Abstract
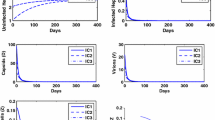
The aim of this work is to investigate a new mathematical model that describes the interactions between Hepatitis B virus (HBV), liver cells (hepatocytes), and the adaptive immune response. The qualitative analysis of this as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) cells and the antibodies. These outcomes are (1) a disease free steady state, which its local stability is characterized as usual by R 0 < 1, (2) and the existence of four endemic steady states when R 0 > 1. The local stability of these steady states depends on functions of R 0. Our study shows that although we give conditions of stability of these steady states, not all conditions are feasible. This rules out the local stability of two steady states. The conditions of stability of the two other steady states (which represent the complete failure of the adaptive immunity and the persistence of the disease) are formulated based on the domination of CTL cells response or the antibody response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed R, Gray D (1996) Immunologycal memory and protective immunity. Understanding their relation. Science 272: 54–60
Anderson V, Sonne J, Sletting S, Prip A (2000) The volume of the liver in patients correlates to body weight and alcohol consumption. Alcohol Alcohol 35(5): 531–532
Bralet M, Branchereau S, Brechot C, Ferry N (1994) Cell lineage study in the liver using retroviral mediated gene transfer. Am J Pathol 144: 896–905
Bertoletti A, Gehring AJ (2006) The immune response during hepatitis B virus infection. J Gen Virol 87: 1439–1449
Bertoletti A, Tan AT, Gehring AJ (2009) HBV-specific adaptive immunity. Viruses 1: 91–103
Boni C, Fisicaro P, Valdatta C, Amadei B, Di Vincenzo P, Giuberti T, Laccabue D, Zerbini A, Cavalli A, Missale G, Bertolli A, Ferrari C (2007) Characterization of HBV-specific T cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J Virol 8(18): 4215–4225
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J et al (2006) Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 295: 65–73
Ciurea A, Hunziker L, Klenerman P, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel RM (2001) Impairment of CD4+ T cell responses during chronic virus infection prevents neutralizing antibody response against virus escape mutants. J Exp Med 193: 297–305
Ciupe SM, de Bivort B, Bortz D, Nelson P (2006) Estimates of kinetic parameters from HIV patient data during primary infection through the eyes of three different models. Math Biosci 200: 1–27
Ciupe SM, Ribeiro RM, Nelson PW, Dusheiko G, Perelson AS (2007a) The role of cells refractory to productive infection in acute hepatitis B viral dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 5050–5055
Ciupe SM, Ribeiro RM, Nelson PW (2007b) Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Theor Biol 247: 23–35
Custer B, Sullivan SD, Hazlet TK, Iloeje U, Veenstra DL, Kowdley KV (2004) Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus. J Clin Gastroenterol 38(10): 158–168
Eikenberry S, Hews S, Nagy JD, Kuang Y (2009) The dynamics of a delay model of HBV infection with logistic hepatocyte growth. Math Biosci Eng 6: 283–299
Gradshteyn IS, Ryzhik IM (2000) Routh–Hurwitz Theorem, 15.715 in tables of integrals, series, and products, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, p 1076
Gourley SA, Kuang Y, Nagy JD (2008) Dynamics of a delay differential model of hepatitis B virus. J Biol Dyn 2: 140–153
Hews S, Eikenberry S, Nagy JD, Kuang Y (2010) Rich dynamics of a Hepatitis B viral infection model with logistic hepatocyte growth. J Math Biol 60: 573–590
Huang CF, Lin SS, Ho YC, Chen FL, Yang CC (2006) The immune response induced by hepatitis B virus principal antigens. Cell Mol Immunol 3(2): 97–106
Kane M (1995) Global programme for control of hepatitis B infection. Vaccine 13(Suppl. 1): S47–49
MacDonald RA (1961) “Lifespan” of liver cells. Autoradio-graphic study using tritiated thymidine in normal, cirrhotic, and partially hepatectomized rats. Arch Intern Med 107: 335–343
Min L, Su Y, Kuang Y (2008) analysis of a basic model of virus infection with application to HBV infection. Rocky Mountain J Math 38(5): 1573–1585
Nowak MA, Bonhoeffer S, Hill A, Boehme R, Thomas H, McDade H (1996) Viral dynamics in hepatitis B infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 4398–4402
Nowak MA, May RM (2000) Viral dynamics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Rehermann B, Nascimbeni M (2005) Immunology of Hepatitis B virus and Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol V5: 215–229
Thieme HR (2003) Mathematics in population biology. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, Purcell RH, Chisari FV (2003) CD8+ T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 77: 68–76
Vierling J (2007) The immunology of Hepatitis B. Clin Liver Dis 727(759): 727–759
Whalley SA, Murray JM, Brown D, Webster GJM, Emery VC, Dusheiko GM, Perelson AS (2001) Kinetics of acute hepatitis B virus infection in humans. J Exp Med 193: 847–853
Wodarz D (2003) Hepatitis C virus dynamics and pathology: the role of CTL and antibody responses. J Gen Virol 84: 1743–1750
Yao W, Hertel L, Wahl LM (2006) Dynamics of recurrent viral infection. Proc Roy Soc B 373: 2193–2199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousfi, N., Hattaf, K. & Tridane, A. Modeling the adaptive immune response in HBV infection. J. Math. Biol. 63, 933–957 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-010-0397-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-010-0397-x