin configuration, and margin continuity) were investigated. Findings were statistically analyzed with regard to local tumor progression.
Results
Mean observation period for follow-up scans was 6.4 months (range: 3–40 months). Attenuation characteristics, safety margin, and congruency had no significant effect on the probability of local tumor progression. Coagulations whose margin was categorized as “discontinuous” were significantly more often associated with local recurrence (p = 0.038). No significant influence on local recurrence could be detected regarding coagulation shape, margin distinction, and configuration.
Conclusion
Computed tomography imaging immediately after RF ablation allows for morphological characterization of the coagulation and provides a valid baseline status for follow-up imaging. However, in CRM, morphological image criteria and attenuation characteristics have limited predictive value for immediate detection of persistent tumor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006 CA Cancer J Clin 56(2):106–130
Livraghi T, Solbiati L (2001) [Percutaneous treatment: radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases in colorectal cancer] Tumori 87(1 Suppl 1):S69
Manfredi S, Lepage C, Hatem C, et al. (2006) Epidemiology and management of liver metastases from colorectal cancer Ann Surg 244(2):254–259
Pereira PL (2007) Actual role of radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases Eur Radiol 17(8):2062–2070
Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, et al. (2001) Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 117 patients Radiology 221(1):159–166
Rhim H, Goldberg SN, Dodd GD 3rd, et al. (2001) Essential techniques for successful radio-frequency thermal ablation of malignant hepatic tumors. Radiographics 21 Spec No:S17–S35; discussion S36–S19
Barker DW, Zagoria RJ, Morton KA, et al. (2005) Evaluation of liver metastases after radiofrequency ablation: utility of 18F-FDG PET and PET/CT AJR Am J Roentgenol 184(4):1096–1102
Kim YS, Rhim H, Cho OK, et al. (2006) Intrahepatic recurrence after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the pattern and risk factors Eur J Radiol 59(3):432–441
Antoch G, Vogt FM, Veit P, et al. (2005) Assessment of liver tissue after radiofrequency ablation: findings with different imaging procedures J Nucl Med 46(3):520–525
Kim SK, Lim HK, Kim YH, et al. (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radio-frequency ablation: spectrum of imaging findings Radiographics 23(1):107–121
Chopra S, Dodd GD 3rd, Chintapalli KN, et al. (2001) Tumor recurrence after radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of findings on dual-phase contrast-enhanced CT AJR Am J Roentgenol 177(2):381–387
Ninomiya T, Seo Y, Yano Y, et al. (2006) Evaluation of the therapeutic effect using MD-CT immediately after RFA for HCC Hepatogastroenterology 53(70):558–560
Dromain C, de Baere T, Elias D, et al. (2002) Hepatic tumors treated with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: CT and MR imaging follow-up Radiology 223(1):255–262
Limanond P, Zimmerman P, Raman SS, et al. (2003) Interpretation of CT and MRI after radiofrequency ablation of hepatic malignancies AJR Am J Roentgenol 181(6):1635–1640
Tsuda M, Rikimaru H, Majima K, et al. (2003) Time-related changes of radiofrequency ablation lesion in the normal rabbit liver: findings of magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology Invest Radiol 38(8):525–531
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, et al. (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria Radiology 235(3):728–739
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2004) Radio-frequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases in 167 patients Eur Radiol 14(12):2261–2267
Aliberti C, Soriani M, Tilli M, et al. (2004) Radiofrequency ablation of liver malignancies: MRI for evaluation of response J Chemother 16(Suppl 5):79–81
Veit P, Antoch G, Stergar H, et al. (2006) Detection of residual tumor after radiofrequency ablation of liver metastasis with dual-modality PET/CT: initial results Eur Radiol 16(1):80–87
Meloni MF, Livraghi T, Filice C, et al. (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: the role of microbubble ultrasound contrast agents Ultrasound Q 22(1):41–47
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2005) Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases Abdom Imaging 30(4):419–426
Paul SB, Gulati MS (2002) Spectrum of hepatocellular carcinoma on triple phase helical CT: a pictorial essay Clin Imaging 26(4):270–279
Chiang SH, Thng CH, Teh CS, et al. (2003) Computed tomographic appearance of colorectal hepatic metastases Ann Acad Med Singapore 32(2):191–195
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR (2000) Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: a unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance AJR Am J Roentgenol 174(2):323–331
Anderson GS, Brinkmann F, Soulen MC, et al. (2003) FDG positron emission tomography in the surveillance of hepatic tumors treated with radiofrequency ablation Clin Nucl Med 28(3):192–197
van Duijnhoven FH, Jansen MC, Junggeburt JM, et al. (2006) Factors influencing the local failure rate of radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases Ann Surg Oncol 13(5):651–658
Ng KK, Poon RT (2005) Radiofrequency ablation for malignant liver tumor Surg Oncol 14(1):41–52
Sutherland LM, Williams JA, Padbury RT, et al. (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: a systematic review Arch Surg 141(2):181–190
Jiao LR, Hansen PD, Havlik R, et al. (1999) Clinical short-term results of radiofrequency ablation in primary and secondary liver tumors Am J Surg 177(4):303–306
Cady B, Jenkins RL, Steele GD Jr., et al. (1998) Surgical margin in hepatic resection for colorectal metastasis: a critical and improvable determinant of outcome Ann Surg 227(4):566–571
Hamady ZZ, Cameron IC, Wyatt J, et al. (2006) Resection margin in patients undergoing hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastasis: a critical appraisal of the 1 cm rule Eur J Surg Oncol 32(5):557–563
Bricault I, Kikinis R, Morrison PR, et al. (2006) Liver metastases: 3D shape-based analysis of CT scans for detection of local recurrence after radiofrequency ablation Radiology 241(1):243–250
Choi H, Loyer EM, DuBrow RA, et al. (2001) Radio-frequency ablation of liver tumors: assessment of therapeutic response and complications. Radiographics 21 Spec No:S41–S54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schraml, C., Clasen, S., Schwenzer, N.F. et al. Diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced computed tomography in the immediate assessment of radiofrequency ablation success in colorectal liver metastases. Abdom Imaging 33, 643–651 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-007-9351-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-007-9351-9