Abstract
Purpose
Devices constantly tracking the blood pressure (BP) of hypertensive patients are highly desired to facilitate effective patient management and to reduce hospitalization. We report on experiences gathered in a pilot study that was designed to evaluate the prototype of a newly developed, minimally invasive implantable sensor system for long-term BP monitoring.
Methods
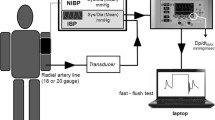
The device was implanted in the femoral artery (FA) of 12 sheep via standard FA catheterization under fluoroscopic control. Accuracy of the recorded blood pressure was determined by comparison with a reference catheter, which was positioned in the contralateral FA immediately after implantation. Regular follow-up included angiography, computed tomography (CT), and control of functionality and position of the BP sensor. Animals were euthanized after 6 months. FA segments with in situ pressure sensor underwent macroscopic and histopathologic examinations.
Results
All implantations of the novel sensor device in the FA were successful and uneventful. High-quality BP recordings were documented. Bland–Altman plots indicate very good agreement. Comparison with measurements taken from the reference sensor revealed mean differences and standard deviations of −0.56 ± 0.85, 0.29 ± 1.44, and 0.85 ± 2.27 mmHg (diastolic, systolic, and pulse pressure, respectively) after exclusion of one outlier. CT uncovered deficiencies in cable stability that were addressed in a redesign. No thrombus formation, necrosis, or apoptosis were detected.
Conclusions
The pilot study proved the technical feasibility of wireless BP measurement in the FA via a novel miniature sensor device.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavijou OA et al (2011) Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123(8):933–944
Mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks, WHO Global Health Risks Report 2009. World Health Organization 2009. http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GlobalHealthRisks_report_full.pdf. Accessed July 2013
World Health Statistics 2012. World Health Organization. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44844/1/9789241564441_eng.pdf. Accessed July 2013
Arima H, Murakami Y, Lam TH et al (2012) Effects of prehypertension and hypertension subtype on cardiovascular disease in the Asia-Pacific region. Hypertension 59(6):1118–1123
Gray L, Lee IM, Sesso HD, Batty D (2011) Blood pressure in early adulthood, hypertension in middle age, and future cardiovascular disease mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(23):2396–2403
Dieterle T (2012) Blood pressure measurement: an overview. Swiss Med Wkly 142:w13517
Shelley D, Tseng TY, Matthews AG et al (2011) Technology-driven intervention to improve hypertension outcomes in community health centers. Am J Manag Care 17(12 Spec No):SP103–110
Agarwal R, Bills JE, Hecht TJ et al (2011) Role of home blood pressure monitoring in overcoming therapeutic inertia and improving hypertension control: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertension 57(1):29–38
Klersy C, De Silvestri A, Gabutti G et al (2009) A meta-analysis of remote monitoring of heart failure patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 54(18):1683–1694
Bui AL, Fonarow GC (2012) Home monitoring for heart failure management. J Am Coll Cardiol 59(2):97–104
Lau CP, Siu DCW, Tse HF (2012) Optimizing heart failure therapy with implantable sensors. J Arrhythmia 28(1):4–18
Smith SA, Abraham WT (2012) Implantable sensors and computers: interventional heart failure strategies. Curr Cardiol Rep 14(5):611–618
Cleven NJ, Müntjes JA, Fassbender H et al (2012) A novel fully implantable wireless sensor system for monitoring hypertension patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(11):3124
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Verdejo HE, Castro PF, Concepción R et al (2007) Comparison of a radiofrequency-based wireless pressure sensor to Swan-Ganz catheter and echocardiography for ambulatory assessment of pulmonary artery pressure in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(25):2375–2382
Rozenman Y, Schwartz RS, Shah H et al (2007) Wireless acoustic communication with a miniature pressure sensor in the pulmonary artery for disease surveillance and therapy of patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(7):784–789
Castro P, Concepción R, Bourge RC et al (2007) A wireless pressure sensor for monitoring pulmonary artery pressure in advanced heart failure: initial experience in man. J Heart Lung Transplant 26(1):85–88
Fiala J, Bingger P, Ruh D et al (2013) An implantable optical blood pressure sensor based on pulse transit time. Biomed Microdevices 15(1):73–81
Bingger P, Zens M, Woias P (2012) Highly flexible capacitive strain gauge for continuous long-term blood pressure monitoring. Biomed Microdevices 14(3):573–581
Troughton RW, Ritzema J, Eigler NL et al (2011) Direct left atrial pressure monitoring in severe heart failure: long-term sensor performance. J Cardiovasc Trans Res 4(1):3–13
Hoppe UC, Vanderheyden M, Sievert H et al (2009) Chronic monitoring of pulmonary artery pressure in patients with severe heart failure: multicentre experience of the monitoring pulmonary artery pressure by implantable device responding to ultrasonic signal (PAPIRUS) II study. Heart 95(13):1091–1097
Hess P, Clozel M, Clozel JP (1996) Telemetry monitoring of pulmonary arterial pressure in freely moving rats. J Appl Physiol 81(2):1027–1032
Hammond RL, Hanna K, Morgan C et al (2012) A wireless and batteryless miniature intracardiac pressure sensor: early implantation studies. ASAIO J 58(1):83–87
Hasan A, Paul V (2011) Telemonitoring in chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 32(12):1457–1464
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research, Grant 16SV5000. The authors would like to thank the Osypka AG, Rheinfelden, Germany; the Fraunhofer Institute for Microelectronic Circuits and Systems, Duisburg, Germany; the Institute of Materials in Electrical Engineering - Chair 1, RWTH Aachen University, Germany and all coworkers for their support and cooperation.
Conflict of interest
Nina J. Cleven, Peter Isfort, Tobias Penzkofer, Anna Woitok, Benita Hermanns-Sachweh, Ulrich Steinseifer, and Thomas Schmitz-Rode declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cleven, N.J., Isfort, P., Penzkofer, T. et al. Wireless Blood Pressure Monitoring with a Novel Implantable Device: Long-Term In Vivo Results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37, 1580–1588 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0842-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0842-0